
Concept explainers
a.
To make: A stem plot for the times customers spent in the restaurant on the next Saturday evening.
a.
Answer to Problem 19.56SE
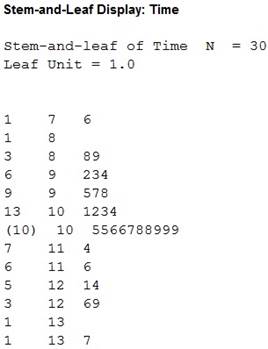
Explanation of Solution
The given data represent the time spent by the customers in the restaurant on the next Saturday evening. The
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to draw stemplot using MINITAB software is as follows:
- Select Graph > Stem and leaf.
- Select the column of Time in Graph variables.
- Select OK.
Observation:
Symmetric distribution:
When the left and right sides of the distribution are approximately equal or mirror images of each other, then it is a symmetric distribution.
In the stemplot, the observations of the data set are extended to the left and to the right in a bell shape. Thus, the stemplot shows that data of times are symmetrically distributed.
The
A observation is a suspected outlier, if it is more than
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure for first
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display
Descriptive Statistics . - In Variables enter the columns Time.
- Choose option statistics, and select first quartile, third quartile, inter quartile
range . - Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is as follows:

From Minitab output, the first quartile is 96.50, third quartile is 110.25, and
Substitute IQR in the
The
b.
To check: Whether there is a reason to think that the lavender odor has increased the mean time customers spent in the restaurant or not.
b.
Answer to Problem 19.56SE
Yes, there is a reason to think that the lavender odor has increased the mean time customers spent in the restaurant.
Explanation of Solution
The standard deviation
Calculation:
STATE:
In France, pizza restaurant owner knows the time customers spend in the restaurant on Saturday evening. The mean time spent by the customers in the restaurant is 90 minutes. Is there any reason to think that the lavender odor increased the mean time spent in the restaurant?
PLAN:
Parameter:
Define the parameter
The hypotheses are given below:
The claim of the problem is increase in mean time of customers spent in the restaurant.
Null Hypothesis:
That is, the mean time is equal to 90 minutes.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the mean time is greater than 90 minutes. Hence, the alternative hypothesis is one sided.
SOLVE:
Conditions for valid test:
A sample of 20 timings of a restaurant is randomly selected and times follow
Test statistic and P-value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain test statistic and P-value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 1-Sample Z.
- In Samples in Column, enter the column of Times.
- In Standard deviation, enter15.
- In Perform hypothesis test, enter the test mean 90.
- Check Options, enter Confidence level as 95.
- Choose greater than in alternative.
- Click OK in all dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:

From the MINITAB output, the test statistic is 5.73 and the P-value is 0.000.
Decision criteria for the P-value method:
If
If
CONCLUDE:
Use a significance level,
Here, P-value is 0.000, which is less than the value of
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Thus, there is good evidence that the mean time of customers who spent in the restaurant is increased.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
The Basic Practice of Statistics
- Please help me with the following question on statisticsFor question (e), the drop down options are: (From this data/The census/From this population of data), one can infer that the mean/average octane rating is (less than/equal to/greater than) __. (use one decimal in your answer).arrow_forwardHelp me on the following question on statisticsarrow_forward3. [15] The joint PDF of RVS X and Y is given by fx.x(x,y) = { x) = { c(x + { c(x+y³), 0, 0≤x≤ 1,0≤ y ≤1 otherwise where c is a constant. (a) Find the value of c. (b) Find P(0 ≤ X ≤,arrow_forwardNeed help pleasearrow_forward7. [10] Suppose that Xi, i = 1,..., 5, are independent normal random variables, where X1, X2 and X3 have the same distribution N(1, 2) and X4 and X5 have the same distribution N(-1, 1). Let (a) Find V(X5 - X3). 1 = √(x1 + x2) — — (Xx3 + x4 + X5). (b) Find the distribution of Y. (c) Find Cov(X2 - X1, Y). -arrow_forward1. [10] Suppose that X ~N(-2, 4). Let Y = 3X-1. (a) Find the distribution of Y. Show your work. (b) Find P(-8< Y < 15) by using the CDF, (2), of the standard normal distribu- tion. (c) Find the 0.05th right-tail percentage point (i.e., the 0.95th quantile) of the distri- bution of Y.arrow_forward6. [10] Let X, Y and Z be random variables. Suppose that E(X) = E(Y) = 1, E(Z) = 2, V(X) = 1, V(Y) = V(Z) = 4, Cov(X,Y) = -1, Cov(X, Z) = 0.5, and Cov(Y, Z) = -2. 2 (a) Find V(XY+2Z). (b) Find Cov(-x+2Y+Z, -Y-2Z).arrow_forward1. [10] Suppose that X ~N(-2, 4). Let Y = 3X-1. (a) Find the distribution of Y. Show your work. (b) Find P(-8< Y < 15) by using the CDF, (2), of the standard normal distribu- tion. (c) Find the 0.05th right-tail percentage point (i.e., the 0.95th quantile) of the distri- bution of Y.arrow_forward== 4. [10] Let X be a RV. Suppose that E[X(X-1)] = 3 and E(X) = 2. (a) Find E[(4-2X)²]. (b) Find V(-3x+1).arrow_forward2. [15] Let X and Y be two discrete RVs whose joint PMF is given by the following table: y Px,y(x, y) -1 1 3 0 0.1 0.04 0.02 I 2 0.08 0.2 0.06 4 0.06 0.14 0.30 (a) Find P(X ≥ 2, Y < 1). (b) Find P(X ≤Y - 1). (c) Find the marginal PMFs of X and Y. (d) Are X and Y independent? Explain (e) Find E(XY) and Cov(X, Y).arrow_forward32. Consider a normally distributed population with mean μ = 80 and standard deviation σ = 14. a. Construct the centerline and the upper and lower control limits for the chart if samples of size 5 are used. b. Repeat the analysis with samples of size 10. 2080 101 c. Discuss the effect of the sample size on the control limits.arrow_forwardConsider the following hypothesis test. The following results are for two independent samples taken from the two populations. Sample 1 Sample 2 n 1 = 80 n 2 = 70 x 1 = 104 x 2 = 106 σ 1 = 8.4 σ 2 = 7.6 What is the value of the test statistic? If required enter negative values as negative numbers (to 2 decimals). What is the p-value (to 4 decimals)? Use z-table. With = .05, what is your hypothesis testing conclusion?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





