
Concept explainers
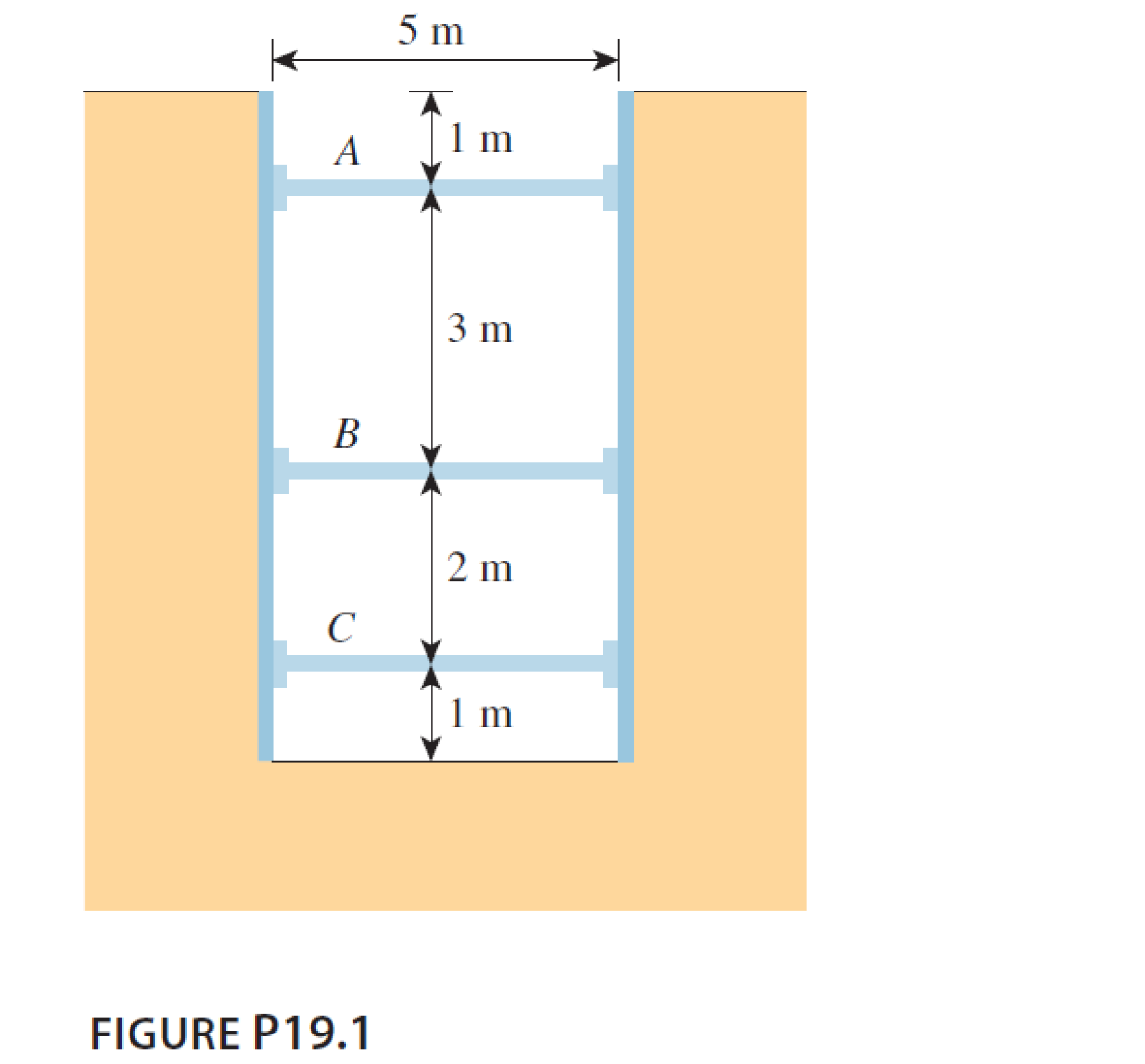
A 5 m wide braced excavation is made in a saturated clay, as shown in Figure P19.1, with the following properties: c = 20 kN/m2, ϕ = 0, and γ = 18.5 kN/m3. The struts are spaced at 5 m center to center in plan.
- a. Determine the strut forces.
- b. Determine the section modulus of the sheet pile required, assuming σall = 170 MN/m2.
- c. Determine the maximum moment for the wales at levels B and C.
a.
Find the strut force.
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The strut load at A, B, C is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The width of excavation is 5 m.
The height of excavation cut H is 7 m.
The unit weight of saturated clay
The coefficient of internal friction
The cohesion (c) is
The center to center spacing of strut s is 5 m.
Calculation:
Check the condition for soft to medium clay as follows:
Hence, the clay is considered as soft to medium clay.
Find the maximum lateral pressure using the formula.
