
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The structure of given compounds has to be drawn.
ethylacetoacetate
Concept introduction: The
Carboxylate ion with a carbonyl group at the 3-position loses
(a)
Answer to Problem 48P
The structure of ethyl acetoacetae is,
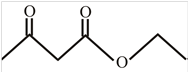
Explanation of Solution
The name given compound ethyl acetoacetate ends with ate. This means the given compound must contain an ester group. The name of compound starts with ethyl group, this means ethyl group is attached to the oxygen of an ester group. The acetone group is attached with the carbonyl carbon of an ester group. The structure of ethyl acetoacetae is,

(b)
Interpretation: The structure of given compounds has to be drawn.
α-methylmalonicacid
Concept introduction: The
Carboxylate ion with a carbonyl group at the 3-position loses
(b)
Answer to Problem 48P
The structure of α-methylmalonic acid is,
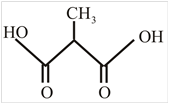
Explanation of Solution
The structure of malonic acid is two

(c)
Interpretation: The structure of given compounds has to be drawn.
β-keto ester
Concept introduction: The
Carboxylate ion with a carbonyl group at the 3-position loses
(c)
Answer to Problem 48P
The structure of β-keto ester is,

Explanation of Solution
The given compound β-keto ester contains a keto group and an ester group. The structure of β-keto ester is,

(d)
Interpretation: The structure of given compounds has to be drawn.
The carboxylic acid obtained from malonic ester synthesis when the
Concept introduction: The
Carboxylate ion with a carbonyl group at the 3-position loses
(d)
Answer to Problem 48P
The structure of enol form of cyclopentanone is,
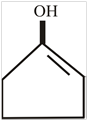
Explanation of Solution
The compound cyclopentanone contain a keto group. After the keto enol tautomerism the keto compound converted into an alcohol and a double bond. The structure of enol form of cyclopentanone is,

(e)
Interpretation: The structure of given compounds has to be drawn.:
The structure of enol form of cyclopentanone
Concept introduction: The
Carboxylate ion with a carbonyl group at the 3-position loses
(e)
Answer to Problem 48P
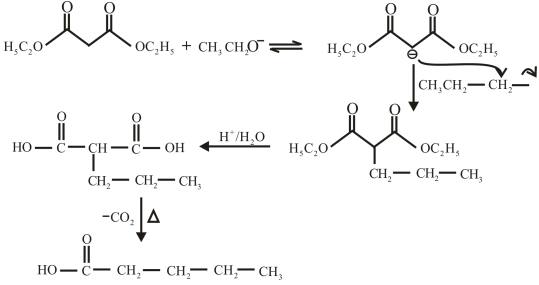
The structure of the carboxylic acid obtained from malonic ester synthesis by using propyl bromide is,
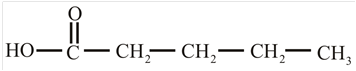
Explanation of Solution
The proton removed from the alpha carbon of malonic ester by the base. Then, there is a nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place between the propyl bromide and carbanion of malonic ester. The third step is acidic hydrolysis of an ester to form carboxylic acid. The fourth step is decarboxylation of the compound to form the desired product. The reaction and structure of given compound is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions Manual, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
