
a)
To determine: The total dollar call premium required to call the old issue, whether it is tax deductible and the net after-tax cost of the call.
a)
Explanation of Solution
The overall premium is
b)
To determine: The dollar floatation cost and whether it is immediately tax deductible and post-tax flotation cost.
b)
Explanation of Solution
On the new issue the currency flotation rate is
c)
To determine: The amounts of old issue floatation cost and not been expensed and whether these deferred costs be expensed immediately if the old issue is refunded and the value of tax savings.
c)
Explanation of Solution
On the old issue the flotation costs were
d)
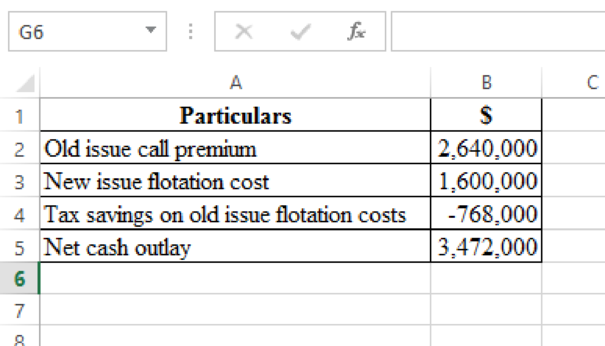
To determine: The net post-tax cash outlay needed to refund the old issue.
d)
Explanation of Solution
e)
To determine: The semiannual tax savings that arises from amortizing the floatation cost and the foregone semiannual tax savings on the old-issue floatation cost.
e)
Explanation of Solution
The $1,600,000 cost of new issue flotation would be
f)
To determine: The semiannually post-tax interest savings that would result from the refunding.
f)
Explanation of Solution
The interest on the old issue is
g)
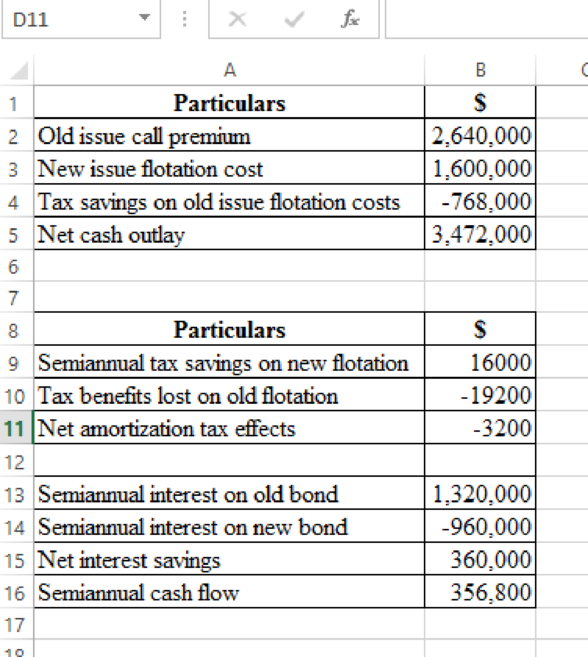
To determine: The sum of these two semiannual cash flows and appropriate discount rate to apply to these two semiannual cash flows and the
g)
Explanation of Solution
The estimated amortization tax benefits over 20 years are about $3,200 per year, while the net interest costs over 20 years are about $360,000 per year. The net semi-annual cash balance, as shown below, is thus $356,800.
The cash flows are predicated on treaty obligations and therefore have about the same level of risk as to the debt of the company. In fact, the cash flows are already tax-net. Consequently, the suitable interest rate is the after-tax cost of debt to GST.(The citation of the cash to fund the net investment expenditure also affects the discount rate, but most companies use debt to finance that expenditure, and in this case, the discount rate should be the after-tax debt cost.)Finally, as we are valuing future flows, the correct debt cost is the cost of today, or the cost of the new issue, and not the debt cost that floated five years ago. The appropriate rate of discount is thus 0.6(8 percent) = 4.8 percent per annum, or 2.4 percent per semi-annual period.
