
a)
To determine: The total dollar call premium required to call the old issue, whether it is tax deductible and the net after-tax cost of the call.
a)
Explanation of Solution
The overall premium is
b)
To determine: The dollar floatation cost and whether it is immediately tax deductible and post-tax flotation cost.
b)
Explanation of Solution
On the new issue the currency flotation rate is
c)
To determine: The amounts of old issue floatation cost and not been expensed and whether these deferred costs be expensed immediately if the old issue is refunded and the value of tax savings.
c)
Explanation of Solution
On the old issue the flotation costs were
d)
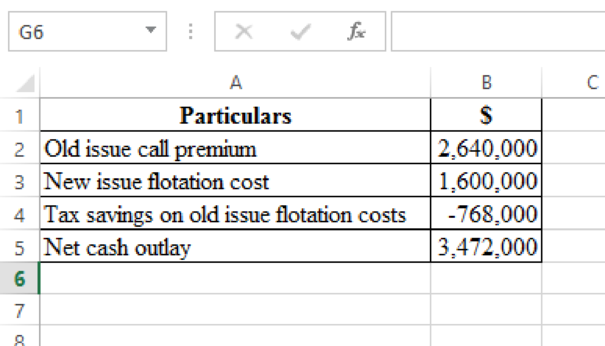
To determine: The net post-tax cash outlay needed to refund the old issue.
d)
Explanation of Solution
e)
To determine: The semiannual tax savings that arises from amortizing the floatation cost and the foregone semiannual tax savings on the old-issue floatation cost.
e)
Explanation of Solution
The $1,600,000 cost of new issue flotation would be
f)
To determine: The semiannually post-tax interest savings that would result from the refunding.
f)
Explanation of Solution
The interest on the old issue is
g)
To determine: The sum of these two semiannual cash flows and appropriate discount rate to apply to these two semiannual cash flows and the
g)
Explanation of Solution
The estimated amortization tax benefits over 20 years are about $3,200 per year, while the net interest costs over 20 years are about $360,000 per year. The net semi-annual cash balance, as shown below, is thus $356,800.
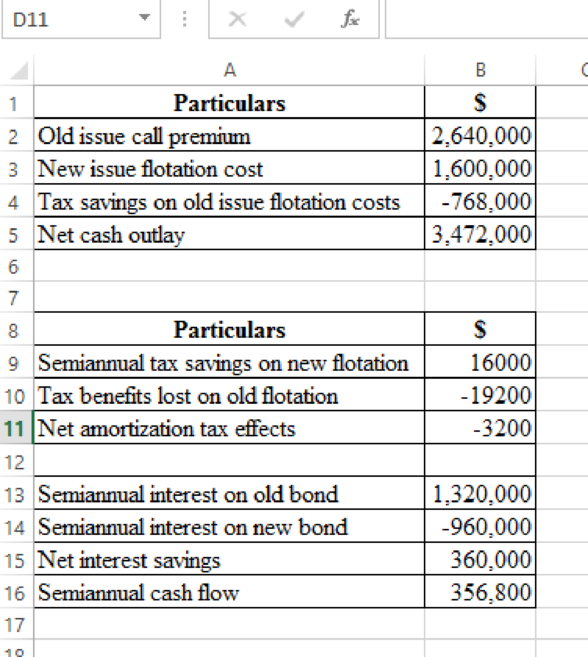
The cash flows are predicated on treaty obligations and therefore have about the same level of risk as to the debt of the company. In fact, the cash flows are already tax-net. Consequently, the suitable interest rate is the after-tax cost of debt to GST.(The citation of the cash to fund the net investment expenditure also affects the discount rate, but most companies use debt to finance that expenditure, and in this case, the discount rate should be the after-tax debt cost.)Finally, as we are valuing future flows, the correct debt cost is the cost of today, or the cost of the new issue, and not the debt cost that floated five years ago. The appropriate rate of discount is thus 0.6(8 percent) = 4.8 percent per annum, or 2.4 percent per semi-annual period.
h)
To determine: The
h)
Explanation of Solution
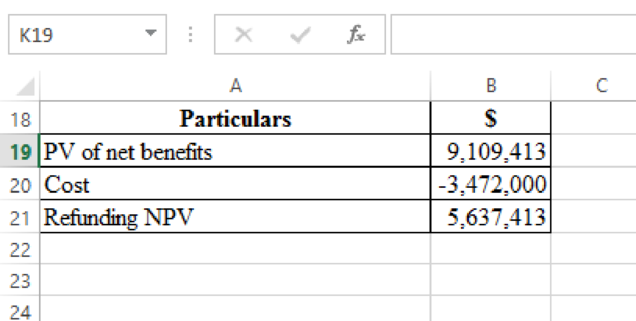
The redemption of bonds would entail a net cash outlay of $3,472,000, but on a present-value basis it would yield $9,109,413 in net savings. The refunding NPV is thus $5,637,413:
The choice to repay instead of wait until later is much harder than finding the refunding NPV now. If interest rates were expected to fall, and therefore GST could issue debt below today's 8 percent rate in the future, then it might pay to wait. Interest rate motions, however, are very difficult to predict, if not impossible, and thus most
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course List)
- What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of a project?A) The initial investment in a projectB) The difference between the present value of cash inflows and outflowsC) The expected cash inflows from a projectD) The total cost of financing a project need help!arrow_forwardWhat is the Net Present Value (NPV) of a project?A) The initial investment in a projectB) The difference between the present value of cash inflows and outflowsC) The expected cash inflows from a projectD) The total cost of financing a projectarrow_forwardWhat is the Payback Period in capital budgeting?A) The time it takes to recover the initial investmentB) The time it takes to achieve profitabilityC) The time it takes to double the investmentD) The time it takes to reach maximum revenuearrow_forward
- Required: Suppose you conduct currency carry trade by borrowing $1 million at the start of each year and investing in the New Zealand dollar for one year. One-year interest rates and the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar ($) and New Zealand dollar (NZ$) are provided below for the period 2000 - 2009. Note that interest rates are one-year interbank rates on January 1st each year, and that the exchange rate is the amount of New Zealand dollar per U.S. dollar on December 31 each year. The exchange rate was NZ$1.9090 per $ on January 1, 2000. Fill out columns (4) - (7) and compute the total dollar profits from this carry trade over the ten-year period. Also, assess the validity of uncovered interest rate parity based on your solution of this problem. You are encouraged to use the Excel spreadsheet software to tackle this problem. Note: Negative value should be entered with a minus sign. Enter profit value answers in dollars, rather than in millions of dollars. Do not round intermediate…arrow_forwardWhich of the following is considered a capital budgeting decision?A) Deciding how to finance a new projectB) Deciding whether to replace a machineC) Deciding how to manage cash reservesD) Deciding how to structure employee benefitsarrow_forwardOmni Advisors, an international pension fund manager, uses the concepts of purchasing power parity (PPP) and the International Fisher Effect (IFE) to forecast spot exchange rates. Omni gathers the financial information as follows: Base price level Current U.S. price level Current South African price level Base rand spot exchange rate Current rand spot exchange rate Expected annual U.S. inflation Expected annual South African inflation 100 105 111 $ 0.195 $ 0.178 7% 5% 10% 8% Expected U.S. one-year interest rate Expected South African one-year interest rate Required: Calculate the following exchange rates (ZAR and USD refer to the South African rand and U.S. dollar, respectively): a. The current ZAR spot rate in USD that would have been forecast by PPP. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places. b. Using the IFE, the expected ZAR spot rate in USD one year from now. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal…arrow_forward
- You invest $5,000 in a project, and it generates $1,250 annually. How long will it take to recover your investment? Exparrow_forwardThe value of an investment grows from $10,000 to $15,000 in 3 years. What is the CAGR?Soovearrow_forwardSuppose that the treasurer of IBM has an extra cash reserve of $100,000,000 to invest for six months. The six-month interest rate is 9 percent per annum in the United States and 8 percent per annum in Germany. Currently, the spot exchange rate is €1.07 per dollar and the six-month forward exchange rate is €1.05 per dollar. The treasurer of IBM does not wish to bear any exchange risk. Where should they invest to maximize the return? Required: The maturity value in six months if the extra cash reserve is invested in Germany:arrow_forward
- The value of an investment grows from $10,000 to $15,000 in 3 years. What is the CAGR?arrow_forwardYou invest $5,000 in a project, and it generates $1,250 annually. How long will it take to recover your investment?arrow_forwardA company pays an annual dividend of $3 per share, and the current stock price is $50. What is the dividend yield?arrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


