
Concept explainers
A small test charge
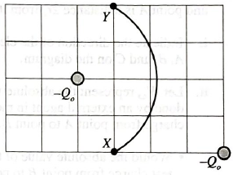
i. Draw an arrow on the diagram at each point (X and Y) to show the direction of the electric force on the test charge at that point. Explain why you drew the arrows as you did.
ii. Is the work done on the charge by the electric field positive, negative, or zero? Explain.
iii. Is the electric potential difference
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- A rectangle measuring 30.0 cm by 40.0 cm is located inside a region of a spatially uniform magnetic field of 1.70 T , with the field perpendicular to the plane of the coil (the figure (Figure 1)). The coil is pulled out at a steady rate of 2.00 cm/s traveling perpendicular to the field lines. The region of the field ends abruptly as shown. Find the emf induced in this coil when it is all inside the field, when it is partly in the field, and when it is fully outside. Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA rectangular circuit is moved at a constant velocity of 3.00 m/s into, through, and then out of a uniform 1.25 T magnetic field, as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The magnetic field region is considerably wider than 50.0 cm . Find the direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) of the current induced in the circuit as it is going into the magnetic field (the first case), totally within the magnetic field but still moving (the second case), and moving out of the field (the third case). Find the magnitude of the current induced in the circuit as it is going into the magnetic field . Find the magnitude of the current induced in the circuit as it is totally within the magnetic field but still moving. Find the magnitude of the current induced in the circuit as it is moving out of the field. Please show all stepsarrow_forwardShrinking Loop. A circular loop of flexible iron wire has an initial circumference of 161 cm , but its circumference is decreasing at a constant rate of 15.0 cm/s due to a tangential pull on the wire. The loop is in a constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.00 T , which is oriented perpendicular to the plane of the loop. Assume that you are facing the loop and that the magnetic field points into the loop. Find the magnitude of the emf E induced in the loop after exactly time 9.00 s has passed since the circumference of the loop started to decrease. Find the direction of the induced current in the loop as viewed looking along the direction of the magnetic field. Please explain all stepsarrow_forward
- A circular loop of wire with radius 0.0480 m and resistance 0.163 Ω is in a region of spatially uniform magnetic field, as shown in the following figure (Figure 1). The magnetic field is directed out of the plane of the figure. The magnetic field has an initial value of 7.88 T and is decreasing at a rate of -0.696 T/s . Is the induced current in the loop clockwise or counterclockwise? What is the rate at which electrical energy is being dissipated by the resistance of the loop? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA 0.333 m long metal bar is pulled to the left by an applied force F and moves to the left at a constant speed of 5.90 m/s. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 46.7 Ω resistor, as shown in (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. You can ignore the resistance of the bar and rails. The circuit is in a uniform 0.625 T magnetic field that is directed out of the plane of the figure. Is the induced current in the circuit clockwise or counterclockwise? What is the rate at which the applied force is doing work on the bar? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Calculate the magnitude of the emf induced in the circuit. Find the direction of the current induced in the circuit. Calculate the current through the resistor.arrow_forward
- In the figure, a conducting rod with length L = 29.0 cm moves in a magnetic field B→ of magnitude 0.510 T directed into the plane of the figure. The rod moves with speed v = 5.00 m/s in the direction shown. When the charges in the rod are in equilibrium, which point, a or b, has an excess of positive charge and where does the electric field point? What is the magnitude E of the electric field within the rod, the potential difference between the ends of the rod, and the magnitude E of the motional emf induced in the rod? Which point has a higher potential? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardExamine the data and % error values in Data Table 2 where the mass of the pendulum bob increased but the angular displacement and length of the simple pendulum remained constant. Describe whether or not your data shows that the period of the pendulum depends on the mass of the pendulum bob, to within a reasonable percent error.arrow_forwardPlease graph, my software isn't working - Data Table 4 of Period, T vs √L . (Note: variables are identified for graphing as y vs x.) On the graph insert a best fit line or curve and display the equation on the graph. Thank you!arrow_forward
- I need help with problems 93 and 94arrow_forwardSince the instruction says to use SI units with the correct sig-fig, should I only have 2 s for each trial in the Period column? Determine the theoretical period of the pendulum using the equation T= 2π √L/g using the pendulum length, L, from Data Table 2. Calculate the % error in the periods measured for each trial in Data Table 2 then recordarrow_forwardA radiography contingent are carrying out industrial radiography. A worker accidentally crossed a barrier exposing themselves for 15 seconds at a distance of 2 metres from an Ir-192 source of approximately 200 Bq worth of activity. What dose would they have received during the time they were exposed?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





