
a) Styrene (PhCH=CH2)
Interpretation:
How to prepare styrene from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols undergo dehydration when treated with POCl3 in pyridine to yield
To state:
How to prepare styrene from 2-phenylethanol.
Answer to Problem 47AP
Styrene can be prepared by treating 2-phenylethanol with POCl3 in pyridine.
Explanation of Solution
2-Phenylethanol when treated with POCl3 in pyridine eliminates a molecule of water from the side chain to yield styrene.
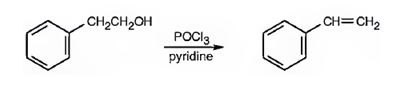
Styrene can be prepared by treating 2-phenylethanol with POCl3 in pyridine.
b) Phenylacetaldehyde (PhCH2CHO)
Interpretation:
How to prepare phenylacetaldehyde from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Dess-Martin periodinate in dichloromethane oxidizes 10alcohols to
To state:
How to prepare phenylacetaldehyde from 2-phenylethanol
Answer to Problem 47AP
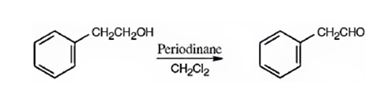
Phenylacetaldehyde can be prepared by oxidizing 2-phenylethanol with Dess-Martin periodinate in dichloromethane.
Explanation of Solution
2-phenylethanol is a 10 alcohol. It gets oxidized to phenylacetaldehyde when treated with Dess-Martin periodinate in dichloromethane.
Phenylacetaldehyde can be prepared by oxidizing 2-phenylethanol with Dess-Martin periodinate in dichloromethane.

c) Phenylacetic acid (PhCH2COOH)
Interpretation:
How to prepare phenylacetic acid from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
CrO3 in acidic solutions oxidize 10 alcohols directly into acids and 20 alcohols to ketones. It does not oxidize 30 alcohols.
To state:
How to prepare phenylacetic acid from 2-phenylethanol.
Answer to Problem 47AP
Phenylacetic acid can be prepared by oxidizing 2-phenylethanol with CrO3 in acidic solutions.
Explanation of Solution
2-phenylethanol is a 10 alcohol. It gets oxidized to phenylacetic acid when treated with CrO3 in acidic solutions.
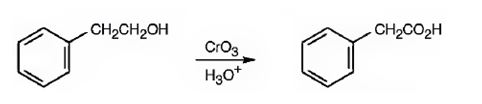
Phenylacetic acid can be prepared by oxidizing 2-phenylethanol with CrO3 in acidic solutions.
d) Benzoic acid
Interpretation:
How to prepare benzoic acid from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
KMnO4 in acidic solutions oxidize
To state:
How to prepare benzoic acid from 2-phenylethanol.
Answer to Problem 47AP
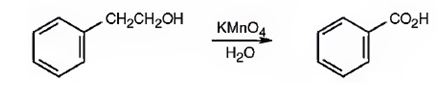
Benzoic acid can be prepared by oxidizing 2-phenylethanol with KMnO4 in acidic solutions.
Explanation of Solution
2-phenylethanol is a 10 alcohol. It gets oxidized to benzoic acid when treated with KMnO4 in acidic solutions.
Benzoic acid can be prepared by oxidizing 2-phenylethanol with KMnO4 in acidic solutions.
e) Ethylbenzene
Interpretation:
How to prepare ethylbenzene from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols undergo dehydration when treated with POCl3 in pyridine to yield an alkene. The alkene upon reduction gives the
To state:
How to prepare ethylbenzene from 2-phenylethanol.
Answer to Problem 47AP
Ethylbenzene can be prepared from 2-phenylethanol by following the steps shown below.
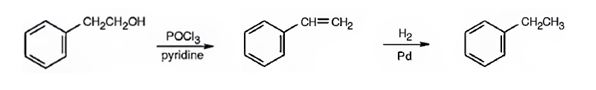
Explanation of Solution
2-Phenylethanol when treated with POCl3 in pyridine eliminates a molecule of water from the side chain to yield styrene. When treated with H2/Pd, the double bond in the side chain gets reduced to yield ethyl benzene.
Ethylbenzene can be prepared from 2-phenylethanol by following the steps shown below.

