
(a)
The total marginal benefit
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The total marginal benefit (MB) is the sum total of individual marginal benefits. There are two consumers of mosquito abatement, such as D and L, where the marginal benefit of consumer D is
Therefore, the total marginal benefit is
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
(b)
The optimal level of mosquito abatement.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The optimal level of mosquito abatement is determined at the point where the total marginal benefit is equal to the marginal cost (MC).
The total marginal benefit is
The total marginal cost is given as
Now, set the two expressions to get the value of optimal quantity:
Therefore, the optimal level of mosquito abatement is 40.
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
Marginal cost (MC): Marginal benefit refers to the amount of additional cost incurred in the process of increasing one more unit of output.
(c)
The individual total benefit at the optimal level of mosquito abatement.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 illustrates the MB, MC, and the optimal quantity of the mosquito abatement of consumer D as follows:
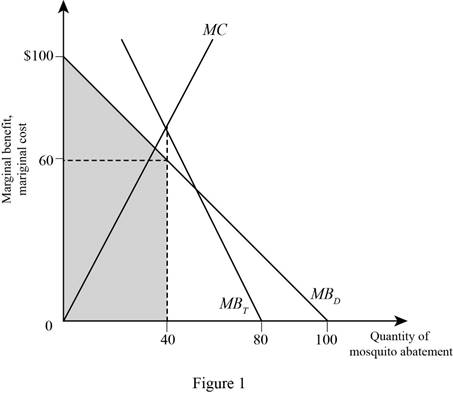
In Figure1, the vertical axis shows the MB and MC of the mosquito abatement and the horizontal axis shows the quantity of mosquito abatement, where the interaction between the total marginal benefit with MC curve determines the optimal quantity of mosquito abatement.
The MB of consumer D can be calculated by substituting the respective value in the MB function of D as follows:
Therefore, 60 is the MB of consumer D.
The MB of consumer L can be calculated by substituting the respective value in the MB function of L as follows:
Therefore, 20 is the MB of consumer D.
Therefore, the total benefit is 80
Now, the total benefit (TB) for consumer D can be calculated using the formula given below:
Now, substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to get the value of total benefit of consumer D.
Therefore, the total benefit of consumer D is 3,200.
Figure 2 illustrates the MB, MC, and the optimal quantity of the mosquito abatement of consumer L as follows:
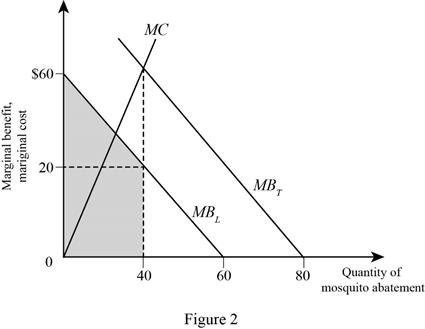
In Figure2, the vertical axis measures the MB and MC of the mosquito abatement and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of mosquito abatement, where the interaction between the total marginal benefit with MC curve determines the optimal quantity of mosquito abatement.
The total benefit (TB) for consumer L can be calculated using the formula given below:
Now, substitute the respective values in Equation (2) to get the value of total benefit of consumer L.
Therefore, the total benefit of consumer L is 1,600.
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
Marginal cost (MC): Marginal benefit refers to the amount of additional cost incurred in the process of increasing one more unit of output.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
EBK MICROECONOMICS
- 1. We want to examine the comparative statics of the Black Scholes model. Complete the following table using the Excel model from class or another of your choice. Provide the call premium and the put premium for each scenario. Underlier Risk-free Scenario price rate Volatility Time to expiration Strike Call premium Put premium Baseline $50 5% 25% 1 year $55 Higher strike $50 5% 25% 1 year $60 Higher volatility $50 5% 40% 1 year $55 Higher risk free $50 8% 25% 1 year $55 More time $50 5% 25% 2 years $55 2. Look at the baseline scenario. a. What is the probability that the call is exercised in the baseline scenario? b. What is the probability that the put is exercised? c. Explain why the probabilities sum to 1.arrow_forwardSome people say that since inflation can be reduced in the long run without an increase in unemployment, we should reduce inflation to zero. Others believe that a steady rate of inflation at, say, 3 percent, should be our goal. What are the pros and cons of these two arguments? What, in your opinion, are good long-run goals for reducing inflation and unemployment?arrow_forwardExplain in words how investment multiplier and the interest sensitivity of aggregate demand affect the slope of the IS curve. Explain in words how and why the income and interest sensitivities of the demand for real balances affect the slope of the LM curve. According to the IS–LM model, what happens to the interest rate, income, consumption, and investment under the following circumstances?a. The central bank increases the money supply.b. The government increases government purchases.c. The government increases taxes.arrow_forward
- Suppose that a person’s wealth is $50,000 and that her yearlyincome is $60,000. Also suppose that her money demand functionis given by Md = $Y10.35 - i2Derive the demand for bonds. Suppose the interest rate increases by 10 percentage points. What is the effect on her demand for bonds?b. What are the effects of an increase in income on her demand for money and her demand for bonds? Explain in wordsarrow_forwardImagine you are a world leader and you just viewed this presentation as part of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal Meeting. Summarize your findings https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v7WUpgPZzpIarrow_forwardPlease draw a standard Commercial Bank Balance Sheet and briefly explain each of the main components.arrow_forward
- Please draw the Federal Reserve System’s Balance Sheet and briefly explain each of the main components.arrow_forward19. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. How does the Federal Reserve currently get the federal funds rate where they want it to be?arrow_forward18. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Carefully compare and contrast fiscal policy and monetary policy.arrow_forward
- 15. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. What are the common arguments for and against high levels of federal debt?arrow_forward17. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Explain the difference between present value and future value. Be sure to use and explain the mathematical formulas for both. How does one interpret these formulas?arrow_forward12. Give the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Show and carefully explain the Taylor rule and all of its components, used as a monetary policy guide.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





