
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781260826791
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.7, Problem 20P
Using the principles of VSEPR theory, you can predict the geometry around any atom in any molecule, no matter how complex. Enanthotoxin is a poisonous compound isolated from a common variety of hemlock grown in England. Predict the geometry around the highlighted atoms in enanthotoxin.
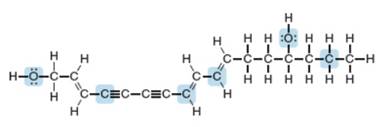
Enanthotoxin
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using Benzene as starting materid show
how each of the Following molecules Contel
Ve syntheswed
CHI
9.
b
-50311
с
CHY
503H
Ночто
d.
อ
•NOV
e
11-0-650
NO2
The molecule PYRIDINE,
6th electrons and is therefore aromatre
and is Assigned the Following structure
contering
Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic
anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo
The Following reaction
+ HNO3
12504
a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products
that could Result From this reaction
18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime
which of these producty would be the major
Product of the hegetion
a. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups
tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should
lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing
Structures
fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura
drccton even though chlorine has a very High
Electronegativity
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 1.1 - While the most common isotope of nitrogen has a...Ch. 1.2 - Label each bond in the following compounds as...Ch. 1.3 - Draw a valid Lewis structure for each species. a....Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 9PCh. 1.4 - Draw Lewis structures for each molecular formula....Ch. 1.6 - Classify each pair of compounds as isomers or...Ch. 1.6 - Prob. 12PCh. 1.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 1.6 - Prob. 14PCh. 1.6 - Prob. 16P
Ch. 1.6 - Prob. 17PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 18PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 19PCh. 1.7 - Using the principles of VSEPR theory, you can...Ch. 1.8 - Convert each condensed formula to a Lewis...Ch. 1.8 - Prob. 22PCh. 1.8 - Prob. 23PCh. 1.8 - Convert each skeletal structure to a complete...Ch. 1 - Citric acid is responsible for the tartness of...Ch. 1 - Zingerone gives ginger its pungent taste. a.What...Ch. 1 - Assign formal charges to each and atom in the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 44PCh. 1 - Prob. 46PCh. 1 - Draw all possible isomers for each molecular...Ch. 1 - 1.45 Draw Lewis structures for the nine isomers...Ch. 1 - Prob. 52PCh. 1 - Prob. 53PCh. 1 - Prob. 54PCh. 1 - Consider compounds A-D, which contain both a...Ch. 1 - Draw in all the carbon and hydrogen atoms in each...Ch. 1 - 1.61 Convert each molecule into a skeletal...Ch. 1 - Prob. 65PCh. 1 - Predict the hybridization and geometry around each...Ch. 1 - Prob. 68PCh. 1 - Ketene, , is an unusual organic molecule that has...Ch. 1 - Rank the following bonds in order of increasing...Ch. 1 - Two useful organic compounds that contain Cl atoms...Ch. 1 - Use the symbols + and to indicate the polarity of...Ch. 1 - Prob. 74PCh. 1 - Anacin is an over-the-counter pain reliever that...Ch. 1 - 1.77 Stalevo is the trade name for a medication...Ch. 1 - 1.78 and are two highly reactive carbon...Ch. 1 - 1.79 The N atom in (acetamide) is hybridized,...Ch. 1 - Prob. 83PCh. 1 - Prob. 84PCh. 1 - Prob. 85PCh. 1 - Prob. 86PCh. 1 - Prob. 87PCh. 1 - Prob. 88P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
More than one choice may apply. Using the terms listed below, fill in the blank with the proper term. anterior ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th Edition)
What were the major microbiological interests of Martinus Beijerinck and Sergei Winogradsky? It can be said tha...
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
2. Why is it that the range of resting blood pressures of humans is best represented by a bell-shaped curve co...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Organic Chemistry
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forward
- Given the electrode Pt | Ag | Ag+ (aq), describe it.arrow_forwardAt 25°C, the reaction Zn2+ + 2e ⇄ Zn has a normal equilibrium potential versus the saturated calomel electrode of -1.0048 V. Determine the normal equilibrium potential of Zn versus the hydrogen electrode.Data: The calomel electrode potential is E° = 0.2420 V versus the normal hydrogen electrode.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. State the difference between E and E0.arrow_forward
- In an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery notation. Is that correct?arrow_forwardIn an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery. Is that correct?arrow_forwardCalculate the free energy of formation of 1 mol of Cu in cells where the electrolyte is 1 mol dm-3 Cu2+ in sulfate solution, pH 0. E° for the Cu2+/Cu pair in this medium is +142 mV versus ENH.Assume the anodic reaction is oxygen evolution.Data: EH2 = -0.059 pH (V) and EO2 = 1.230 - 0.059 pH (V); 2.3RT/F = 0.059 Varrow_forward
- If the normal potential for the Fe(III)/Fe(II) pair in acid at zero pH is 524 mV Hg/Hg2Cl2 . The potential of the saturated calomel reference electrode is +246 mV versus the NHE. Calculate E0 vs NHE.arrow_forwardGiven the galvanic cell whose scheme is: (-) Zn/Zn2+ ⋮⋮ Ag+/Ag (+). If we know the normal potentials E°(Zn2+/Zn) = -0.76V and E°(Ag+/Ag) = 0.799 V. Indicate the electrodes that are the anode and the cathode and calculate the E0battery.arrow_forwardIndicate the functions that salt bridges have in batteries.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY