
(a)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of
For
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(a)
Explanation of Solution
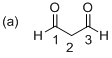
The given molecule is drawn. The parent indicates three carbon atoms, and suffix ‘
Further the parent chain numbered so that the two carbonyl groups is assigned the lowest possible locate (1 indicates that the keto groups is located between C1 and C2). Hence the systematic structure for the molecule (a) is Propanediol.
(b)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
IUPAC Nomenclature Method
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(b)
Explanation of Solution
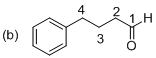
The given molecule is drawn. In molecule (b) parent (butanol) indicates four carbon atoms and the suffix ‘al’ and indicates an on aldehyde group at C1 position. Another one phenyl substituent is located at C4 position. The systematic structure for the molecule (b) is 4-phenyl butanal.
(c)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
IUPAC Nomenclature Method
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(c)
Explanation of Solution
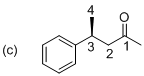
The stereo chemical structure for given molecule is drawn as shown above. The parent (butanol) indicates a chain of four carbon atoms, and suffix ‘al’ indicates an aldehyde group at C1 position. In molecule presence of one phenyl substituent is located at C3, which is a chirality center with the (S) configuration. The corresponding molecule (c) is (S)-3-phenyl butanal.
(d)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
IUPAC Nomenclature Method
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(d)
Explanation of Solution
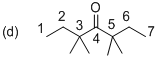
The systematic structure of given molecule (d) has drawn as shown above. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton the chain which contains 7 carbons with one carbonyl group. Hence the root name of the molecule is ‘Heptanone’ and the suffix ‘one’ indicates a ketone.
Further the carbonyl is located at C4 position and four methyl groups are present at C3 and C5 position is 3,3,5,5-Tetramethyl-4-heptanone. So the systematic name for the molecule (d) is 3,3,5,5-Tetramethyl-4-heptanone.
(e)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
IUPAC Nomenclature Method
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(e)
Explanation of Solution
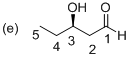
The stereo chemical structure of given molecule drawn. In the parent carbon skeleton in the chain which contains five carbons with one hydroxyl, one keto group. Hence the name of the molecule is ‘Pentanal’ and the suffix ‘al’ indicates an one aldehyde group. Then the molecule one carbonyl group located at C1 place and one hydroxyl group is present at C3, which is a chirality center with the R configuration.
Hence the systematic structure for the given molecule (e) is a (R)-hydroxy pentanol.
(f)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
IUPAC Nomenclature Method
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(f)
Explanation of Solution
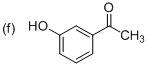
The systematic structure of given molecule drawn. The parent is acetophenone, and there is an one hydroxyl group (OH) in the meta position at C3 place of the ring.
The systematic structure for the given molecule (f) is a Meta-Hydroxy acetophenone.
(g)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
IUPAC Nomenclature Method
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(g)
Explanation of Solution
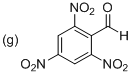
The given parent phenyl group as a benzaldehyde and there are three nitro groups located at C2, C4 and C6 place. The given structure is 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzaldehyde.
(h)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
IUPAC Nomenclature Method
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(h)
Explanation of Solution
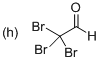
The systematic structure of given molecule drawn. In the parent carbon skeleton in the chain which contains two carbon atoms with three bromo groups. Hence the name of the molecules is ‘Ethanal’ and the suffix ‘al’ indicates a one alcohol group. Further the molecule has one aldehyde group located at C1 place and three bromine atoms present in C2 position.
Hence the systematic structure for the given molecule (h) is a Tribromo acetaldehyde.
(i)
Interpretation:
The target molecule should be drawn for the given statements by using its molecular structure.
Concept introduction:
The structure the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms which are attached to that carbon atom are not to show, rather the bonds in between carbon atoms and to the hetero atoms are drawn as line segments. For acyclic, linear carbon chains it draws as in a zig-zag fashion and for cyclic chains of carbon it draws as a cyclic polygon. For representing a heteroatom attached to the carbon, use a line segment and label the heteroatom at the end of their line segment.
IUPAC Nomenclature Method
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
For example alkane molecule, suffix will be ‘ane’, compound presence of carbonyl group ‘one’ and presence of alcohol group suffix will be ‘ol’
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an saturated alkane molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
To identify: The systematic structure for the given molecule
(i)
Explanation of Solution
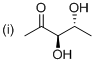
The simple stereo chemical structure of given molecule drawn. The given parent indicates five carbon atoms with one keto group and two hydroxyl groups, hence the name of the molecule is ‘Pentanone’ (it is a general name) and suffix ‘one’ indicates a one keto group. Further this molecule carbonyl group located at C2 position and two hydroxyl group located at C3 and C4 position, both of which are chirality with the (R) configuration.
The systematic structure and name of the compound as showed above.
Finally the systematic structure for the given molecule (i) is a (3 4R)-3,4-dihydroxy-2-pentanone.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY,SOLN.MAN.+...-ACCESS
- Assign all the protonsarrow_forwardAssign all the carbonsarrow_forward9 7 8 C 9 8 200 190 B 5 A -197.72 9 8 7 15 4 3 0: ང་ 200 190 180 147.52 134.98 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 90 OH 10 4 3 1 2 -143.04 140. 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 CI 3 5 1 2 141.89 140.07 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 ៖- 90 129. 126.25 80 70 60 -60 50 40 10 125.19 -129.21 80 70 3.0 20 20 -8 60 50 10 ppm -20 40 128.31 80 80 70 60 50 40 40 -70.27 3.0 20 10 ppm 00˚0-- 77.17 30 20 20 -45.36 10 ppm -0.00 26.48 22.32 ―30.10 ―-0.00arrow_forward
- Assign all the carbonsarrow_forwardC 5 4 3 CI 2 the Righ B A 5 4 3 The Lich. OH 10 4 5 3 1 LOOP- -147.52 T 77.17 -45.36 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm B -126.25 77.03 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 TO LL <-50.00 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 45.06 30.18 -26.45 22.36 --0.00 45.07 7.5 1.93 2.05 -30.24 -22.36 C A 7 8 5 ° 4 3 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 8 5 4 3 ཡི་ OH 10 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 5 4 3 2 that th 7 I 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 115 2.21 4.00 1.0 ppm 6.96 2.76 5.01 1.0 ppm 6.30 1.00arrow_forwardCurved arrows were used to generate the significant resonance structure and labeled the most significant contribute. What are the errors in these resonance mechanisms. Draw out the correct resonance mechanisms with an brief explanation.arrow_forward
- What are the: нсе * Moles of Hice while given: a) 10.0 ml 2.7M ? 6) 10.ome 12M ?arrow_forwardYou are asked to use curved arrows to generate the significant resonance structures for the following series of compounds and to label the most significant contributor. Identify the errors that would occur if you do not expand the Lewis structures or double-check the mechanisms. Also provide the correct answers.arrow_forwardhow to get limiting reactant and % yield based off this data Compound Mass 6) Volume(mL Ben zaphone-5008 ne Acetic Acid 1. Sam L 2-propanot 8.00 Benzopin- a col 030445 Benzopin a Colone 0.06743 Results Compound Melting Point (°c) Benzopin acol 172°c - 175.8 °c Benzoping to lone 1797-180.9arrow_forward
- Assign ALL signals for the proton and carbon NMR spectra on the following pages.arrow_forward7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forwardAssign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