h)
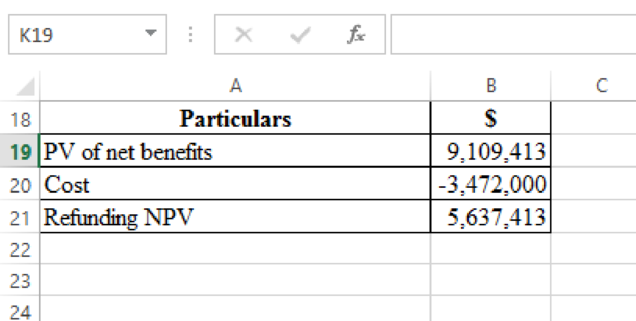
To determine: The
h)
Explanation of Solution
The redemption of bonds would entail a net cash outlay of $3,472,000, but on a present-value basis it would yield $9,109,413 in net savings. The refunding NPV is thus $5,637,413:
The choice to repay instead of wait until later is much harder than finding the refunding NPV now. If interest rates were expected to fall, and therefore GST could issue debt below today's 8 percent rate in the future, then it might pay to wait. Interest rate motions, however, are very difficult to predict, if not impossible, and thus most
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
- Dynamic Energy Wares (DEW) has decided to change the manner in which it distributes its products to large companies. The change in the distribution system comes at a time when DEW’s profits are declining. The declining profits might not be the sole reason for the change, but it appears to be the primary impetus for the decision. It also appears that the new policy requiring DEW’s distributors to increase inventory levels before the end of the fiscal year will artificially inflate DEW’s sales for the current year. However, DEW’s new policy does not require the distributors to pay for any increased inventory until next year (six months), and any unsold inventory can be returned after nine months. So, if the demand for DEW’s products actually is decreasing, the impact will appear on next year’s financial statements. If the financial manager actually intends to artificially inflate DEW’s profits this year, she must realize that such actions eventually will “catch up” with her. Discussion…arrow_forwardwhat is distributors’ meeting?arrow_forwardWhat is ethical dilemma?arrow_forward
- $1.35 Million for the below question is incorrect, Machine A is $1.81 and Machine B is $0.46 Million. The Perez Company has the opportunity to invest in one of two mutually exclusive machines that will produce a product it will need for the foreseeable future. Machine A costs $8 million but realizes after-tax inflows of $4.5 million per year for 4 years. After 4 years, the machine must be replaced. Machine B costs $17 million and realizes after-tax inflows of $4 million per year for 8 years, after which it must be replaced. Assume that machine prices are not expected to rise because inflation will be offset by cheaper components used in the machines. The cost of capital is 13%. Using the replacement chain approach to project analysis, by how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better machine? Round your answer to two decimal places. 1.) $1.35 millionarrow_forwardBuggies-Are-Us Steady Freddie, Inc Gang Buster Group g = 0 g = 55% Year 1 $3.51 (i.e., dividends are expected to remain at $3.053.05/share) (for the foreseeable future) Year 2 $4.04 Year 3 $4.63 Year 4 $5.36 Year 5 $6.15 Year 6 and beyond: g = 55%arrow_forwardProject S has a cost of $10,000 and is expected to produce benefits (cash flows) of $3,000 per year for 5 years. Project L costs $25,000 and is expected to produce cash flows of $7,400 per year for 5 years. Calculate the two projects' NPVs, assuming a cost of capital of 12%. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Calculate the two projects' PIs, assuming a cost of capital of 12%. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to three decimal places. Project L is not 1.07arrow_forward
- Wilbur and Orville are brothers. They're both serious investors, but they have different approaches to valuing stocks. Wilbur, the older brother, likes to use the dividend valuation model. Orville prefers the free cash flow to equity valuation model. As it turns out, right now, both of them are looking at the same stock-Wright First Aerodynmaics, Inc. (WFA). The company has been listed on the NYSE for over 50 years and is widely regarded as a mature, rock-solid, dividend-paying stock. The brothers have gathered the following information about WFA's stock: Current dividend (D) = $2.30/share Current free cash flow (FCF) = $1.5 million Expected growth rate of dividends and cash flows (g) = 5% Required rate of return (r) = 14% Shares outstanding 500,000 shares How would Wilbur and Orville each value this stock?arrow_forwardCompany P/S Multiples Facebook 13.33 Snap 18.22 Twitter 13.27arrow_forwardThe Perez Company has the opportunity to invest in one of two mutually exclusive machines that will produce a product it will need for the foreseeable future. Machine A costs $8 million but realizes after-tax inflows of $4.5 million per year for 4 years. After 4 years, the machine must be replaced. Machine B costs $17 million and realizes after-tax inflows of $4 million per year for 8 years, after which it must be replaced. Assume that machine prices are not expected to rise because inflation will be offset by cheaper components used in the machines. The cost of capital is 13%. Using the replacement chain approach to project analysis, by how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better machine? Round your answer to two decimal places. 1.) $ millionarrow_forward
- Wilbur and Orville are brothers. They're both serious investors, but they have different approaches to valuing stocks. Wilbur, the older brother, likes to use the dividend valuation model. Orville prefers the free cash flow to equity valuation model. As it turns out, right now, both of them are looking at the same stock-Wright First Aerodynmaics, Inc. (WFA). The company has been listed on the NYSE for over 50 years and is widely regarded as a mature, rock-solid, dividend-paying stock. The brothers have gathered the following information about WFA's stock: Current dividend (D) = $3.30/share Current free cash flow (FCF) = $1.5 million Expected growth rate of dividends and cash flows (g)=8% Required rate of return (r) = 13% Shares outstanding 500,000 shares How would Wilbur and Orville each value this stock? The stock price from Wilbur's valuation is $ (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forwardThe Perez Company has the opportunity to invest in one of two mutually exclusive machines that will produce a product it will need for the foreseeable future. Machine A costs $8 million but realizes after-tax inflows of $4.5 million per year for 4 years. After 4 years, the machine must be replaced. Machine B costs $17 million and realizes after-tax inflows of $4 million per year for 8 years, after which it must be replaced. Assume that machine prices are not expected to rise because inflation will be offset by cheaper components used in the machines. The cost of capital is 13%. Using the replacement chain approach to project analysis, by how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better machine? Round your answer to two decimal places. 1.) $ million What is the equivalent annual annuity for each machine? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. 2.) Machine A: $ million 3.) Machine B: $ millionarrow_forwardYou expect to have $29,865. You plan to make X savings contribution of $1,690 per month. The expected return is 0.92 percent per month and the first regular savings contribution will be made later today. What is X? Round to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


