
1.
Discuss the
1.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation effect for given accounts is as follows:
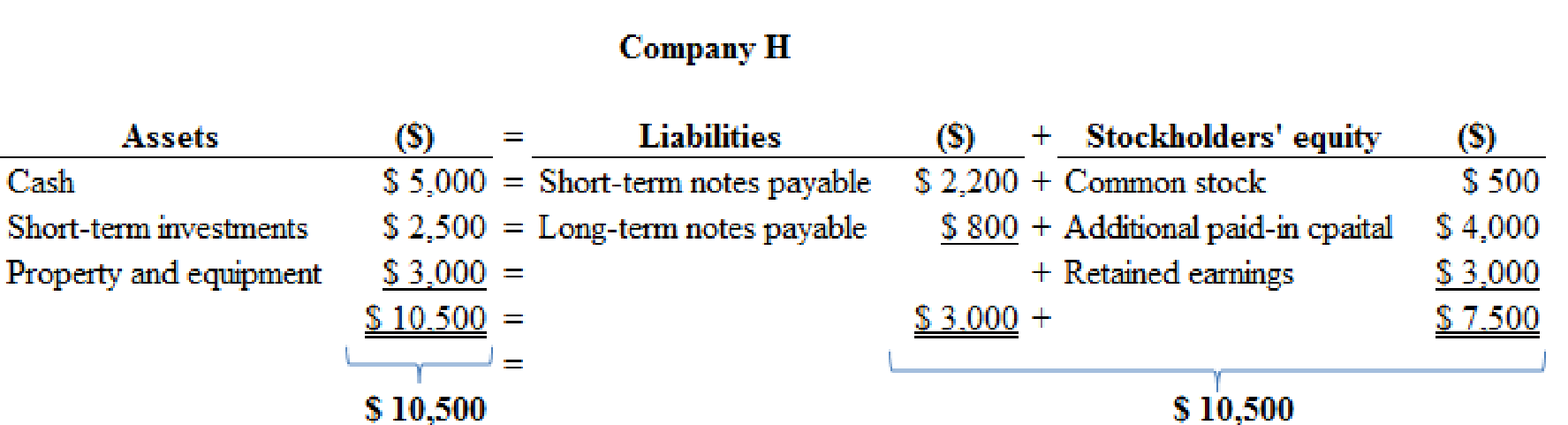
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets are equal to the liabilities and
2.
Prepare
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions as shown below:
| No. | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| a. | Cash (+A) | $4,000 | |
| Notes payable (+L) | $4,000 | ||
| b. | Cash (+A) | $1,500 | |
| Investments (-A) | $1,500 | ||
| c. | Cash (+A) | $1,500 | |
| Property and Equipment (-A) | $1,500 | ||
| d. | $800 | ||
| Dividends payable (+L) | $800 | ||
| e. | Dividends payable (-L) | $800 | |
| Cash (-A) | $800 |
Table (1)
3.
Prepare T-accounts and also report the given transactions for the current year.
3.
Explanation of Solution
T-account: T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
T-accounts for the given accounts are as follows:
| Cash | |||
| Beg. | 5,000 | ||
| (a) | 4,000 | ||
| (b) | 1,500 | ||
| (c) | 1,500 | 800 | (d) |
| End. | 11,200 | ||
| Short-Term Investments | |||
| Beg. | 2,500 | ||
| 1,500 | (b) | ||
| End. | 1,000 | ||
| Property & Equipment | |||
| Beg. | 3,000 | ||
| 1,500 | (c) | ||
| End. | 1,500 | ||
| Short-Term Notes Payable | |||
| 2,200 | Beg. | ||
| 2,200 | End. | ||
| Long-Term Notes Payable | |||
| 800 | Beg. | ||
| 4,000 | (a) | ||
| 4,800 | End. | ||
| Common Stock | |||
| 500 | Beg. | ||
| 500 | |||
| Additional Paid-in Capital | |||
| 4,000 | Beg. | ||
| 4,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings | |||
| 3,000 | Beg. | ||
| (d) | 800 | ||
| 2,200 | |||
4.
Prepare
4.
Explanation of Solution
Trail balance is given below:
| Company H | ||
| Trial Balance | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31 | ||
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $11,200 | |
| Short-term investments | $1,000 | |
| Property and equipment | $1,500 | |
| Notes payable (current) | $2,200 | |
| Notes payable (noncurrent) | $4,800 | |
| Dividends payable | $0 | |
| Common stock | $500 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | $4,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $2,200 | |
| Totals | $13,700 | $13,700 |
Table (2)
5.
Prepare a classified
5.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a classified balance sheet.
| Company H | |
| Balance Sheet | |
| At December 31 | |
| Assets | |
| Current Assets: | |
| Cash | $11,200 |
| Short-term investments | 1,000 |
| Total current assets | 12,200 |
| Property and equipment | 1,500 |
| Total assets | $13,700 |
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | |
| Current Liabilities: | |
| Notes payable | $2,200 |
| Total current liabilities | 2,200 |
| Notes payable | 4,800 |
| Total liabilities | 7,000 |
| Stockholders’ Equity | |
| Common stock | 500 |
| Additional paid-in capital | 4,000 |
| Retained earnings | 2,200 |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 6,700 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $13,700 |
Table (3)
6.
Calculate the
6.
Explanation of Solution
Current Ratio: A part of liquidity ratios, current ratio reflects the ability to oblige the short term debts of a company. It is calculated based on the current assets and current liabilities; a company has in an accounting period. A current ratio is a useful tool for analysis of financials of a company.
Calculate the current ratio of Company H:
Therefore, the current ration of Company H during the current year is 5.55.
In this case, Company H’s current ratio is more than the industrial average. It indicates Company H has better position to repay the current liabilities.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Pedro Manufacturing expects overhead costs of $360,000 per year and direct production costs of $15 per unit. The estimated production activity for the 2023 accounting period is as follows: 1st 2nd 3rd 4th Quarter Units Produced 10,000 9,500 8,000 10,500| The predetermined overhead rate based on units produced is (rounded to the nearest penny): a. $9.47 per unit b. $10.00 per unit c. $8.05 per unit d. $11.25 per unitarrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forward
- On March 1, 20X1, your company,which uses Units-of-Production (UOP) Depreciation, purchases a machine for $300,000.arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardI am searching for the right answer to this financial accounting question using proper techniques.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





