
Concept explainers
Propose structures for molecules that meet the following descriptions. Assume that the kinds of carbons (1°, 2°, 3°, or 4°) have been assigned by DEPT-NMR.
a) C6H12O;IR: 1715 cm-1; 13C NMR: 8.0 δ (1°), 18.5 δ (1°), 33.5 δ (2°), 40.6 δ (3°), 214.0 δ (4°)
b) C5H10O; IR: 1730 cm-1; 13C NMR: 22.6δ (1°), 23.6 8 (3°), 52.8 8 (2°), 202.4 8 (3°)
c) C6H8O; IR: 1680 cm-1; 13C NMR: 22.9 δ (2°), 25.8 8 (2°), 38.2 δ (2°). 129.8 8 (3°), 150.6 8 (3°), 198.7 δ (4°)
a)

Interpretation:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given is to be assigned.
C6H12O; IR: 1715 cm-1; 13CNMR: 8.0 δ (10), 18.5 δ (10), 33.5 δ (20), 40.6 δ (30), 214.0 δ (40)
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones show a strong absorption band in IR from 1660-1770 cm-1. Aldehydes show two characteristic C-H absorptions between 2700-2760cm-1 and 2800-2860 cm-1. Saturated aldehydes absorb near 1730 cm-1 while aromatic aldehydes and α, β- unsaturated aldehydes absorb near 1705 cm-1. Saturated ketones and cyclohexanones absorb near 1715 cm-1 while aromatic ketones and α, β- unsaturated ketones absorb near 1685-1690 cm-1. Cyclopentanones absorb around 1750 cm-1.
In 13CNMR, carbons in double bond which are sp2 hybridized absorb from 110 to 220 δ. Saturated aldehydes and ketones usually absorb in the region from 200 to 215 δ While aromatic and unsaturated carbonyl compounds absorb in the 190 to 200 δ region. The primary alkyl carbon absorbs in the range 10-15 δ, a secondary alkyl radical in the range 16-25 δ while a tertiary alkyl in the range 25-35 δ. The signals will be observed at downfield if these alkyl groups are attached to electron withdrawing groups.
To assign:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given.
C6H12O; IR: 1715 cm-1; 13CNMR: 8.0 δ (10), 18.5 δ (10), 33.5 δ (20), 40.6 δ (30), 214.0 δ (40)
Answer:
Answer to Problem 69AP
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is
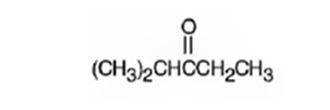
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C6H12O. Ignoring oxygen the molecular formula of the parent compound becomes C6H14. Thus the compound has two hydrogen atoms (14-12) less than the parent and hence has one unsaturation unit perhaps a C=O.
The IR absorption at 1715 cm-1 and 13CNMR peak at 214.0 δ indicate that the compound is a ketone. The 13CNMR further indicates that the carbonyl group is flanked by a secondary and tertiary carbon indicated by the two downfield signals at 33.5 δ and 40.6 δ. The remaining three carbons has to be primary, of which one is attached as methyl(8.0 δ) to the secondary carbon and two others are attached as two methyl groups (18.5δ) on the tertiary carbon. Hence the compound is 2-methyl-3-pentanone.
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is

b)

Interpretation:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given is to be assigned.
C5H10O; IR: 1730 cm-1; 13CNMR: 22.6 δ (10), 23.6 δ (30), 52.8 δ (20), 202.4 δ (30).
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones show a strong absorption band in IR from 1660-1770 cm-1. Aldehydes show two characteristic C-H absorptions between 2700-2760cm-1 and 2800-2860 cm-1. Saturated aldehydes absorb near 1730 cm-1 while aromatic aldehydes and α, β- unsaturated aldehydes absorb near 1705 cm-1. Saturated ketones and cyclohexanones absorb near 1715 cm-1 while aromatic ketones and α, β- unsaturated ketones absorb near 1685-1690 cm-1. Cyclopentanones absorb around 1750 cm-1.
In 13CNMR, carbons in double bond which are sp2 hybridized absorb from 110 to 220 δ. Saturated aldehydes and ketones usually absorb in the region from 200 to 215 δ While aromatic and unsaturated carbonyl compounds absorb in the 190 to 200 δ region. The primary alkyl carbon absorbs in the range 10-15 δ, a secondary alkyl radical in the range 16-25 δ while a tertiary alkyl in the range 25-35 δ. The signals will be observed at downfield if these alkyl groups are attached to electron withdrawing groups.
To assign:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given.
C5H10O; IR: 1730 cm-1; 13CNMR: 22.6 δ (10), 23.6 δ (30), 52.8 δ (20), 202.4 δ (30).
Answer to Problem 69AP
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is

Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C6H12O. Ignoring oxygen the molecular formula of the parent compound becomes C6H14. Thus the compound has two hydrogen atoms less than the parent and hence has one unsaturation unit, a carbonyl group.
The IR absorption at 1730 cm-1 and 13CNMR peak at 202.4 δ indicate that the compound is a saturated aldehyde. The 13CNMR further indicates that the carbonyl group is attached to a secondary carbon indicated by the downfield signal at 52.8 δ. Of the remaining three carbons one has to be tertiary(23.6 δ) which is attached to two methyl groups(22.6 δ). Hence the compound is 2-methylbutanal.
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is

c)
Interpretation:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given is to be assigned.
C6H8O; IR: 1680 cm-1; 13CNMR: 22.9 δ (20), 25.8 δ (20), 38.2 δ (20), 129.8 δ (30) 150.6 δ (30), 198.7 δ (40).
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones show a strong absorption band in IR from 1660-1770 cm-1. Aldehydes show two characteristic C-H absorptions between 2700-2760cm-1 and 2800-2860 cm-1. Saturated aldehydes absorb near 1730 cm-1 while aromatic aldehydes and α, β- unsaturated aldehydes absorb near 1705 cm-1. Saturated ketones and cyclohexanones absorb near 1715 cm-1 while aromatic ketones and α, β- unsaturated ketones absorb near 1685-1690 cm-1. Cyclopentanones absorb around 1750 cm-1.
In 13CNMR, carbons in double bond which are sp2 hybridized absorb from 110 to 220 δ. Saturated aldehydes and ketones usually absorb in the region from 200 to 215 δ While aromatic and unsaturated carbonyl compounds absorb in the 190 to 200 δ region. The primary alkyl carbon absorbs in the range 10-15 δ, a secondary alkyl radical in the range 16-25 δ while a tertiary alkyl in the range 25-35 δ.
To assign:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given.
C6H8O; IR: 1680 cm-1; 13CNMR: 22.9 δ (20), 25.8 δ (20), 38.2 δ (20), 129.8 δ (30) 150.6 δ (30), 198.7 δ (40).
Answer to Problem 69AP
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is
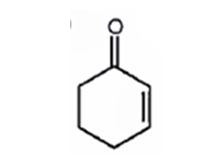
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C6H8O. Ignoring oxygen the molecular formula of the parent compound becomes C6H14. Thus the compound has six hydrogen atoms (14-8= 6) less than the parent and hence has three unsaturation units.
The IR absorption at 1680 cm-1 and 13CNMR peak at 198.7 δ indicate that the compound is an α, β- unsaturatedketone. The compound has three unsaturated units. α, β- unsaturatedketone accounts for two unsaturation units. Hence the compound contains a six membered ring. The signals at 129.8 δ (30) 150.6 δ (30) can be attributed to the carbons in double bond. The other three signals at 22.9 δ (20), 25.8 δ (20), 38.2 δ (20) can be attributed to three methylene groups. The signal at 38.2 δ (20) can be assigned to methylene carbon attached to carbonyl carbon, that at 25.8 δ (20) to the methylene carbon carbon attached to C4 while that at 22.9 δ (20) is due to methylene carbon C5.
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EP ORGANIC CHEMISTRY,24 MONTH-OWLV2
- please help with synthesisarrow_forward10. Stereochemistry. Assign R/S stereochemistry for the chiral center indicated on the following compound. In order to recieve full credit, you MUST SHOW YOUR WORK! H₂N CI OH CI カー 11. () Stereochemistry. Draw all possible stereoisomers of the following compound. Assign R/S configurations for all stereoisomers and indicate the relationship between each as enantiomer, diastereomer, or meso. NH2 H HNH, -18arrow_forwardb) 8. Indicate whether the following carbocation rearrangements are likely to occur Please explain your rational using 10 words or less not likely to occur • The double bond is still in the Same position + Likely to oc occur WHY? -3 H3C Brave Chair Conformers. Draw the chair conformer of the following substituted cyclohexane. Peform a RING FLIP and indicate the most stable conformation and briefly explain why using 20 words or less. CI 2 -cobs ?? MUST INDICATE H -2 -2 Br EQ Cl OR AT Br H& most stable WHY? - 4arrow_forward
- CH 12 Conformational Analysis. Draw all 6 conformers (one above each letter) of the compound below looking down the indicated bond. Write the letter of the conformer with the HIGHEST and LOWEST in energies on the lines provided. NOTE: Conformer A MUST be the specific conformer of the structure as drawn below -4 NOT HOH OH 3 Conformer A: Br OH A Samo Br H 04 Br H H3 CH₂ H anti stagere Br CH clipsed H Brott H IV H MISSING 2 -2 B C D E F X 6 Conformer with HIGHEST ENERGY: 13. (1 structure LOWEST ENERGY: Nomenclature. a) Give the systematic (IUPAC) name structure. b) Draw the corresponding to this name. HINT: Do not forget to indicate stereochemistry when applicable. a) ८८ 2 "Br {t༐B,gt)-bemn€-nehpརི་ཚ༐lnoa Parent name (noname) 4 Bromo Sub = 2-methylethyl-4 Bromo nonane b) (3R,4S)-3-chloro-4-ethyl-2,7-dimethyloctane # -2 -2arrow_forwardin the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forward
- Molecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forwardIndicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


