
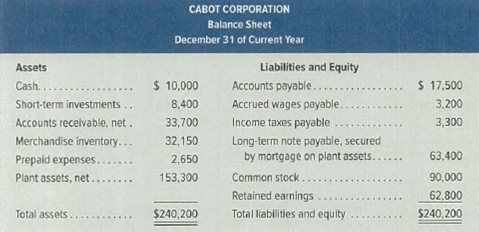
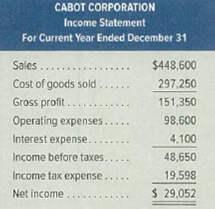
Selected current year-end financial statements of Cabot Corporation follow. All sales were on credit; selected balance sheet amounts at December 31 of the prior year were inventory, $48,900; total assets, $189,400; common stock, $90,000; and
Required
Compute the following: (1)
(1)
Compute current ratio for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the liquidity ratios, which measures the capacity of the company to meet its short-term obligations using its current assets. Current ratio is calculated by using the formula:
Determine the current ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Cash | $10,000 |
| Short term investments | $8,400 |
| Accounts receivables, net | $33,700 |
| Merchandise inventory | $32,150 |
| Prepaid expenses | $2,650 |
| Current assets (A) | $86,900 |
| Accounts payable | $17,500 |
| Accrued wages payable | $3,200 |
| Income taxes payable | $3,300 |
| Current liabilities (B) | $24,000 |
| Current ratio | 3.62:1 |
Table (1)
Hence, the current ratio is 3.62:1.
(2)
Compute acid-test ratio for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Acid-test ratio: It is a ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay back its current liabilities by liquid assets that are current assets except inventory and prepaid expenses.
Determine the acid-test ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Cash | $10,000 |
| Short term investments | $8,400 |
| Accounts receivables, net | $33,700 |
| Quick assets (A) | $52,100 |
| Accounts payable | $17,500 |
| Accrued wages payable | $3,200 |
| Income taxes payable | $3,300 |
| Current liabilities (B) | $24,000 |
| Acid-test ratio | 2.2:1 |
Table (2)
Hence, the acid-test ratio is 2.2:1.
(3)
Compute days’ sales uncollected for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Days’ sales uncollected: This ratio is used to determine the number of days a particular company takes to collect accounts receivables.
Determine the days’ sales uncollected.
| Ratio | Result |
| Accounts receivables, net | $33,700 |
| Ending net accounts (including notes) receivables (A) | $33,700 |
| Net credit sales (B) | $448,600 |
| Days’ sales uncollected | 27.4 days |
Table (3)
Hence, the days’ sales uncollected are 27.4 days.
(4)
Compute inventory turnover for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Inventory Turnover Ratio: This ratio is a financial metric used by a company to quantify the number of times inventory is used or sold during the accounting period. It is calculated by using the formula:
Determine the inventory turnover ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Ending inventory (A) | $32,150 |
| Beginning inventory (B) | $48,900 |
| Total inventory (C) = | $81,050 |
| Average inventory (D) = | $40,525 |
| Cost of goods sold (E) | $297,250 |
| Inventory turnover ratio | 7.3 times |
Table (4)
Hence, the inventory turnover ratio is 7.3 times.
(5)
Compute days’ sales in inventory for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Days’ sales in inventory: Days’ in inventory is determined as the number of days a particular company takes to make sales of the inventory available with them.
Determine the days’ sales in inventory.
| Ratio | Result |
| Ending inventory (A) | $32,150 |
| Cost of goods sold (B) | $297,250 |
| Days’ sales in inventory | 39.5 days |
Table (5)
Hence, the days’ sales in inventory are 39.5 days.
