
a)
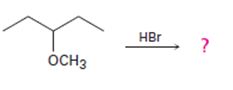
Interpretation:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which it/they is/are formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr.
Answer to Problem 23MP
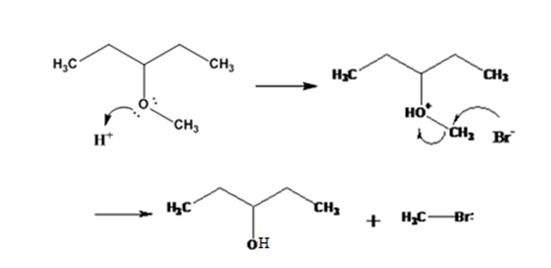
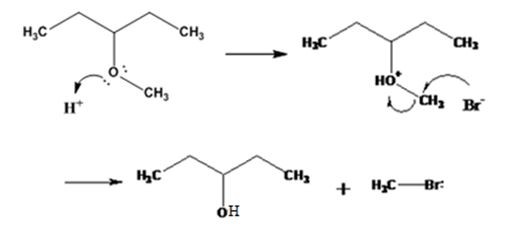
The products formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr are 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The Br- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The products formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr are 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
b)
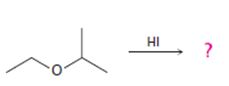
Interpretation:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI.
Answer to Problem 23MP
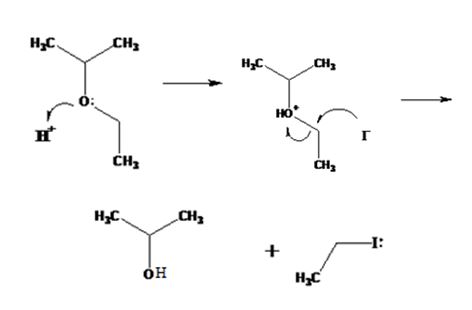
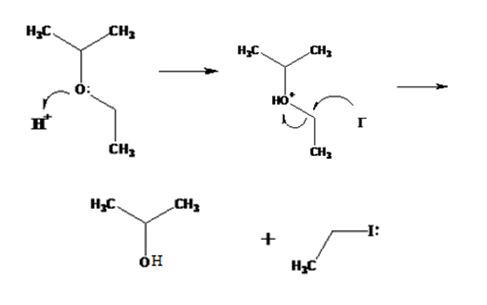
The products formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HBr are 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The I- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The products formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HBr are 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
c)
Interpretation:
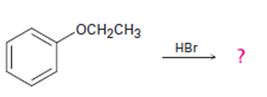
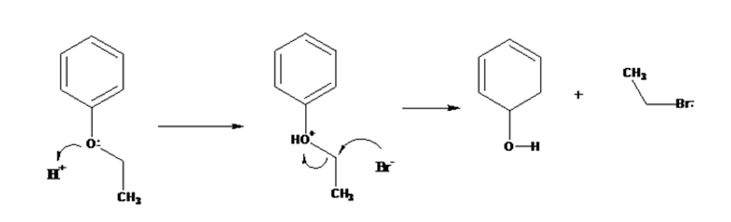
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr.
Answer to Problem 23MP
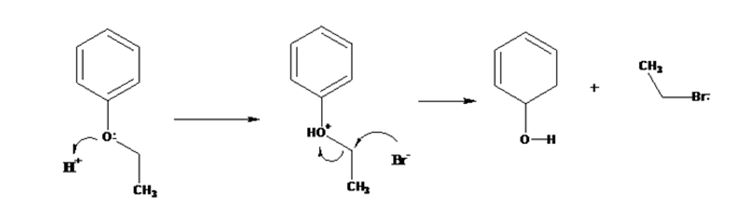
The products formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr are phenol and ethyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a benzene ring and a methyl group attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The Br- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield phenol and ethyl bromide.
The products formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr are phenol and ethyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
d)
Interpretation:
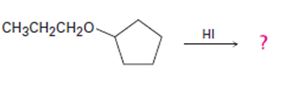
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI.
Answer to Problem 23MP
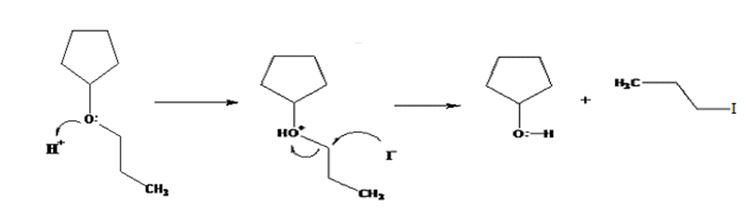
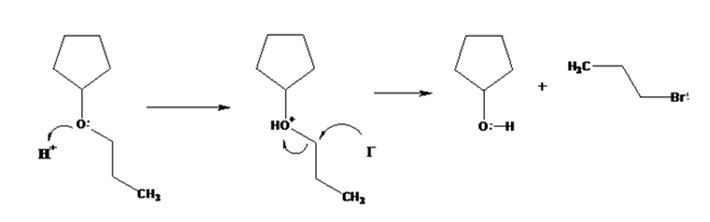
The products formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are cyclopentanol and 1-iodopropane.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The I- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield cyclopentanol and 1-iodopropane.
The products formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are cyclopentanol and 1-bromopropane.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
All the reactions, (a), (b), (c) and (d) take place following SN2 mechanism and the attack of the halide ion on the protonated
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/OWL
- The cobalt mu-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forwardThe cobalt mi-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forward3. Arrange the different acids in Exercise B # 2 from the strongest (1) to the weakest acid (10). 1. 2. (strongest) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10 10. (weakest)arrow_forward
- Name Section Score Date EXERCISE B pH, pOH, pка, AND PKD CALCULATIONS 1. Complete the following table. Solution [H+] [OH-] PH РОН Nature of Solution A 2 x 10-8 M B 1 x 10-7 M C D 12.3 6.8 2. The following table contains the names, formulas, ka or pka for some common acids. Fill in the blanks in the table. (17 Points) Acid Name Formula Dissociation reaction Ka pka Phosphoric acid H₂PO₁ H3PO4 H++ H₂PO 7.08 x 10-3 Dihydrogen H₂PO H₂PO H+ HPO 6.31 x 10-6 phosphate Hydrogen HPO₁ 12.4 phosphate Carbonic acid H2CO3 Hydrogen HCO 6.35 10.3 carbonate or bicarbonate Acetic acid CH,COOH 4.76 Lactic acid CH₂CHOH- COOH 1.38 x 10 Ammonium NH 5.63 x 10-10 Phenol CH₂OH 1 x 10-10 Protonated form CH3NH3* 3.16 x 10-11 of methylaminearrow_forwardIndicate whether it is true that Co(III) complexes are very stable.arrow_forwardMnO2 acts as an oxidant in the chlorine synthesis reaction.arrow_forward
- In Potassium mu-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate K4[Co2(C2O4)4(OH)2], indicate whether the OH ligand type is bidentate.arrow_forwardImagine an electrochemical cell based on these two half reactions with electrolyte concentrations as given below: Oxidation: Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq, 0.10 M) + 2 e– Reduction: MnO4–(aq, 1.50 M) + 4 H+(aq, 2.0 M) + 3 e– → MnO2(s) + 2 H2O(l) Calculate Ecell (assuming temperature is standard 25 °C).arrow_forward: ☐ + Draw the Fischer projection of the most common naturally-occurring form of aspartate, with the acid group at the top and the side chain at the bottom. Important: be sure your structure shows the molecule as it would exist at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓arrow_forward
- For a silver-silver chloride electrode, the following potentials are observed: E°cell = 0.222 V and E(saturated KCl) = 0.197 V Use this information to find the [Cl–] (technically it’s the activity of Cl– that’s relevant here, but we’ll just call it “concentration” for simplicity) in saturated KCl.arrow_forwardA concentration cell consists of two Sn/Sn2+ half-cells. The cell has a potential of 0.10 V at 25 °C. What is the ratio of [Sn2+] (i.e., [Sn2+left-half] / [Sn2+right-half])?arrow_forwardElectrochemical cell potentials can be used to determine equilibrium constants that would be otherwise difficult to determine because concentrations are small. What is Κ for the following balanced reaction if E˚ = +0.0218 V? 3 Zn(s) + 2 Cr3+(aq) → 3 Zn2+(aq) + Cr(s) E˚ = +0.0218 Varrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

