
(a)
The velocity of the car after each second.
(a)
Answer to Problem 18E
The velocities after 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s and 5s are
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The car accelerates at
Write the formula for average acceleration.
Here,
a is the average acceleration
t is the time
Re-arrange the equation to get
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
The velocity time graph is given below.
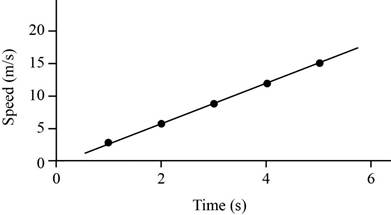
Figure (1)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the velocities after 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s and 5s are
(b)
The distance travelled after each second.
(b)
Answer to Problem 18E
The distances after 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s and 5s are
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Acceleration is
Write the formula to calculate the distance.
Here,
d is the distance
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
For
Substitute 0 m/s for
The distance time graph is,
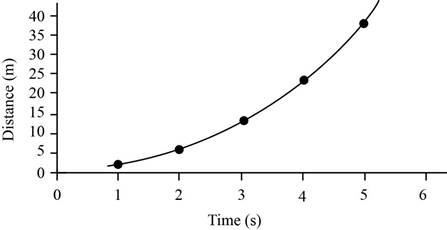
Figure(2)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distances after 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s and 5s are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
The Physics of Everyday Phenomena
- An object is placed 24.1 cm to the left of a diverging lens (f = -6.51 cm). A concave mirror (f= 14.8 cm) is placed 30.2 cm to the right of the lens to form an image of the first image formed by the lens. Find the final image distance, measured relative to the mirror. (b) Is the final image real or virtual? (c) Is the final image upright or inverted with respect to the original object?arrow_forwardConcept Simulation 26.4 provides the option of exploring the ray diagram that applies to this problem. The distance between an object and its image formed by a diverging lens is 5.90 cm. The focal length of the lens is -2.60 cm. Find (a) the image distance and (b) the object distance.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





