
Concept explainers
a. 1
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the Molding Department during April.
a. 1
Explanation of Solution
It is a method of cost accounting used by an enterprise with processes categorised by continuous production. The cost for manufacturing those products are assigned to the manufacturing department before the averaged over units are being produced.
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the Molding Department during April.
| Particulars | Units |
| Flow of physical units: Molding Department | |
| Units in beginning inventory, April 1 | 2,800 |
| Units started in April | 48,200 |
| Units in process during April | 51,000 |
| Units in ending inventory, April 30 | (3,400) |
| Units transferred to Finishing Department in April | 47,600 |
| Units in beginning inventory, April 1 | (2,800) |
| Units started and completed in April | 44,800 |
(Table 1)
Therefore, the units started and completed in the Molding Department during April is 44,800.
a. 2
Compute the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Molding Department in April.
a. 2
Explanation of Solution
Compute the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Molding Department in April.
| Particulars | Input Resources | |
| Direct Materials | Conversion | |
| To finish units in process on April 1: | ||
| Direct materials (2,800 units require 10% to complete) | 280 | |
| Conversion (2,800 units require 70% to complete) | 1,960 | |
| To start and complete 44,800 units in April | 44,800 | 44,800 |
| To start units in process on April 30: | ||
| Direct materials (3,400 units 80% complete) | 2,720 | |
| Conversion (3,400 units 20% complete) | 680 | |
| Equivalent units of resources in April | 47,800 | 47,440 |
(Table 2)
Therefore, the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Molding Department in April are 47,800 and 47,440.
a. 3
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Molding Department during April.
a. 3
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Molding Department during April.
| Particulars | Direct Materials in $ | Conversion Cost in $ |
| Cost per equivalent unit in April : | ||
| Costs incurred by Molding Department in April (A) | 669,200 | 521,840 |
| Equivalent units in April (B) | 47,800 | 47,440 |
| Cost per equivalent unit in April (A÷B) | 14 | 11 |
(Table 3)
Therefore, the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Molding Department during April is $14 per unit and $11 per unit respectively.
a. 4
Prepare
a. 4
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the transfer units from the Molding Department to the Finishing Department during April.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|
Work in process: Finishing Department (4) | 1,190,000 | ||
| Work in process: Molding Department | 1,190,000 | ||
| (To record the transfer of 47,600 units to the Finishing department in April) |
(Table 4)
- Work in process: Finishing department is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the work in process: finishing department by $1,190,000.
- Work in process: Molding department is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the work in process: molding department by $1,190,000.
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of beginning inventory:
(1)
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month April:
(2)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month April:
(3)
Calculate the total cost of units transferred:
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Cost of beginning inventory, April 1 (1) | 44,520 |
| April direct materials cost (2) | 631,120 |
| April conversion cost (3) | 514,360 |
| Total cost of units transferred | 1,190,000 |
(Table 5)
(4)
a.5
Compute the costs assigned to ending inventory in the Molding Department on April 30.
a.5
Explanation of Solution
Compute the costs assigned to ending inventory in the Molding Department on April 30.
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Work in Process: Molding Department, April 30: | |
| Direct materials cost (5) | 38,080 |
| Conversion cost (6) | 7,480 |
| Ending inventory in process, April 30 | 45,560 |
(Table 6)
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month end of April 30:
(5)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month end of April 30:
(6)
b. 1
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the Finishing Department during April.
b. 1
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the finishing Department during April.
| Particulars | Units |
| Flow of physical units: Finishing Department | |
| Units in beginning inventory, April 1 | 5,000 |
| Units started in April | 47,600 |
| Units in process during April | 52,600 |
| Units in ending inventory, April 30 | (2,000) |
| Units transferred to Finishing Department in April | 50,600 |
| Units in beginning inventory, April 1 | (5,000) |
| Units started and completed in April | 45,600 |
(Table 7)
Therefore, the units started and completed in the Finishing Department during April is 45,600
b. 2
Compute the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Finishing Department in April.
b. 2
Explanation of Solution
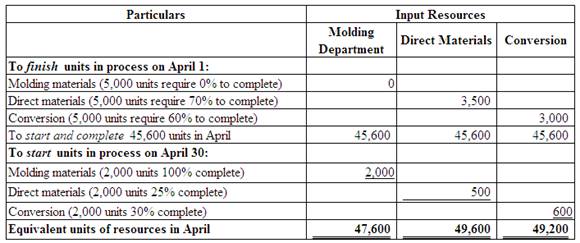
(Figure 4)
b. 3
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Finishing Department during April.
b. 3
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Finishing Department during April.
| Particulars | Input Resources | ||
| Molding materials in $ | Direct Materials in $ | Conversion in $ | |
| Cost per equivalent unit in April | |||
| Costs charged to Finishing Department in April (A) | 1,190,000 | 496,000 | 147,600 |
| Equivalent units in April (B) | 47,600 | 49,600 | 49,200 |
| Cost per equivalent unit in April (A÷B) | 25 | 10 | 3 |
(Table 8)
Note:
Total cost of Molding Department $1,190,000 is transferred to the Finishing Department in April.
b.4
Prepare journal entry to record the units transferred from the Finishing Department to Finished goods inventory during April.
b.4
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the transfer of units from the Finishing Department to Finished goods inventory during April.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Finished goods inventory | 1,922,800 | ||
|
Work in process: Finishing Department (9) | 1,922,800 | ||
| (To record the transfer of 50,600 units to the Finishing goods in April) |
(Table 9)
- Finished goods inventory is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the finished goods inventory by $1,922,800
- Work in process: Molding department is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the work in process: molding department by $1,922,800.
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of beginning inventory:
(5)
Calculate the cost of molding department during the month April:
(6)
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month April for finishing department:
(7)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month April for finishing department:
(8)
Calculate the total cost of units transferred:
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Cost of beginning inventory, April 1 (5) | 146,000 |
| April molding materials (6) | 1,140,000 |
| April direct materials cost (7) | 491,000 |
| April conversion cost (8) | 145,800 |
| Total cost of units transferred | 1,922,800 |
(Table 10)
(9)
a.5
Compute the costs assigned to ending inventory in the Finishing Department on April 30.
a.5
Explanation of Solution
Compute the costs assigned to ending inventory in the Finishing Department on April 30.
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Work in Process: Finishing department, April 30: | |
| Molding materials (10) | 50,000 |
| Direct materials cost (11) | 5,000 |
| Conversion cost (12) | 1,800 |
| Ending inventory in process, April 30 | 56,800 |
(Table 11)
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of molding materials during the month end of April 30 for finishing department:
(10)
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month end of April 30 for finishing department:
(11)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month end of April 30 for finishing department:
(12)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting With Connect Plus Access Code: The Basis For Business Decisions
- General accountingarrow_forwardAfter several profitable years running her business, Ingrid decided to acquire the assets of a small competing business. On May 1 of year 1, Ingrid acquired the competing business for $354,000. Ingrid allocated $59,000 of the purchase price to goodwill. Ingrid's business reports its taxable income on a calendar-year basis. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. a. How much amortization expense on the goodwill can Ingrid deduct in year 1, year 2, and year 3? Year 1 Deductible Amortization Expense Year 2 Year 3arrow_forwardChapter 19 Homework 15 0.87 points eBook Saved Exercise 19-20 (Algo) Contribution margin ratio by sales territory LO A1 Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work Big Bikes manufactures and sells mountain bikes in two sales territories, West Coast and East Coast. Information for the year follows. The company sold 550 bikes in each territory. Per unit Sales price Variable cost of goods sold West Coast $ 1,500 East Coast $ 1,440 830 70 830 Variable selling and administrative expenses 160 Ask a. Compute contribution margin (in dollars) for each sales territory. b. Compute contribution margin ratio for each sales territory. Which sales territory has the better contribution margin ratio? Print Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. References Required A Required B Compute contribution margin (in dollars) for each sales territory. Sales Variable expenses Variable cost of goods sold Variable selling and administrative expenses Contribution margin West Coast East Coast…arrow_forward
- Chapter 19 Homework 15 0.87 points eBook Saved Exercise 19-20 (Algo) Contribution margin ratio by sales territory LO A1 Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work Big Bikes manufactures and sells mountain bikes in two sales territories, West Coast and East Coast. Information for the year follows. The company sold 550 bikes in each territory. Per unit Sales price Variable cost of goods sold West Coast $ 1,500 East Coast $ 1,440 830 70 830 Variable selling and administrative expenses 160 Ask a. Compute contribution margin (in dollars) for each sales territory. b. Compute contribution margin ratio for each sales territory. Which sales territory has the better contribution margin ratio? Print Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. References Required A Required B Compute contribution margin (in dollars) for each sales territory. Sales Variable expenses Variable cost of goods sold Variable selling and administrative expenses Contribution margin West Coast East Coast…arrow_forwardDetermine the gross margin of this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardNeed help with this accounting questionarrow_forward
- Solve this accounting problemarrow_forwardA machine costing $77,500 with a 5-year life and $4,700 residual value was purchased January 2. Compute depreciation for each of the 5 years, using the double-declining-balance method. Year1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5arrow_forwardSolare Company acquired mineral rights for $536,800,000. The diamond deposit is estimated at 48,800,000 tons. During the current year, 3,390,000 tons were mined and sold. Required: 1.Determine the depletion rate. 2. Determine the amount of depletion expense for the current year. 3.Journalize the adjusting entry to recognize the depletion expense. Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles. _____________ Debit / Credit _____________ Debit / Crditarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





