
In many manufacturing processes, the term work-in-process (often abbreviated WIP) is used. At the LSS Publishing book manufacturing plants, WIP represents the time it takes for sheets from a press to be folded, gathered, sewn, tipped on end sheets, and bound together to form a book, and the book placed in a packing carton. The operational definition of the variable of interest, processing time, is the number of days (measured in hundredths) from when the sheets come off the press to when the book is placed in a packing cartoon. The company has the business objective of determining whether there are differences in the WIP between plants. Data have been collected from samples of 20 books at each production plants. The data, stored in WIP, are as follows:
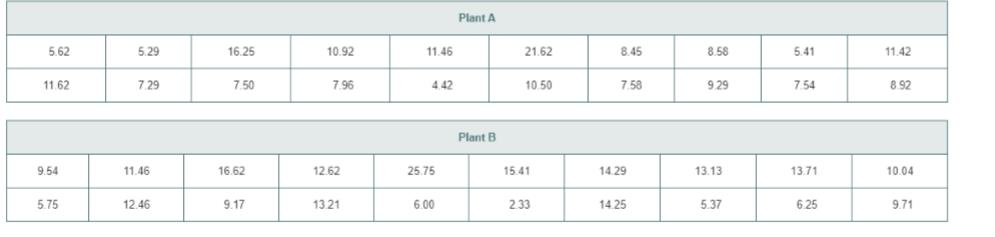
Completely analyse the data.
Completely analyze the data to determine whether there are differences in the WIP between both plants.
Explanation of Solution
The data is provided for work-in-process (WIP) for Plant A and Plant B. The data has been collected from samples of 20 books at each of the two production plants.
The descriptive statistics of the data can be calculated using the Minitab as follows:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to find the descriptive statistics by Minitab software is as follows:
Enter the data for Plant A and Plant B in the worksheet.
Go to Stat < Basic Statistics < Display Descriptive Statistics.
Click on Variables section.
Double-click C1 Plant A and C2 Plant B to add in the Variables box.
Click on the Statistics option and check the required statistics option.
Click Ok.
The output of Minitab software is:
It can be assumed that the data of the two plants A and B are from independent groups rather being from matched or paired group.
Either the pooled-variance t-test or the separate variance t-test for the difference in two means if the distribution of the time is normal in both plants. If the distribution is not normal, the results of t test can be compared to Wilcoxon rank sum test.
The assumption of Normality can be checked with the help of Minitab software.
The normal probability plot for Plant A is:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to find the descriptive statistics by Minitab software is as follows:
Go to Graph < Probability Plot < Single.
Click Ok.
Click on Variables section.
Double-click C1 Plant A to add in the Graph Variables box.
Click Ok.
The output of Minitab software is:
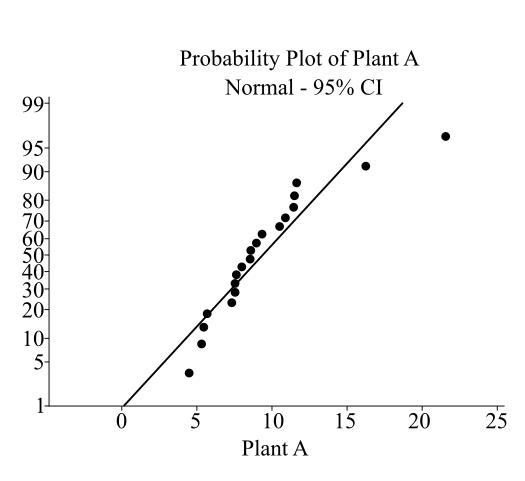
The normal probability plot for Plant B is
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to find the descriptive statistics by Minitab software is as follows:
Go to Graph < Probability Plot < Single.
Click Ok.
Click on Variables section.
Double-click C1 Plant A to add in the Graph Variables box.
Click Ok.
The output of Minitab software is:
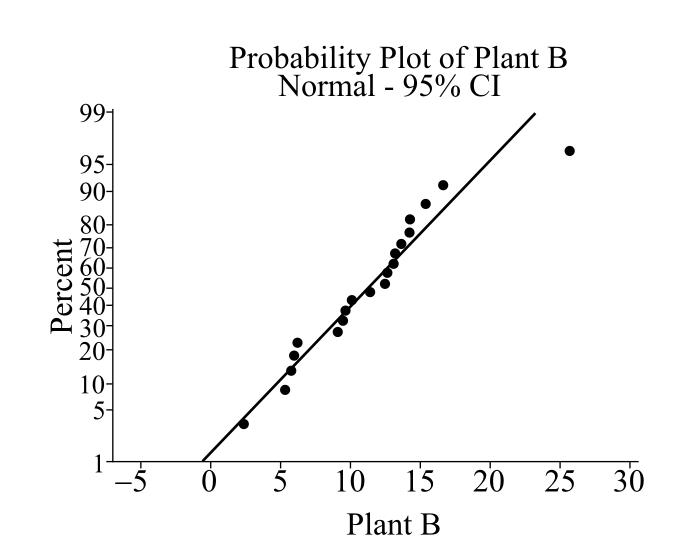
From the obtained normal probability plots, the processing time appears to be right-skewed as they largely deviate from the straight line.
Both the t tests, whether it is pooled variance or similar variance, give relevant result when the parent population follows normal distribution. Nevertheless, a Wilcoxon rank sum test might be more appropriate.
Further, equality of variance should be checked.
Test whether there is difference in variance of processing time of plant A and plant B or not.
Answer to Problem 1CRP
There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the variances of processing time of plant A and plant B differ significantly.
Explanation of Solution
The following steps are followed to test whether variances are equal or not.
Step 1:
The null and the alternative hypotheses are:
Here,
Step 2:
The size of both the samples is 20. The level of significance
Step 3:
The
Step 4:
Use Minitab to find test statistic and
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform 2 variances test is given below:
Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2 Variances.
From the drop down, select Each sample is in its own column.
Click on Variables section.
Double-click C1 Plant A to add in the Sample 1 box and double-click C2 Plant B to add in the Sample 2 box.
Click Options and check Use test and confidence interval based in normal distribution.
Click Ok.
The Minitab output shows that the test statistic is 1.64 and
Step 5:
Decision based on the
If
If
Since
At
Test whether the mean processing time of plant A and plant B is different.
Answer to Problem 1CRP
There is insufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant difference in the mean processing time of plant A and plant B.
Explanation of Solution
The following steps are followed to test whether population means are equal or not.
Step 1:
The null and the alternative hypotheses are:
Here,
Step 2:
The size of both the samples is 20. The level of significance
Step 3:
From the above part, it was concluded that the variance processing time of plant A and plant B are significantly not different. Thus, pooled variance
Step 4:
Use Minitab to find test statistic and
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform 2 sample t test is given below:
Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Sample t.
From the drop down, select Each sample is in its own column.
Click on Variables section.
Double-click C1 Plant A to add in the Sample 1 box and double-click C2 Plant B to add in the Sample 2 box.
Click Options.
Tick the option Assume equal variances.
Click Ok.
Click Ok.
The Minitab output shows that the test statistics is
Step 5:
Decision based on the
If
If
Since
There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the population means are significantly different.
Test whether the median processing time of plant A and plant B is different.
Answer to Problem 1CRP
There is insufficient evidence to conclude that there is significant difference in the median processing time of plant A and plant B.
Explanation of Solution
The following steps are followed to test the median of the two populations.
Step 1:
The null and the alternative hypotheses are:
Here,
Step 2:
The size of both the samples is 20. The level of significance
Step 3:
From the above parts, it was concluded that the mean processing time of plant A and plant B are significantly not different as well as the population deviate from the normal distribution. Thus, Mann Whitney test (Wilcoxon rank sum test) is used to compare the medians and to validate the results.
Step 4:
Use Minitab to find test statistic and
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform 2 sample t test is given below:
Choose Stat > Nonparametrics > Mann-Whitney.
Click on Variables section.
Double-click C1 Plant A to add in the First Sample box and double-click C2 Plant B to add in the Second Sample box.
Click Ok.
The Minitab output shows that test statistics is 345.5 and
Step 5:
Decision based on the
If
If
Since
There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the population medians are significantly different.
