
Find the
Answer to Problem 1P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to given figure in the textbook.
Formula used:
Write the expression to find inverse hybrid or
Here,
Write the expression to find hybrid or
Here,
Calculation:
When port 2 is open
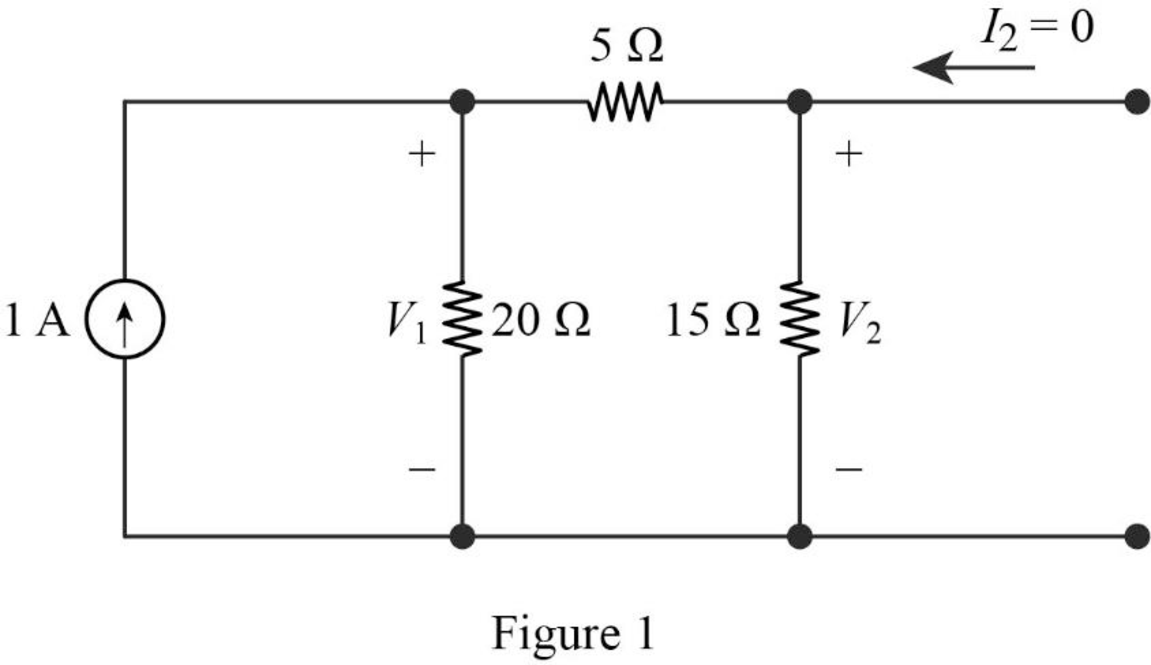
Find the equivalent impedance of the circuit in Figure 1.
Write the expression to calculate voltage
Substitute
Calculate the voltage
Substitute
Substitute
When port 1 is short circuited
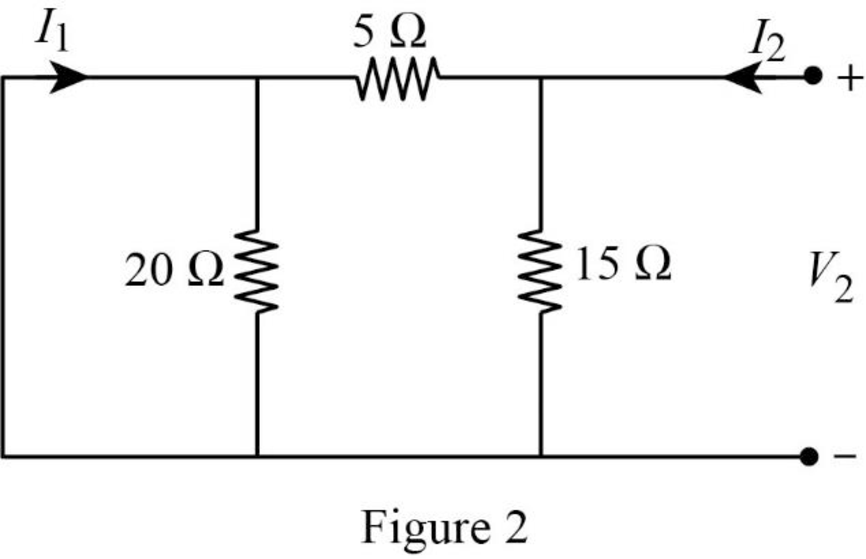
In Figure 2, the short circuit path neglects the effect of
From Figure 2, write the expression for current
Substitute equation (9) in (4) to find
From Figure 2, write the expression for current
Substitute equation (10) in (3) to find
When port 1 is open
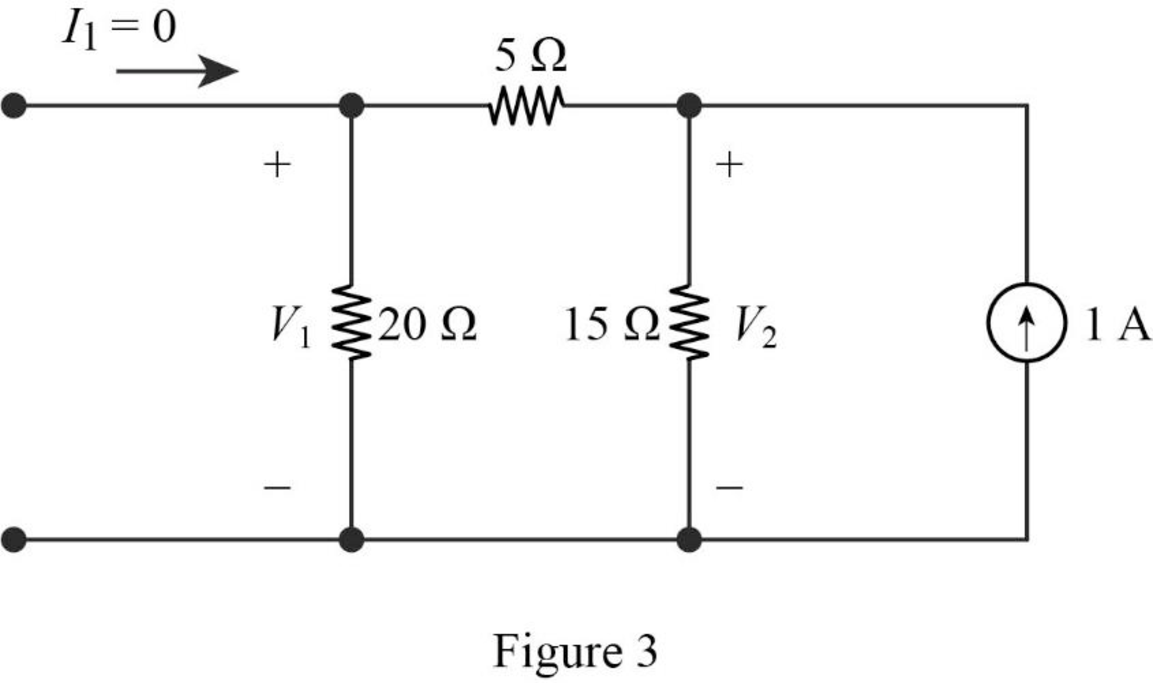
Find the equivalent impedance of the circuit in Figure 3.
Write the expression to calculate voltage
Substitute
Calculate the voltage
Substitute
Substitute
When port 2 is short circuited
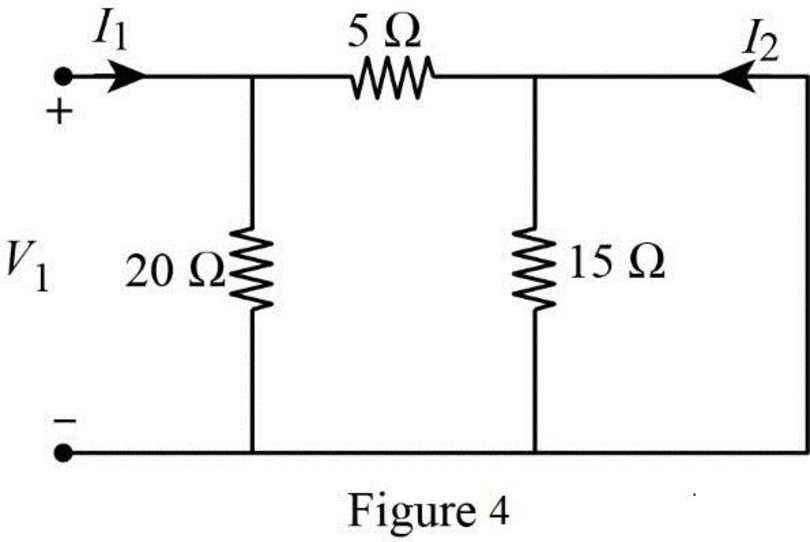
In Figure 4, the short circuit path neglects the effect of
From Figure 1, write the expression for current
Substitute equation (11) in (5) to find
From Figure 4, write the expression for current
Substitute equation (12) in (6) to find
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Electric Circuits Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText 2.0 - Access Card Package (11th Edition) (What's New in Engineering)
- find the inverse Laplace transform of X(s)= i) Re[s]> 3 ii) Re[s]<1 s+5 for (s-1)(s-2)(s-3) iii) 1arrow_forwardFor R1, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R1, what the current in mA? For R1, what is the voltage in V? For R1, what is the power in W? For R2, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R2, what the current in mA? For R2, what is the voltage in V? For R2, what is the power in W? For R3, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R3, what the current in mA? For R3, what is the voltage in V? For R3, what is the power in W? For R4, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R4, what the current in mA? For R4, what is the voltage in V? For R4, what is the power in W? For R5, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R5, what the current in mA? For R5, what is the voltage in V? For R5, what is the power in W? What is the total resistance in Ω? What is the total current in mA? What is the total voltage in V? What is the total power in W?arrow_forwardPlease answer allarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





