
Concept explainers
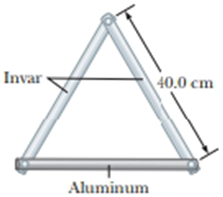
Two metal bars are made of invar and a third bar is made of aluminum. At 0°C, each of the three bars is drilled with two holes 40.0 cm apart. Pins are put through the holes to assemble the bars into an equilateral triangle as in Figure P18.31. (a) First ignore the expansion of the invar. Find the angle between the invar bars as a function of Celsius temperature. (b) Is your answer accurate for negative as well as positive temperatures? (c) Is it accurate for 0°C? (d) Solve the problem again, including the expansion of the invar. Aluminum melts at 660°C and invar at 1 427°C. Assume the tabulated expansion coefficients are constant. What are (e) the greatest and (f) the smallest attainable angles between the invar bars?
Figure P18.31
(a)
Answer to Problem 31AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The distance between two holes drilled at
In the given diagram consider the right triangle that each invar bar makes with one half of the aluminum bar.
Then, the angle is,
Here,
Rearrange the above equation for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle between the invar bars as a function of Celsius temperature is
(b)
Answer to Problem 31AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The distance between two holes drilled at
If the temperature drops, the Celsius temperature becomes negative. The negative value of the Celsius temperature describes the contraction of the bars. So the answer is accurate for the negative temperature same as the positive temperature.
Conclusion:
Therefore, yes the answer is accurate for negative as well as positive temperature.
(c)
Answer to Problem 31AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The distance between two holes drilled at
The expression for the angle between the invar bars is,
Substitute
The value of each angle of the right angle triangle is
Conclusion:
Therefore, Yes, the answer is accurate at
(d)
Answer to Problem 31AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The distance between two holes drilled at
In the given diagram consider the right triangle that each invar bar makes with one half of the aluminum bar.
Then, the angle between invar bars and aluminum bar is,
Here,
Rearrange the above equation for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle between the invar bars and the aluminum bar as a function of Celsius temperature is
(e)
Answer to Problem 31AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The distance between two holes drilled at
The average coefficient of linear expansion of the aluminum is
The average coefficient of linear expansion of the invar is
The greatest angle is occur at
The equation for the angel between the invar bars is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the greatest attainable angle between the invar bars is
(f)
Answer to Problem 31AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The distance between two holes drilled at
The average coefficient of linear expansion of the aluminum is
The average coefficient of linear expansion of the invar is
The smallest angle is occur at
The equation for the angel between the invar bars is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the smallest attainable angle between the invar bars is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
PHYSICS FOR SCI.AND ENGR W/WEBASSIGN
- Is work function of a metals surface related to surface energy and surface tension? What is the need to the work function component in the math of tension of metal surfaces that cannot be provided by existing equations of surface energy and surface tension? What are the key differences in each parameter and variables that allow for a differentiation of each function? What has a more significant meaning work function, surface tension or surface energy? Are there real differences and meaning? Please clarify and if possible provide examples . Does surface tension dependant on thickness of a metal or type of metal surface all having the same thickness? Clearly temperature has a profound change on surface tension what other variables besides temperature are key to surface tension. What if any is there a connection between crystal structure of the element and surface energy and tension? This is NOT a Assignment Question!!!arrow_forwardThe cylindrical beam of a 12.7-mW laser is 0.920 cm in diameter. What is the rms value of the electric field? V/marrow_forwardConsider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...? a. Both rods have less mass b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass c. both rods have more mass d. the masses of both rods are unchanged e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe massarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





