
Concept explainers
a.1
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the forging department during July.
a.1
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the forging department during July as follows:
| Flow of Physical units: Forging Department | |
| Particulars | Units |
| Beginning work in process inventory | 5,000 |
| Add: units started | 75,000 |
| Units in process | 80,000 |
| Less: Ending work in process invnetory | 8,000 |
| Units transferred to assembly department | 72,000 |
| Less: beginning work in process inventory | 5,000 |
| Units started and completed | 67,000 |
Table (1)
2.
Compute the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the forging department during July.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the forging department during July as follows:
| Particulars | Direct materials | Conversion |
| Beginning work in process inventory | 0 | 3,000 |
| Units start and complete | 67,000 | 67,000 |
| Ending work in process inventory | 8,000 | 6,000 |
| Equivalent units of production | 75,000 | 76,000 |
Table (2)
Working note:
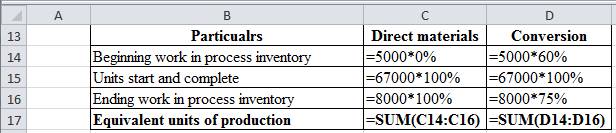
Figure (1)
3.
Identify the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the forging department during July.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the forging department during July as follows:
| Particulars | Direct materials | Conversion |
| Cost incurred by Forging department (A) | $675,000 | $608,000 |
| Equivalent units (B) | 75,000 | 76,000 |
| Cost per equivalent unit (A ÷ B) | $9 | $8 |
Table (3)
4.
Prepare the
4.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to transfer units from Forging department to the assembly department during July as follows:
| Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| Work in process inventory - Assembly department | $1,224,000 | |
| Work in process inventory - Forging department | $1,224,000 | |
| (To record transfer of 72,000 units to the assembly department) |
Table (4)
Working note:
Calculate total unit cost transferred.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Beginning work in process inventory ($45,000 +$16,000) | $61,000 |
| Add: Start and complete cost: | |
| Materials (67,000 units × $9) | $603,000 |
| Conversion (70,000 units × $8) | $560,000 |
| Total cost of units transferred | $1,224,000 |
Table (5)
- Work in process inventory – Assembly department is a current asset, and it is increased. Therefore, debit work in process inventory account for $1,224,000.
- Work in process inventory – Forging department is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit work in process inventory –Forging department account for $1,224,000.
5.
Compute cost assigned to ending inventory in the forging department on July 31.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Compute cost assigned to ending inventory in the forging department on July 31 as follows:
b.1
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the assembly department during July.
b.1
Explanation of Solution
| Flow of Physical units: Assembly Department | |
| Particulars | Units |
| Beginning work in process inventory | 4,000 |
| Add: units started | 72,000 |
| Units in process | 76,000 |
| Less: Ending work in process inventory | 16,000 |
| Units transferred to assembly department | 60,000 |
| Less: beginning work in process inventory | 4,000 |
| Units started and completed | 56,000 |
Table (6)
2.
Compute equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the assembly department in July.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the assembly department in July as follows:
| Particulars | Direct materials | Conversion |
| Beginning work in process inventory | 4,000 | 3,000 |
| Units start and complete | 56,000 | 56,000 |
| Ending work in process inventory | - | 4,800 |
| Equivalent units of production | 60,000 | 63,800 |
Table (7)
Working note:
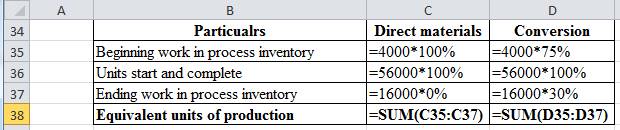
Figure (2)
3.
Compute equivalent cost per unit of input resource for the assembly department during July.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Compute equivalent cost per unit of input resource for the assembly department during July as follows:
| Particulars | Direct materials | Conversion |
| Cost incurred by department (A) | $720,000 | $191,400 |
| Equivalent units (B) | 60,000 | 63,800 |
| Cost per equivalent unit (A ÷ B) | $12 | $3 |
Table (8)
4.
Prepare journal entry to record transfer units from the assembly department to finished goods inventory during July.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record transfer units from the assembly department to finished goods inventory during July as follows:
| Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| Work in process inventory - Assembly department | $1,920,000 | |
| Work in process inventory - Forging department | $1,920,000 | |
| (To record transfer of 72,000 units to the assembly department) |
Table (9)
Working note:
Calculate total unit cost transferred.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Beginning work in process inventory ($68,000 +$3,000) | $71,000 |
| Add: Start and complete cost: | |
| Materials (60,000 units × $12) | $720,000 |
| July forging materials (56,000 units × $17) | $952,000 |
| Conversion (59,000 units × $3) | $117,000 |
| Total cost of units transferred | $1,920,000 |
Table (10)
- Finished goods inventory is a current asset, and it is increased. Therefore, debit finished goods inventory account for $1,920,000.
- Work in process inventory – Assembly department is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit work in process inventory –Assembly department account for $1,920,000.
5.
Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory in the assembly department.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Compute cost assigned to ending inventory in the forging department on July 31 as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting
- General accounting questionarrow_forwardi am also posting you can answer my question also you answered my question can i give unhelpful?? You are posting questions and giving unhelpful i am also positing you can give my answer i will not give unhelpful but If you unhelpful my answer then I will unhelpful your answer. Also you know unhelpful will remove after coureshero review. So coperate.arrow_forwardPlease given correct answer for General accounting question I need step by step explanationarrow_forward
- I am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardYou are posting questions and giving unhelpful i am also positing you can give my answer i will not give unhelpful but If you unhelpful my answer then I will unhelpful your answer. Also you know unhelpful will remove after coureshero review. So coperate.arrow_forwardWhat is the average price paid by the stockholders for a share of common stock ?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