(6)
Compute debt–to-equity ratio for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Debt–to-equity ratio or Debt equity ratio: The debt-to-equity ratio indicates that the company’s debt as a proportion of its stockholders’ equity. The debt-to-equity ratio is calculated using the formula:
Determine debt-to-equity ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Accounts payable | $17,500 |
| Accrued wages payable | $3,200 |
| Income taxes payable | $3,300 |
| Long term note payable | $63,400 |
| Total liabilities (A) | $87,400 |
| Common stock | $90,000 |
| Retained earnings | $62,800 |
| Total stockholders’ equity (B) | $152,800 |
| Debt-to-Equity ratio | 0.57:1 |
Table (6)
Hence, the debt to equity ratio is 0.57:1.
(7)
Compute times interest earned ratio for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Times interest earned ratio: The times interest earned ratio quantifies the number of times the earnings before interest and taxes can pay the interest expense. First, determine the sum of income before income tax and interest expense. Then, divide the sum by interest expense.
Determine times interest earned ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Net income | $29,052 |
| Interest expense | $4,100 |
| Income taxes | $19,598 |
| Income before interest expense and income taxes (A) | $52,750 |
| Interest expense (B) | $4,100 |
| Times interest earned ratio | 12.9 times |
Table (7)
Hence, the times interest earned ratio is 12.9 times.
(8)
Compute profit margin for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Profit margin: It is one of the profitability ratios. Profit margin ratio is used to measure the percentage of net income that is being generated per dollar of revenue or sales.
Determine profit margin ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Net income (A) | $29,052 |
| Net sales (B) | $448,600 |
| Profit margin ratio | 6.5% |
Table (8)
Hence, the profit margin ratio is 6.5%.
(9)
Compute total asset turnover for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Total asset turnover: Total asset turnover is a ratio that measures the productive capacity of the total assets to generate the sales revenue for the company. Thus, it shows the relationship between the net sales and the average total assets. Turnover of assets is calculated as follows:
Determine total asset turnover ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Ending total assets (A) | $240,200 |
| Beginning total assets (B) | $189,400 |
| Average total assets (C) | $214,800 |
| Net sales (D) | $448,600 |
| Total asset turnover ratio | 2.08 times |
Table (9)
Hence, the total asset turnover ratio is 2.08 times.
(10)
Compute return on total assets for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Return on total assets: Return on total assets is the financial ratio that determines the amount of net income earned by the business with the use of total assets owned by it. It indicates the magnitude of the company’s earnings with relative to its total assets. Return on investment is calculated as follows:
Determine return on asset ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Ending total assets (A) | $240,200 |
| Beginning total assets (B) | $189,400 |
| Average total assets (C) | $214,800 |
| Net income (D) | $29,052 |
| Return on asset ratio | 13.5% |
Table (10)
Hence, the return on asset ratio is 13.5%.
(11)
Compute return on common stockholders’ equity for Corporation C.
Explanation of Solution
Return on common stockholders’ equity ratio: It is a profitability ratio that measures the profit generating ability of the company from the invested money of the shareholders. The formula to calculate the return on equity is as follows:
Determine return on common stockholders’ equity ratio.
| Ratio | Result |
| Common stock | $90,000 |
| Retained earnings | $62,800 |
| Ending total stockholders’ equity (A) | $152,800 |
| Common stock | $90,000 |
| Retained earnings | $22,748 |
| Beginning total stockholders’ equity (B) | $112,748 |
| Average common stockholders’ equity (C) | $132,774 |
| Net income (D) | $29,052 |
| Return on common stockholders’ equity ratio | 21.88% |
Table (11)
Hence, the return on common stockholders’ equity ratio is 21.88%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- Kindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this Financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this Financial accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
- Echo Tone Technologies reports annual sales of $90,000, and it expects sales to increase to $135,000 next year. The company has a degree of operating leverage (DOL) of 4.2. By what percentage should net income increase? A. 70% B. 189% C. 150% D. 210%arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardCan you explain the process for solving this financial accounting question accurately?arrow_forward
- I need help with this situation and accounting questionarrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forward
- I need help with this financial accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardI need help Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forwardWhich account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalhelparrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





