
Review. A house roof is a perfectly flat plane that makes an angle θ with the horizontal. When its temperature changes, between Ti before dawn each day and Tk in the middle of each afternoon, the roof expands and contracts uniformly with a coefficient of thermal expansion α1. Resting on the roof is a flat, rectangular metal plate with expansion coefficient α2, greater than α1. The length of the plate is L, measured along the slope of the roof. The component of the plate’s weight perpendicular to the roof is supported by a normal force uniformly distributed over the area of the plate. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the plate and the roof is μk. The plate is always at the same temperature as the roof, so we assume its temperature is continuously changing. Because of the difference in expansion coefficients, each bit of the plate is moving relative to the roof below it, except for points along a certain horizontal line running across the plate called the stationary line. If the temperature is rising, parts of the plate below the stationary line are moving down relative to the roof and feel a force of kinetic friction acting up the roof. Elements of area above the stationary line are sliding up the roof, and on them kinetic friction acts downward parallel to the roof. The stationary line occupies no area, so we assume no force of static friction acts on the plate while the temperature is changing. The plate as a whole is very nearly in equilibrium, so the net
below the top edge of the plate. (b) Analyze the forces that act on the plate when the temperature is falling and prove that the stationary line is at that same distance above the bottom edge of the plate. (c) Show that the plate steps down the roof like an inchworm, moving each day by the distance
(d) Evaluate the distance an aluminum plate moves each day if its length is 1.20 m, the temperature cycles between 4.00°C and 36.0°C, and if the roof has slope 18.5°, coefficient of linear expansion 1.50 × 10−5 (°C) −1, and coefficient of friction 0.420 with the plate. (e) What If? What if the expansion coefficient of the plate is less than that of the roof? Will the plate creep up the roof?
(a)
To show: The stationary line is at distance of
Answer to Problem 44CP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The angle made by the roof with the horizontal plane is
Consider the figure given below.
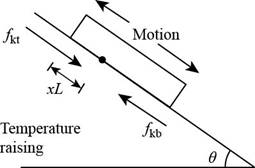
Figure 1
Consider that
The normal force on the lower part of the plane is,
Here,
The force due to gravity is,
The equation for the kinematic friction force is,
The equation for the downward force is,
The force equation for the plate is,
Further, solve for
The distance of the stationary line below the top edge is,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance at which stationary line lie is
(b)
To show: The stationary line is at that same distance above the bottom edge of the plate.
Answer to Problem 44CP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The angle made by the roof with the horizontal plane is
Consider the figure given below.
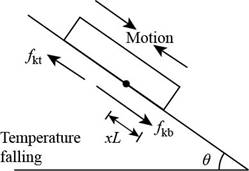
Figure 2
With the temperature falling, the plate contracts faster than the roof. The upper part slides down and feels an upward frictional force,
Then the force equation remains same as in part (a) and the stationary line is above the bottom edge by,
Conclusion:
Therefore, it is proved that the stationary line is at that same distance above the bottom edge of the plate.
(c)
To show: The plate steps down the roof like an inchworm moving each day by the distance
Answer to Problem 44CP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The angle made by the roof with the horizontal plane is
Consider the figure given below.
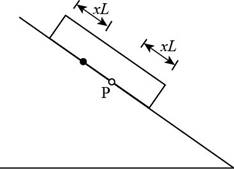
Figure 3
Consider the plate at dawn, as the temperature starts to rise. As in part (a), a line at distance
In the above figure, the point
The change in the length of the plate is,
The change in the length of the roof is,
The point on the roof originally under point
When the temperature drops, point
The displacement for a day is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance by which the plate steps down the roof like an inchworm moving each day is
(d)
Answer to Problem 44CP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The angle made by the roof with the horizontal plane is
The length of the plate is
The coefficient of linear expansion for aluminum is
The formula for the displacement for a day is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance an aluminum plate moves each day is
(e)
To explain: The effect on the plate if the expansion coefficient of the plate is less than the expansion coefficient of the roof.
Answer to Problem 44CP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The angle made by the roof with the horizontal plane is
If
The figure I, applies to the temperature falling and figure II applies to temperature rising. A point on the plate
The plate creeps down the roof each day by an amount given by,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the plate creeps down the roof each day by an amount given by
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





