
a)
To ascertain: The
a)
Explanation of Solution
If there is no trade, the price of wine in terms of cloth in E is = 8/2 = 4 yards of cloth/ barrel of wine.
| Country | Cloth in yards | wine in barrels | Opportunity cost of P in terms of cloth | |
| E | 8 | 2/8 = 0.25 | 2 | 8/2 = 4 |
| P | 12 | 6/12 = 0.5 | 6 | 12/6 = 2 |
b)
To ascertain: The price of wine in terms of cloth in country P.
b)
Explanation of Solution
If there is no trade, the price of wine in terms of cloth in P is = 12/6 = 2 yards of cloth/ barrel of wine.
| Country | Cloth in yards | Opportunity cost of E in terms of wine | wine in barrels | Opportunity cost of P in terms of cloth |
| E | 8 | 2/8 = 0.25 | 2 | 8/2 = 4 |
| P | 12 | 6/12 = 0.5 | 6 | 12/6 = 2 |
c)
To draw: The
c)
Explanation of Solution
The construction of PPF for both the countries is as follows:-
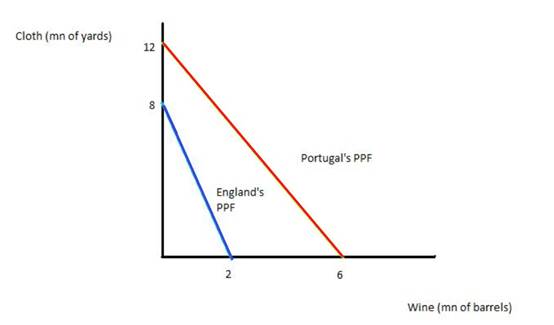
d)
To ascertain: The country that has
d)
Explanation of Solution
| Absolute adv. | Comparative adv. | |
| Wine | P | P |
| Cloth | P | E |
P can produce more of cloth and wine using a week of labour; hence, it has an absolute advantage in both these products. However, the opportunity cost of producing cloth for P is more (6/12) than the same cost in E (2/8). Therefore, P has a comparative advantage in production of wine whereas E has a comparative advantage in production of cloth.
e)
To ascertain: The country that specialize in particular good and exporting the same.
e)
Explanation of Solution
A country which has comparative advantage in production of good should specialize in production of that particular good and trade it with another country for another good.
E should produce cloth and export cloth and import wine from P. P should specialize and export wine for cloth with E.
f)
To ascertain: The price at which the trade should take place.
f)
Explanation of Solution
An offer of 3 yards of cloth/1 barrel of wine is better than P's own production of 2 yards of cloth/1 barrel of wine
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Published in 1980, the book Free to Choose discusses how economists Milton Friedman and Rose Friedman proposed a one-sided view of the benefits of a voucher system. However, there are other economists who disagree about the potential effects of a voucher system.arrow_forwardThe following diagram illustrates the demand and marginal revenue curves facing a monopoly in an industry with no economies or diseconomies of scale. In the short and long run, MC = ATC. a. Calculate the values of profit, consumer surplus, and deadweight loss, and illustrate these on the graph. b. Repeat the calculations in part a, but now assume the monopoly is able to practice perfect price discrimination.arrow_forwardThe projects under the 'Build, Build, Build' program: how these projects improve connectivity and ease of doing business in the Philippines?arrow_forward
- Critically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardOutline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forward
 Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning








