
Analyzing a Quality Cost Report LO1—8
Mercury, Inc., produces cell phones at its plant in Texas. In recent years, the company’s market share has been eroded by stiff competition from overseas. Price and product quality are the two key areas in which companies compete in this market.
A year ago, the company’s cell phones had been ranked low in product quality in a consumer survey. Shocked by this result, Jorge Gomez, Mercury’s president, initiated an intense effort to improve product quality. Gomez set up a task force to implement a formal quality improvement program. Included on this task force were representatives from the Engineering. Marketing. Customer Service. Production, and Accounting departments. The broad representation was needed because Gomez believed that this was a companywide program and that all employees should share the responsibility for its success.
After the first meeting of the task force, Holly Elsoe, manager of the Marketing Department, asked John Tran, production manager, what he thought of the proposed program. Tran replied. "I have reservations. Quality is too abstract to be attaching costs to it and then to be holding you and me responsible for cost improvements. I like to work with goals that I can see and count! I’m nervous about having my annual bonus based on a decrease in quality costs; there are too many variables that we have no control over.”
Mercury’s quality improvement program has now been in operation for one year. The company’s most recent quality cost report is shown below.
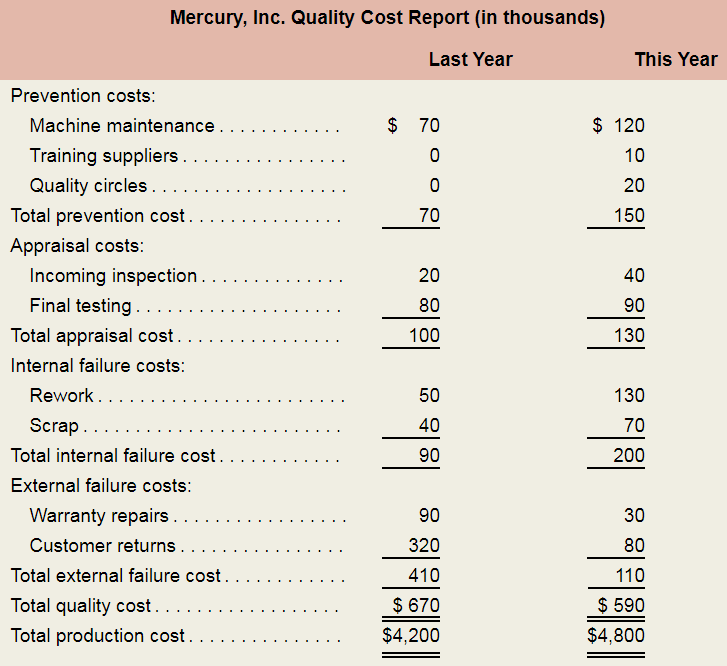
As they were reviewing the report, Elsoe asked Tran what he now thought of the quality improvement program. Tran replied. “I’m relieved that the new quality improvement program hasn’t hurt our bonuses, but the program has increased the workload in the Production Department. It is true that customer returns are way down, but the cell phones that were returned by customers to retail outlets were rarely sent back to us for rework.”
Required:
- Expand the company’s quality cost report by showing the costs in both years as percentages of both total production cost and total quality cost. Carry all computations to one decimal place. By analyzing the report, determine if Mercury, Inc.’s quality improvement program has been successful. List specific evidence to support your answer.
- Do you expect the improvement program as it progresses to continue to increase the workload in the Production Department?
- Jorge Gomez believed that the quality improvement program was essential and that Mercury. Inc., could no longer afford to ignore the importance of product quality. Discuss how Mercury? Inc., could measure the cost of nor implementing the quality improvement program. (CMA, adapted)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1A Solutions
MANAG ACCT F/..(LL)+CONNECT W/PROCTORIO+
- I need help with this General accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardKindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forward
- I am searching for the correct answer to this Financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this Financial accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardEcho Tone Technologies reports annual sales of $90,000, and it expects sales to increase to $135,000 next year. The company has a degree of operating leverage (DOL) of 4.2. By what percentage should net income increase? A. 70% B. 189% C. 150% D. 210%arrow_forward
- Please provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