The maximum lateral pressure is
Step-1:
Indicate the struts are labeled as A, B, and C and its carrying load as
Draw the pressure diagram as shown in Figure.
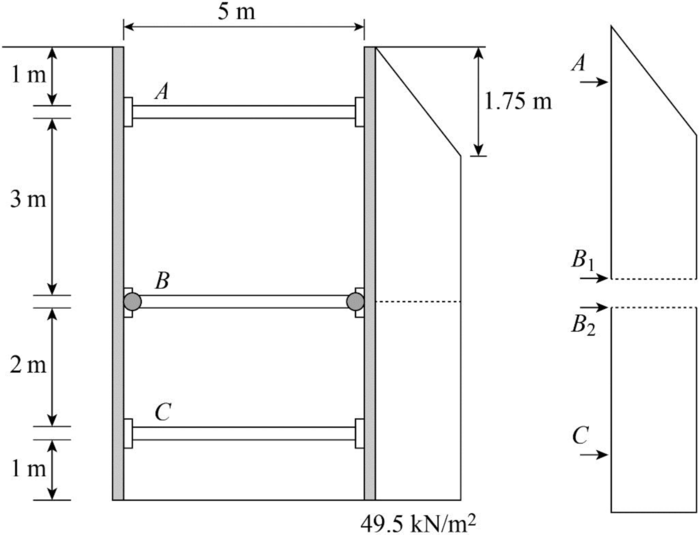
The strut sheet pile connection at B is assumed to be hinge.
Find the strut load per meter width of excavation as follows:
At the top block,
For the bottom block,
Find the strut force at A
Find the strut load at B
Find the strut load at C
Therefore, The strut load at A, B, C is
b.
Find the required section modulus for sheet pile section.
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The section modulus is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The allowable pressure
Calculation:
For top block,
Consider the maximum moment occurs at distance
Find the maximum moment as follows:
The maximum moment occurs at C in the lower block
Find the maximum moment at lower block as follows:
Consider that the higher value of maximum moment is
Find the required section modulus using the formula:
Refer Table 18.1, “Properties of some commercially available sheet-pile section” in the textbook.
Take the section designation as PZ-22 according to the values.
Therefore, the section modulus is
c.
Find the maximum moment for the two wales.
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The maximum moment for the wall at B is
The maximum moment for the wall at C is
Explanation of Solution
Find the maximum moment for the wall at B,
Find the maximum moment for the wall at C,
The maximum moment for the wall at B is
The maximum moment for the wall at C is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- Thank you for your help if you would also provide the equations used .arrow_forwardThe sectors are divided as follows:top right = 1, top left = 2, middle = 3, bottom = 4.(a) Determine the distance yˉ to the centroid of the beam’s cross-sectional area.Solve the next questions by building a table. (Table format Answers) (b) Determine the second moment of area (moment of inertia) about the x′ axis. (c) Determine the second moment of area (moment of inertia) about the y-axis.arrow_forwardinstructions: make sure to follow the instructions and provide complete and detailed solution create/draw a beam with uniformly distributed load and concentrated load after, find the shear and moment equation and ensure to draw it's shear and moment diagram once done, write it's conclusion or observation 4:57 PMarrow_forward
- Solve for forces on pin C and Darrow_forwardBorrow pit soil is being used to fill an 900,00 yd3 of depression. The properties of borrowpit and in-place fill soils obtained from laboratory test results are as follows:• Borrow pit soil: bulk density 105 pcf, moisture content = 8%, and specific gravity = 2.65• In-place fill soil: dry unit weight =120 pcf, and moisture content = 16%(a) How many yd3 of borrow soil is required?(b) What water mass is needed to achieve 16% moisture in the fill soil?(c) What is the in-place density after a long rain?arrow_forwardsolve for dt/dx=f(t,x)=x+t^2arrow_forward
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the slope deflection method, draw the resulting shear force diagran and bending moment diagram. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m, L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200 GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardProblem 2 (A is fixed and C is a pin) Find the reactions and A and C. 10 k- 6 ft 6 ft B A 2 k/ft 15 ftarrow_forward6. A lake with no outlet is fed by a river with a constant flow of 1200 ft3/s. Water evaporates from the surface at a constant rate of 13 ft3/s per square mile of surface area. The surface area varies with the depth h (in feet) as A (square miles) = 4.5 + 5.5h. What is the equilibrium depth of the lake? Below what river discharge (volume flow rate) will the lake dry up?arrow_forward
- Problem 5 (A, B, C and D are fixed). Find the reactions at A and D 8 k B 15 ft A -20 ft C 10 ft Darrow_forwardProblem 4 (A, B, E, D and F are all pin connected and C is fixed) Find the reactions at A, D and F 8 m B 6m E 12 kN D F 4 marrow_forwardProblem 1 (A, C and D are pins) Find the reactions and A, C and D. D 6 m B 12 kN/m 8 m A C 6 marrow_forward
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning



