
Concept explainers
1.
Process costs
It is a method of cost accounting, which is used where the production is continuous, and the product needs various processes to complete. This method is used to ascertain the cost of the product at each process or stage of production.
Equivalents units for production
The activity of a processing department in terms of fully completed units is known as equivalent units. It includes the completed units of direct materials and conversion cost of beginning work in process, units completed and transferred out, and ending work in process.
Production cot report
A production cost report is a comprehensive report prepared for each department separately at the end of a particular period, which represents the physical flow and cost flow of product for the concerned department.
To Prepare: The four column account for work in process inventory balance rolling department from September to October of Company PA.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the four column account for work in process inventory balance rolling department from September to October of Company PA as shown below:
| Work in Process - Rolling | |||||
| Date | Item | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Debit | Credit | ||||
| Sept 1 | Balance, 2,600 units | $45,825 | |||
| Sept 30 | Smelting department | $462,400 | $508,225 | ||
| Sept 30 | Direct labor | $158,920 | $667,145 | ||
| Sept 30 | Factory |
$101,402 | $768,547 | ||
| Sept 30 | Finished goods | $702,195 | $66,352 | ||
| Sept 30 | Balance, 2,900 units | $66,352 | |||
| Oct 31 | Smelting department | $511,500 | $577,852 | ||
| Oct 31 | Direct labor | $162,850 | $740,702 | ||
| Oct 31 | Factory overhead | $104,494 | $845,196 | ||
| Oct 31 | Finished goods | $805,156 | $40,040 | ||
| Oct 31 | Balance, 2,000 units | $40,040 | |||
Table (1)
Hence, Work in process inventory ending balance for the month of September is $66,352 and for the month of October is $40,040.
a.
To Prepare: The equivalents units for production of direct materials and conversion cost of Company PA.
a.
Answer to Problem 18.4BPR
Prepare the equivalent units for production of direct materials and conversion cost of Company PA as shown below:
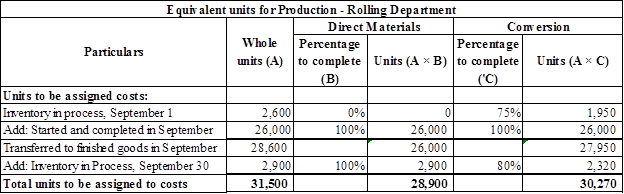
Figure (1)
Explanation of Solution
Working notes:
Calculate opening work in process inventory for conversion percentage to complete as shown below:
Calculate units started and completed in September as shown below:
Calculate ending work in process inventory units as shown below:
Total units to be assigned to costs is calculated by adding opening work in process inventory, units started and completed and ending work in process inventory.
Therefore, direct material equivalent units for production is 28,900 units and conversion cost equivalent units for production is 30,270 units.
b.
To Prepare: The cost per equivalent unit for direct material and conversion cost of Company PA.
b.
Answer to Problem 18.4BPR
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit for direct material and conversion cost of Company PA as shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Working note:
Calculate conversion cost for the month of September of Company PA as shown below:
Equivalent cost per unit for direct materials is calculated by dividing direct material cost by equivalent units for direct materials. Equivalent cost per unit for conversion cost is calculated by dividing conversion cost by equivalent units for conversion.
Therefore, equivalent cost per unit for direct material is $16.00 per unit and for conversion cost is $8.60 per unit.
c.
To Prepare: The cost of goods finished, between units stared in the prior period and units started and finished in September of Company PA.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the cost of goods finished, between units stared in the prior period and units started and finished in September of Company PA as shown below:

Figure (2)
Costs transferred to finished goods is calculated by adding opening inventory in September balance, to complete opening work in process inventory in September, and cost of units started and completed in September.
Hence, cost of completed work in process inventory in September 1 is $62,595, cost for started and completed in September is $639,600, and transferred to finished goods is $702,195.
d.
To Prepare: The ending work in
d.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the ending work in process inventory cost of the month September for the Company PA as shown below:
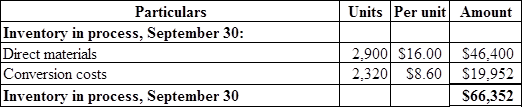
Figure (3)
Ending work in process inventory cost is calculated by adding ending direct material cost and ending conversion costs.
Hence, ending work in process inventory cost for the month of September is $66,352.
2.
a.
To Prepare: The equivalents units for production of direct materials and conversion cost during the month of October for Company PA.
2.
a.
Answer to Problem 18.4BPR
Prepare the equivalents units for production of direct materials and conversion cost during the month of October for Company PA as shown below:
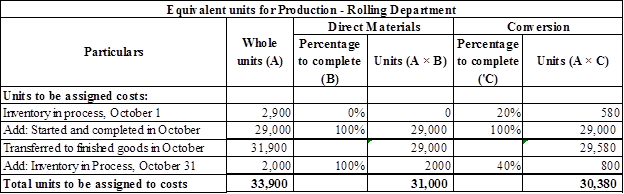
Figure (5)
Explanation of Solution
Working notes:
Calculate opening work in process inventory for conversion percentage to complete as shown below:
Calculate units started and completed in October as shown below:
Calculate ending work in process inventory units as shown below:
Total units to be assigned to costs is calculated by adding opening work in process inventory, units started and completed and ending work in process inventory.
Therefore, direct material equivalent units for production is 31,000 units and conversion cost equivalent units for production is 30,380 units.
b.
To Prepare: The cost per equivalent unit for direct material and conversion cost during the month of October for Company PA.
b.
Answer to Problem 18.4BPR
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit for direct material and conversion cost during the month of October for Company PA as shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Working note:
Calculate conversion cost for the month of September of Company PA as shown below:
Equivalent cost per unit for direct materials is calculated by dividing direct material cost by equivalent units for direct materials. Equivalent cost per unit for conversion cost is calculated by dividing conversion cost by equivalent units for conversion.
Therefore, equivalent cost per unit for direct material is $16.50 per unit and for conversion cost is $8.80 per unit.
c.
To Prepare: The cost of goods finished, between units stared in the prior period and units started and finished in October of Company PA.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the cost of goods finished, between units stared in the prior period and units started and finished in October of Company PA as shown below:
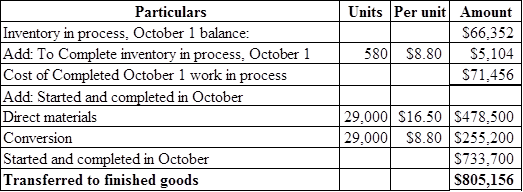
Figure (6)
Costs transferred to finished goods is calculated by adding opening inventory in September balance, to complete opening work in process inventory in September, and cost of units started and completed in September.
Hence, cost of completed work in process inventory in October 1 is $71,456, cost for started and completed in October is $733,700, and transferred to finished goods is $805,156.
d.
To Prepare:
The ending work in process inventory cost of the month October for the Company PA.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the ending work in process inventory cost of the month October for the Company PA as shown below:
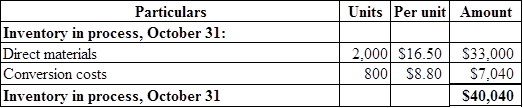
Figure (7)
Ending work in process inventory cost is calculated by adding ending direct material cost and ending conversion costs.
Hence, ending work in process inventory cost for the month of October is $40,040.
3.
To Mention: The change in cost per equivalent unit for August through October for direct materials and conversion costs.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The cost per equivalent unit for direct material in August is $15.50 per unit, in September is $16.00 per unit, and in October is $16.50 per unit. Constantly direct material cost per unit is increased from August to October. Likewise, the cost per equivalent unit for conversion cost in August is $8.50 per unit, in September is $8.60 per unit, and in October $8.80 per unit. Constantly conversion cost per unit is increased from August to October. The Company PA scrutinizes for their underlying reasons, and any required remedial actions would be taken.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting
- Below is information for Blue Company. Using this information, answer the following questions on the "Calculation" tab in the file. Show your work (how you got your answer) and format appropriately. Blue company has prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 to 1,500 units): Sales $ 40,000 Variable expenses 24,000 Contribution margin 16,000 NOTE: Use the amounts in the original fact pattern to the left as your basis for the questions below. Fixed expenses 12,000 Net operating income $ 4,000 Questions: 1. What is the contribution margin per unit? 2. What is the contribution margin ratio? 3. What is…arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this financial accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardRobin Corporation has ordinary income from operations of $30,000, net long-term capital gain of $10,000, and net short-term capital loss of $15,000. What is the taxable income for 2010? a) $25,000. b) $27,000. c) $28,500. d) $30,000. e) None of the above.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this financial accounting problem using the correct financial principles.arrow_forward
- I need the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using the proper financial approach.arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