Therefore, from the above results, it can be concluded that both t test and Wilcoxon rank sum test give the same result that is processing time of Plant A and Plant B does not differ significantly.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
- A smallish urn contains 25 small plastic bunnies – 7 of which are pink and 18 of which are white. 10 bunnies are drawn from the urn at random with replacement, and X is the number of pink bunnies that are drawn. (a) P(X = 5) ≈ (b) P(X<6) ≈ The Whoville small urn contains 100 marbles – 60 blue and 40 orange. The Grinch sneaks in one night and grabs a simple random sample (without replacement) of 15 marbles. (a) The probability that the Grinch gets exactly 6 blue marbles is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.054", "≈ 0.043", "≈ 0.061"] . (b) The probability that the Grinch gets at least 7 blue marbles is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.922", "≈ 0.905", "≈ 0.893"] . (c) The probability that the Grinch gets between 8 and 12 blue marbles (inclusive) is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.801", "≈ 0.760", "≈ 0.786"] . The Whoville small urn contains 100 marbles – 60 blue and 40 orange. The Grinch sneaks in one night and grabs a simple random sample (without replacement) of 15 marbles. (a)…arrow_forwardSuppose an experiment was conducted to compare the mileage(km) per litre obtained by competing brands of petrol I,II,III. Three new Mazda, three new Toyota and three new Nissan cars were available for experimentation. During the experiment the cars would operate under same conditions in order to eliminate the effect of external variables on the distance travelled per litre on the assigned brand of petrol. The data is given as below: Brands of Petrol Mazda Toyota Nissan I 10.6 12.0 11.0 II 9.0 15.0 12.0 III 12.0 17.4 13.0 (a) Test at the 5% level of significance whether there are signi cant differences among the brands of fuels and also among the cars. [10] (b) Compute the standard error for comparing any two fuel brands means. Hence compare, at the 5% level of significance, each of fuel brands II, and III with the standard fuel brand I. [10] �arrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forward
- What would you say about a set of quantitative bivariate data whose linear correlation is -1? What would a scatter diagram of the data look like? (5 points)arrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forwardAnalyze the residuals of a linear regression model and select the best response. yes, the residual plot does not show a curve no, the residual plot shows a curve yes, the residual plot shows a curve no, the residual plot does not show a curve I answered, "No, the residual plot shows a curve." (and this was incorrect). I am not sure why I keep getting these wrong when the answer seems obvious. Please help me understand what the yes and no references in the answer.arrow_forward
- a. Find the value of A.b. Find pX(x) and py(y).c. Find pX|y(x|y) and py|X(y|x)d. Are x and y independent? Why or why not?arrow_forwardAnalyze the residuals of a linear regression model and select the best response.Criteria is simple evaluation of possible indications of an exponential model vs. linear model) no, the residual plot does not show a curve yes, the residual plot does not show a curve yes, the residual plot shows a curve no, the residual plot shows a curve I selected: yes, the residual plot shows a curve and it is INCORRECT. Can u help me understand why?arrow_forwardYou have been hired as an intern to run analyses on the data and report the results back to Sarah; the five questions that Sarah needs you to address are given below. please do it step by step on excel Does there appear to be a positive or negative relationship between price and screen size? Use a scatter plot to examine the relationship. Determine and interpret the correlation coefficient between the two variables. In your interpretation, discuss the direction of the relationship (positive, negative, or zero relationship). Also discuss the strength of the relationship. Estimate the relationship between screen size and price using a simple linear regression model and interpret the estimated coefficients. (In your interpretation, tell the dollar amount by which price will change for each unit of increase in screen size). Include the manufacturer dummy variable (Samsung=1, 0 otherwise) and estimate the relationship between screen size, price and manufacturer dummy as a multiple…arrow_forward
- Here is data with as the response variable. x y54.4 19.124.9 99.334.5 9.476.6 0.359.4 4.554.4 0.139.2 56.354 15.773.8 9-156.1 319.2Make a scatter plot of this data. Which point is an outlier? Enter as an ordered pair, e.g., (x,y). (x,y)= Find the regression equation for the data set without the outlier. Enter the equation of the form mx+b rounded to three decimal places. y_wo= Find the regression equation for the data set with the outlier. Enter the equation of the form mx+b rounded to three decimal places. y_w=arrow_forwardYou have been hired as an intern to run analyses on the data and report the results back to Sarah; the five questions that Sarah needs you to address are given below. please do it step by step Does there appear to be a positive or negative relationship between price and screen size? Use a scatter plot to examine the relationship. Determine and interpret the correlation coefficient between the two variables. In your interpretation, discuss the direction of the relationship (positive, negative, or zero relationship). Also discuss the strength of the relationship. Estimate the relationship between screen size and price using a simple linear regression model and interpret the estimated coefficients. (In your interpretation, tell the dollar amount by which price will change for each unit of increase in screen size). Include the manufacturer dummy variable (Samsung=1, 0 otherwise) and estimate the relationship between screen size, price and manufacturer dummy as a multiple linear…arrow_forwardExercises: Find all the whole number solutions of the congruence equation. 1. 3x 8 mod 11 2. 2x+3= 8 mod 12 3. 3x+12= 7 mod 10 4. 4x+6= 5 mod 8 5. 5x+3= 8 mod 12arrow_forward

 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning


