
Concept explainers
Exercise 19-9
P2
Use information in Exercise 19- 7 to prepare journal entries for the following events for the month of May.
1. Direct lab or usage.
2. Indirect labor usage.
3. Total payroll paid in cash.
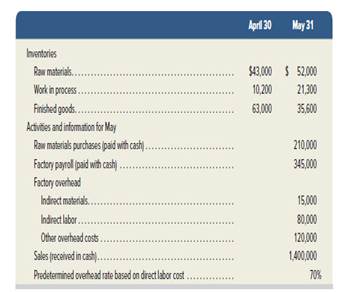
Exercise 19-7
Cost flows in a
P1 P2 P3 P4
The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system.
Compute the following amounts for the month of May.
1. Cost of direct materials used.
2. Cost of direct labor used.
3. Cost of goods manufactured.
4. Cost of goods sold.*
5. Gross profit.
6. Overapplied or underapplied
*Do not consider any underapplied or overapplied overhead. Check (3) $625,400
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
FUND OF ACCOUNTING PRIN W/ACC <CUSTOM>
- I am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this financial accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem using the correct accounting process?arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forward
- I am looking for the correct answer to this financial accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardPlease show me the correct approach to solving this financial accounting question with proper techniques.arrow_forward
- I need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this financial accounting problem using the correct accounting process?arrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





