
To find:
a) Sketch the titration curve for the titration of
b) Label the curve with the
c) Draw the structures of the species present in the solution at the equivalence point.
Answer to Problem 19.77QA
Solution:
a) and b) Labeled titration curve for the titration of
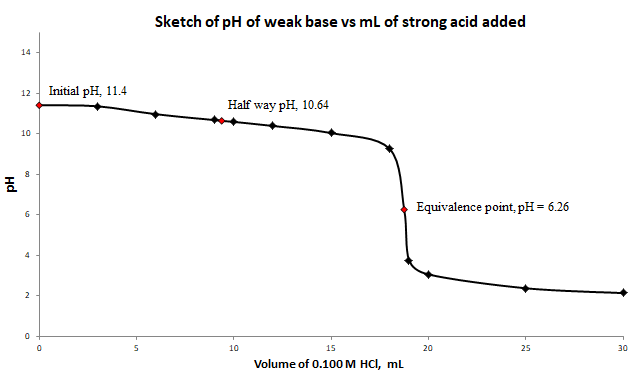
c) At the equivalence point, the structure of the species present in the solution is
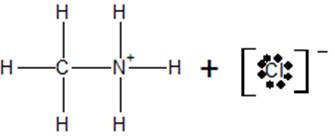
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
We can calculate moles of weak base present and the moles of
We know how much of the weak base remains and how much of its conjugate acid produced because one mole of base reacts with one mole of
2) Formula:
i)
ii)
iii)
iv)
v)
vi)
vii)
3) Given:
i)
ii) Volume of methylamine =
iii)
iv) For methylamine,
v) For methylamine,
4) Calculation:
a) Calculation of initial
| Reaction | |||
| Initial | |||
| Change | |||
| Final | |||
Applying law of mass action,
Solving this equation using quadratic equation formula:
The negative value of concentration has no significance. Therefore, we will proceed with
So,
Therefore, initial
At half way to the equivalence point,
Therefore, at half way to the equivalence point,
At equivalence point, the moles of base is the same as moles of acid.
Calculation of moles of weak base methylamine:
Calculation of moles of
Calculation of volume of
| Reaction | |||
| Initial | |||
| Change | |||
| Final | |||
Therefore, at equivalence point, only
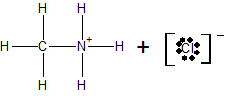
Calculation of total volume of solution at equivalence point:
Total volume =
Calculation of concentration of
| Reaction | |||
| Initial | |||
| Change | |||
| Final | |||
Calculation of
Applying the law of mass action:
We assume that the value of
Therefore,
At equivalence point, the
b) Label the curve with the

c) At the equivalence point, the structure of the species present in the solution is
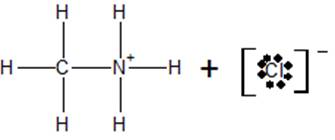
Conclusion:
The initial
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
SMARTWORKS FOR CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FOCUSED
- Draw the Zaitsev product of the dehydration of this alcohol. + I X 5 OH ざ~ TSOH Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardPlease help with identifying these.arrow_forwardFor the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forward
- Can I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardDraw the Hofmann product of the dehydroiodination of this alkyl iodide. ☐ : + Explanation Check esc F1 2 3 I 88 % 5 F5 I. X © tBuOK Click and drag to sta drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te BI BB F6 W E R Y S H Karrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph, if you could show exactly where it needs to pass through please.arrow_forward
- Draw the condensed structure of 1,3-dihydroxy-2-pentanone. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. Х C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of use +arrow_forward0.500 moles of NOCl are placed into a 1.00 L vessesl at 700K and after the system comes to equilibrium, the consentration of NOCl is 0.440 M. Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction: 2NOCL (g) --> 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g)arrow_forwardWhat is the hydronium ion concentration in a solution of water that has a hydroxide ion concentrationof 1.0 x 10-2 M?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