f) benzaldehyde
Interpretation:
How to prepare benzaldehyde from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols undergo dehydration when treated with POCl3 in pyridine to yield an alkene. The alkene upon ozonolyzis followed by reduction will yield the aldehyde required.
To state:
How to prepare benzaldehyde from 2-phenylethanol.
Answer to Problem 47AP
Benzaldehyde can be prepared from 2-phenylethanol by following the steps shown below.
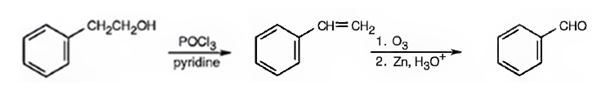
Explanation of Solution
2-Phenylethanol when treated with POCl3 in pyridine eliminates a molecule of water from the side chain to yield styrene. When styrene is subjected to ozonolysis followed by reduction, the double bond in side chain gets cleaved resulting in the formation of benzaldehyde.
Benzaldehyde can be prepared from 2-phenylethanol by following the steps shown below.

g) 1-phenylethanol
Interpretation:
How to prepare 1-phenylethanol from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols undergo dehydration when treated with POCl3 in pyridine to yield an alkene. The alkene adds a molecule of water following oxymercuration-demercuration process. The addition will take place following Markovnikov regiochemistry.
To state:
How to prepare 1-phenylethanol from 2-phenylethanol.
Answer to Problem 47AP
1- Phenylethanol can be prepared from 2-phenylethanol by following the steps shown below.
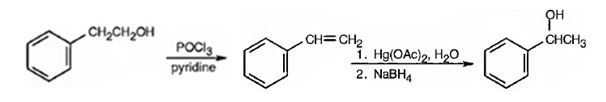
Explanation of Solution
2-Phenylethanol, when treated with POCl3 in pyridine eliminates a molecule of water from the side chain to yield styrene. When styrene is subjected oxymercuration-demercuration processes, a molecule of water is added, following Markovnikov regiochemistry, to the double bond. The –OH adds on to the more alkyl substituted carbon and H to the less alkyl substituted carbon in double bond to yield 1-phenylethanol.
1-Phenylethanol can be prepared from 2-phenylethanol by following the steps shown below.

h) 1-Bromo-2-phenylethane
Interpretation:
How to prepare 1-bromo-2-phenylethane from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols yield the corresponding alkyl bromides when treated with PBr3.
To state:
How to prepare 1-bromo-2-phenylethane from 2-phenylethanol is to be stated.
Answer to Problem 47AP
1-Bromo-2-phenylethane can be prepared from 2-phenylethanol by following the steps shown below.
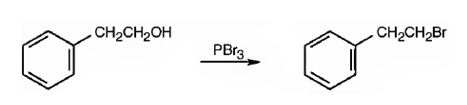
Explanation of Solution
When 2-phenylethanol is treated with PBr3, a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution of –OH by Br takes place to yield 1-bromo-2-phenylethane.
1-Bromo-2-phenylethane can be prepared from 2-phenylethanol by following the steps shown below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Student Value Bundle: Organic Chemistry, + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card (NEW!!)
- i need help identifying the four carbon oxygen bonds in the following:arrow_forwardImagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule HO H3N + The solution is... X O acidic OH O basic H3N-CH-C-O O neutral ○ (unknown) O acidic ○ basic CH2 CH 3-S-CH2 O neutral ○ (unknown) H3N O OH O acidic O basic Oneutral O (unknown) 0 H3N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 O acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? olo Ar BHarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughs need other product (product in picture is wrong dont submit the same thing)arrow_forward
- I have a 2 mil plastic film that degrades after 22 days at 88C and at 61C takes 153 days. What is the failure at 47C in days.arrow_forwardIf a 5 film plastic film degraded in 30 days at 35C and the same film degraded in 10 days at 55 C and 2 days at 65C what would the predicted life time be at 22C for the same film?arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- I have a aqueous solution (175 ml) of iridium trichloride containing 8,750 ppm Iridium by ICP OES analysis. What is the percent concentration of Iridium trichloride in aquous solution and provide the concentration in moles per liter, percentage by weight.arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





