
1.
Discuss the
1.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation effect for given accounts is as follows:
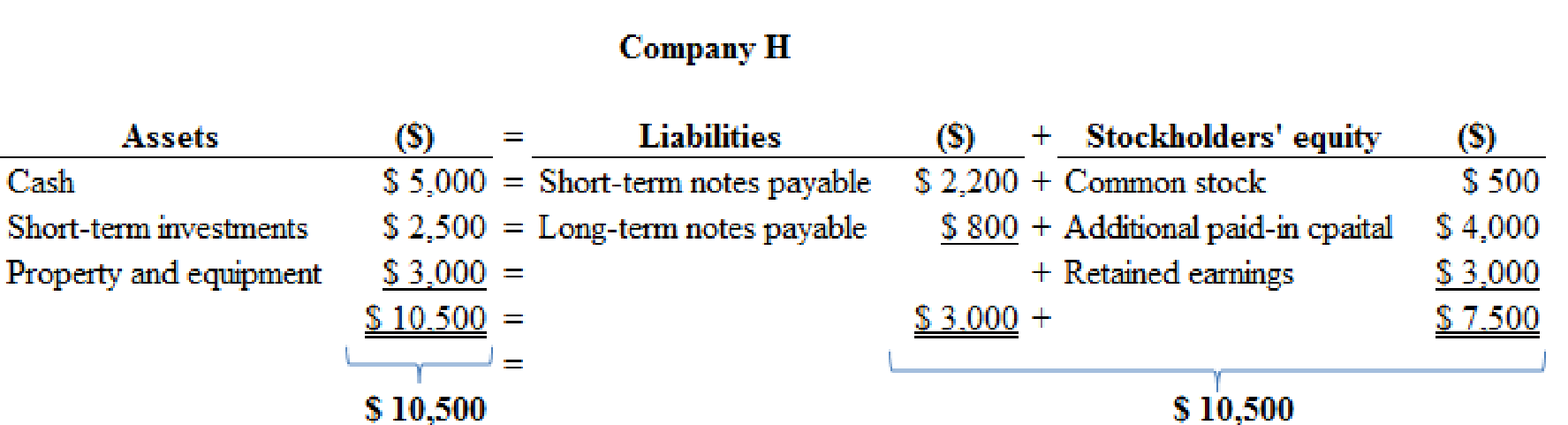
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets are equal to the liabilities and
2.
Prepare
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions as shown below:
| No. | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| a. | Cash (+A) | $4,000 | |
| Notes payable (+L) | $4,000 | ||
| b. | Cash (+A) | $1,500 | |
| Investments (-A) | $1,500 | ||
| c. | Cash (+A) | $1,500 | |
| Property and Equipment (-A) | $1,500 | ||
| d. | $800 | ||
| Dividends payable (+L) | $800 | ||
| e. | Dividends payable (-L) | $800 | |
| Cash (-A) | $800 |
Table (1)
3.
Prepare T-accounts and also report the given transactions for the current year.
3.
Explanation of Solution
T-account: T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
T-accounts for the given accounts are as follows:
| Cash | |||
| Beg. | 5,000 | ||
| (a) | 4,000 | ||
| (b) | 1,500 | ||
| (c) | 1,500 | 800 | (d) |
| End. | 11,200 | ||
| Short-Term Investments | |||
| Beg. | 2,500 | ||
| 1,500 | (b) | ||
| End. | 1,000 | ||
| Property & Equipment | |||
| Beg. | 3,000 | ||
| 1,500 | (c) | ||
| End. | 1,500 | ||
| Short-Term Notes Payable | |||
| 2,200 | Beg. | ||
| 2,200 | End. | ||
| Long-Term Notes Payable | |||
| 800 | Beg. | ||
| 4,000 | (a) | ||
| 4,800 | End. | ||
| Common Stock | |||
| 500 | Beg. | ||
| 500 | |||
| Additional Paid-in Capital | |||
| 4,000 | Beg. | ||
| 4,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings | |||
| 3,000 | Beg. | ||
| (d) | 800 | ||
| 2,200 | |||
4.
Prepare
4.
Explanation of Solution
Trail balance is given below:
| Company H | ||
| Trial Balance | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31 | ||
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $11,200 | |
| Short-term investments | $1,000 | |
| Property and equipment | $1,500 | |
| Notes payable (current) | $2,200 | |
| Notes payable (noncurrent) | $4,800 | |
| Dividends payable | $0 | |
| Common stock | $500 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | $4,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $2,200 | |
| Totals | $13,700 | $13,700 |
Table (2)
5.
Prepare a classified
5.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a classified balance sheet.
| Company H | |
| Balance Sheet | |
| At December 31 | |
| Assets | |
| Current Assets: | |
| Cash | $11,200 |
| Short-term investments | 1,000 |
| Total current assets | 12,200 |
| Property and equipment | 1,500 |
| Total assets | $13,700 |
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | |
| Current Liabilities: | |
| Notes payable | $2,200 |
| Total current liabilities | 2,200 |
| Notes payable | 4,800 |
| Total liabilities | 7,000 |
| Stockholders’ Equity | |
| Common stock | 500 |
| Additional paid-in capital | 4,000 |
| Retained earnings | 2,200 |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 6,700 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $13,700 |
Table (3)
6.
Calculate the
6.
Explanation of Solution
Current Ratio: A part of liquidity ratios, current ratio reflects the ability to oblige the short term debts of a company. It is calculated based on the current assets and current liabilities; a company has in an accounting period. A current ratio is a useful tool for analysis of financials of a company.
Calculate the current ratio of Company H:
Therefore, the current ration of Company H during the current year is 5.55.
In this case, Company H’s current ratio is more than the industrial average. It indicates Company H has better position to repay the current liabilities.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- Please give me true answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardRaptors Inc. creates aluminum alloy parts for commercial aircraft. In a recent transaction Raptors leased a high precision lathe machine from Grizzlies Corp. on January 1, 2024. The following information pertains to the leased asset and the lease agreement: Cost of lathe to lessor $140,000 Grizzlies normal selling price for lathe 178,268 Useful life 7 years Estimated value at end of useful life 8,000 Lease provisions Lease term 5 years Payment frequency Annual Start date of lease January 1 Payment timing December 31 Estimated residual value at end of lease (unguaranteed) 20,000 Interest rate implicit in the lease (readily determinable by lessee) 7% Lessee's incremental borrowing rate 8% The lathe machine will revert back to the lessor at end of lease term, title does not transfer to lessee at any time, and there is not a bargain purchase option. Required…arrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forward
- Can you please solve this financial accounting problem without use Ai?arrow_forwardHobbiton Tours Ltd. has the following details related to its defined benefit pension plan as at December 31, 2024: Pension fund assets of $1,900,000 and actuarial obligation of $1,806,317. The actuarial obligation represents the present value of a single benefit payment of $3,200,000 that is due on December 31, 2030, discounted at an interest rate of 10%; i.e. $3,200,000 / 1.106 = $1,806,317. Funding during 2025 was $55,000. The actual value of pension fund assets at the end of 2025 was $2,171,000. As a result of the current services received from employees, the single payment due on December 31, 2030, had increased from $3,200,000 to $3,380,000. Required Compute the current service cost for 2025 and the amount of the accrued benefit obligation at December 31, 2025. Perform this computation for an interest rate of 8%. Derive the pension expense for 2025 under various assumptions about the expected return and discount rate. Complete the following table: Case…arrow_forwardCalculate Debt Ratios and Debt to Equity Ratio for 2016arrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forwardIn 2026, Maple Leafs Co. sells its single machine, which cost $100,000 and has an undepreciated capital cost (UCC) of $25,000 for tax purposes. For financial reporting, the machine has carrying amount of $40,000. The sale price of the machine is $30,000. Aside from the sale of the machine, the company has other income (before taxes) of $600,000, which includes non-taxable dividends of $120,000 dollars received during the year. There are no other permanent or temporary differences. The company faces an income tax rate of 35%. Required Provide the journal entries for the company for 2026.arrow_forwardBlue Jays Corporation started operations on March 1, 2025. It needs to acquire a special piece of equipment for its manufacturing operations. It is evaluating two options as follows. Option 1: Lease the equipment for 5 years. Lease payments would be $11,000 per year, due at the beginning of each fiscal year (March 1). Blue Jays incremental borrowing rate is 5%. There is not a bargain purchase or renewal option. Blue Jays is responsible for all non-lease costs of operating the equipment. Option 2: Purchase the equipment for $50,000 by borrowing the full purchase amount at 5% over 5 years. This price is considered the fair value of the equipment. Payments are due at the end of each fiscal year (February 28). The equipment has a useful life of 5 years and would be depreciated on a straight-line basis. No residual value is expected to exist at the end of 5 years. Required Calculate the present value of the lease payments (Option 1). Calculate the payment that would be…arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





