
Concept explainers
Connecting the Concepts
1. In the primate phylogenetic tree below, fill in groups (a)–(e). Of the groups, which are anthropoids and which are apes?
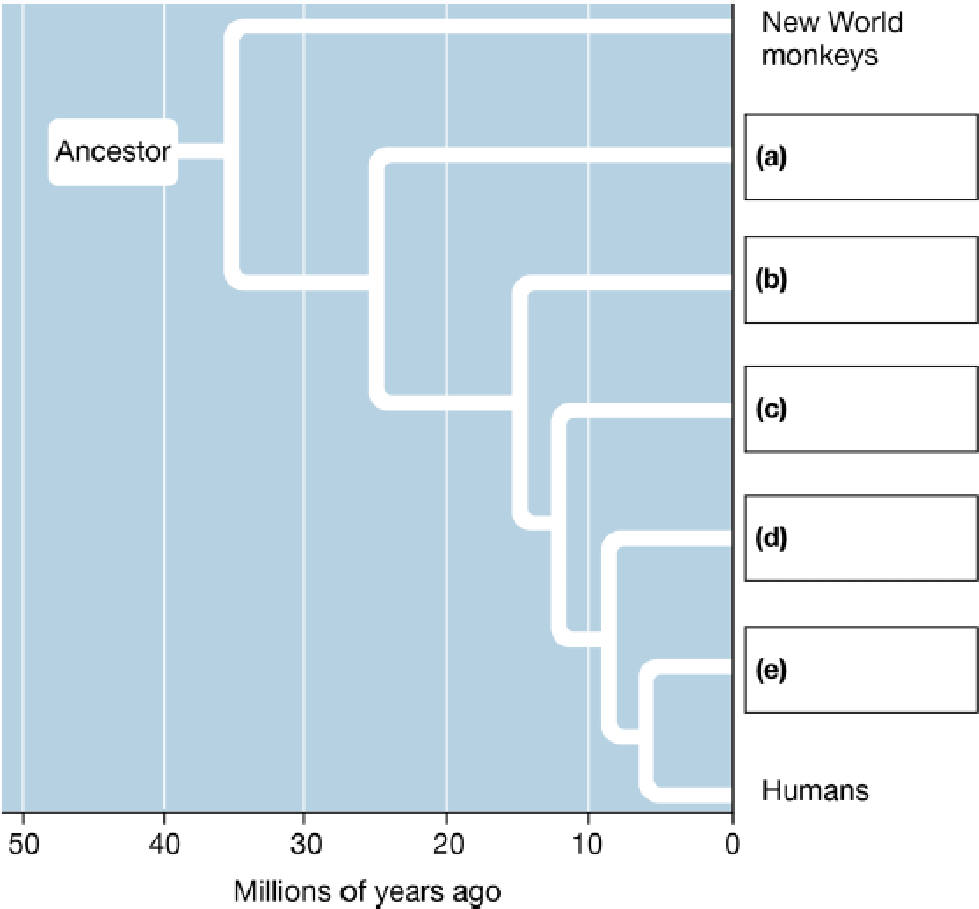
To complete: The primate phylogenic tree (containing apes and anthropoids).
Introduction:
Primates are evolved about 65 million years ago. The characters of primates include limber joints, grasping hands and feet with flexible digits, a short snout, and forward-pointing eyes. Living primates are lorises, bush babies, and lemurs; the tarsiers; and anthropoids (monkeys and apes).
All primates are anthropoids: gibbons, orangutans, gorillas, monkeys, chimpanzees, and humans, but humans and chimpanzees are apes. Apes have larger brains than other primates, which include gibbons, orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Fig. 1 represents various groups of the primate phylogenic tree.
Pictorial representation: A phylogenetic tree showing various groups of primates is given in Fig. 1.
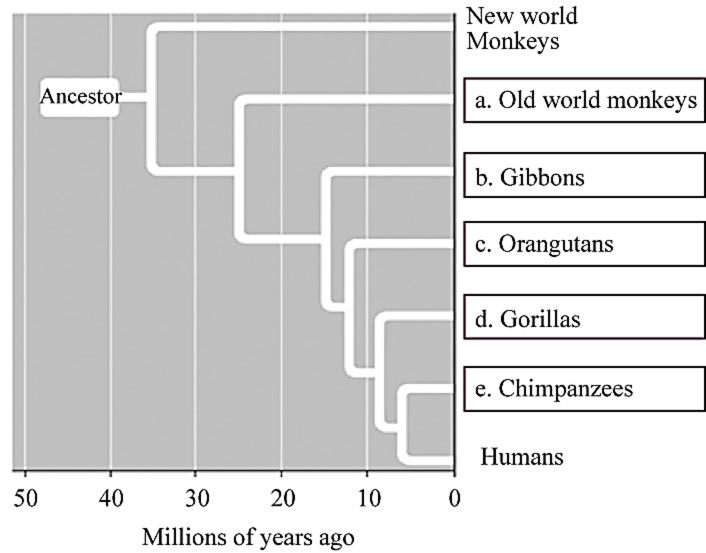
Fig.1: The primate phylogenic tree.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Old world monkeys.
Old world monkeys are primates that belong to the super family Cercopithecoidea. Old world monkeys have tails. Hence, the correct answer is old world monkeys.
(b)
Correct answer: Gibbons.
Gibbons are the small, arboreal apes. They are distributed in the wild, in the tropical and subtropical forests of Southeast Asia. Hence the correct answer is gibbons.
(c)
Correct answer: Orangutans.
Orangutans are great apes, and they are closely related to humans. Hence, the correct answer is orangutans.
(d)
Correct answer: Gorillas.
Gorillas are ground-dwelling, herbivorous apes. They live mostly in the forests of central Sub-Saharan Africa. They show many human-like behaviors and emotions, (laughter and sadness). Hence, the correct answer is gorillas.
(e)
Correct answer: Chimpanzees.
Chimpanzees are the species of apes that are most closely related to humans. Chimpanzees are found in tropical forests and savannas of equatorial Africa. Hence, the correct answer is chimpanzees.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
CAMPBELL BIO: CONCEPTS&CONNECTIONS (LL)
- Not part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNoggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- Explain in a flowcharts organazing the words down below: genetics Chromosomes Inheritance DNA & Genes Mutations Proteinsarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





