
Concept explainers
a.
Prepare general ledger accounts, Prepare
a.
Explanation of Solution
General ledger:
General ledger is a ledger which is used to summarize all the entries of the subsidiary ledger. The general ledger is used to record the correcting, adjusting and closing entries.
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and
stockholders’ equities . - Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
T-account:
T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the journal
Prepare cash account:
| Cash | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| July 1 | Balance | $6,800 | ||||
Table (1)
Prepare
| Accounts Receivable | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| July 1 | Balance | $9,800 | ||||
Table (2)
Prepare Accounts Payable Account:
| Accounts Payable | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| July 1 | Balance | $2,100 | ||||
Table (3)
Prepare Notes Payable Account:
| Notes Payable | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| July 1 | Balance | $3,300 | ||||
Table (4)
Prepare Common Stock Account:
| Common Stock | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| July 1 | Balance | $2,000 | ||||
Table (5)
Prepare
| Retained Earnings | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| July 1 | Balance | $9,200 | ||||
Table (6)
Record the journal entries for the transactions that occurred during July 1 to July 14:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 1 | Rent Expense (E–) | 510 | |
| Cash (A–) | 510 | |||
| (To record rent expense payment) | ||||
Table (7)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 2 | Cash (A+) | 7,100 | |
| Accounts Receivable (A–) | 7,100 | |||
| (To record amount collected from customers) | ||||
Table (8)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 3 | Notes Payable (A–) | 1,800 | |
| Cash (A–) | 1,800 | |||
| (To record cash paid for notes payable) | ||||
Table (9)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 4 | Accounts Receivable (A+) | 16,550 | |
| Service Fees Earned (E+) | 16,550 | |||
| (To record services rendered on account) | ||||
Table (10)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 5 | Cash (A+) | 1,200 | |
| Service Fees Earned (E+) | 1,200 | |||
| (To record services rendered for cash) | ||||
Table (11)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 6 | Accounts Payable (A–) | 1,400 | |
| Cash (A–) | 1,400 | |||
| (To record cash paid for creditors on account) | ||||
Table (12)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 7 | Cash (A+) | 12,750 | |
| Accounts Receivable (A–) | 12,750 | |||
| (To record amount collected from customers on account) | ||||
Table (13)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 8 | Delivery Expense (E–) | 650 | |
| Cash (A–) | 650 | |||
| (To record delivery expense payment) | ||||
Table (14)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 9 | Salaries Expense (E–) | 4,600 | |
| Cash (A–) | 4,600 | |||
| (To record salaries expense payment) | ||||
Table (15)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 10 | Advertising Expense (E–) | 600 | |
| Accounts Payable (L+) | 600 | |||
| (To record advertising expense bill) | ||||
Table (16)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 11 | Utility Expense (E–) | 250 | |
| Cash (A–) | 250 | |||
| (To record utility expense payment) | ||||
Table (17)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 12 | Dividends (E–) | 2,000 | |
| Cash (A–) | 2,000 | |||
| (To record dividends payment) | ||||
Table (18)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 13 | Supplies Expense (E–) | 2,260 | |
| Accounts Payable (L+) | 2,260 | |||
| (To record receipt of advertising expense bill) | ||||
Table (19)
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| July | 14 | Equipment (A+) | 6,300 | |
| Cash (A–) | 6,300 | |||
| (To record purchase of computer) | ||||
Table (20)
Post the journal entries into T-accounts.
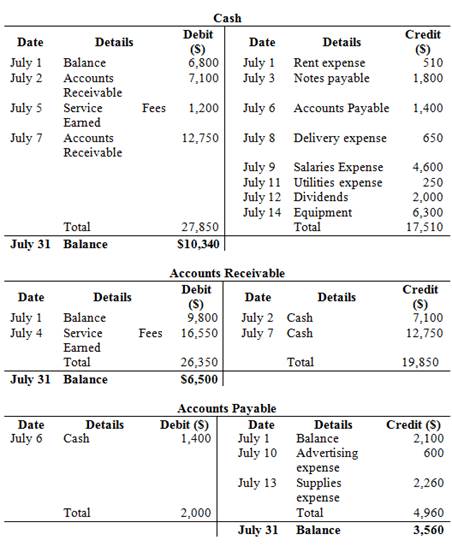
Figure (1)
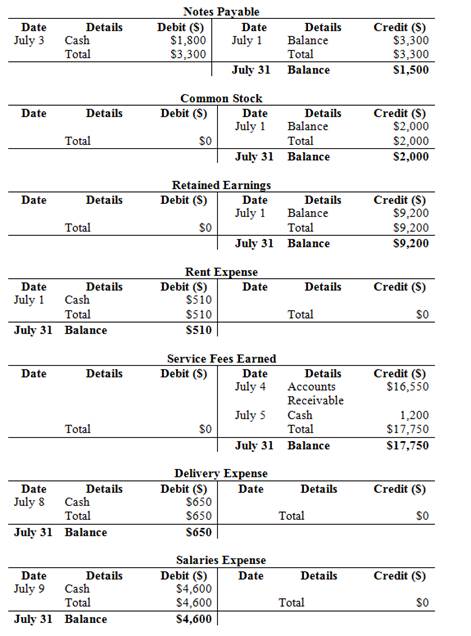
Figure (2)
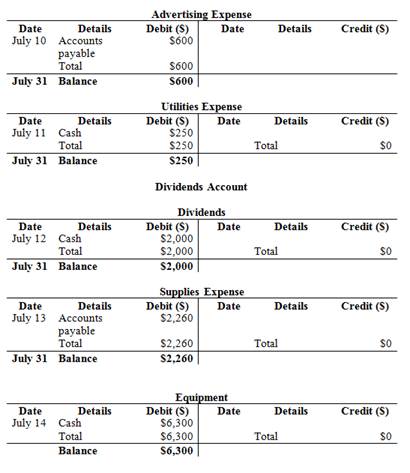
Figure (3)
b.
Prepare a
b.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is the summary of accounts, and their debit and credit balances at a given time. It is usually prepared at end of the accounting period. Debit balances are listed in left column and credit balances are listed in right column. The totals of debit and credit column should be equal. Trial balance is useful in the preparation of the financial statements.
Preparation of trial balance:
| Company P | ||
| Trial Balance | ||
| As of July 30 | ||
| Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 10,340 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 6,500 | |
| Equipment | 6,300 | |
| Accounts Payable | 3,560 | |
| Notes Payable | 1,500 | |
| Common Stock | 2,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 9,200 | |
| Service Fees Earned | 17,750 | |
| Rent Expense | 510 | |
| Delivery Expense | 650 | |
| Salaries Expense | 4,600 | |
| Advertising Expense | 600 | |
| Utilities Expense | 250 | |
| Dividends | 2,000 | |
| Supplies Expense | 2,260 | |
| Total | 34,010 | 34,010 |
Table (21)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCT.F/UNDERGRADS-W/ACCESS
- Please provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardCan you solve this financial accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forward
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forward
- Can you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardI am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forward
- I need assistance with this financial accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





