
(a)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when
Concept introduction:
The addition reaction of the
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compound that is formed when
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
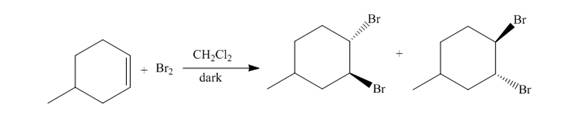
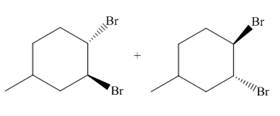
Figure 1
The addition of the bromine molecule on the double bond of the alkene takes place to give the dibromo product. The addition of bromine to the double bond is the anti-addition.
The principal organic compound that is formed when
(b)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when
Concept introduction:
The addition reactions of the alkene are very well known reactions. The electron density on the alkene double bond makes it nucleophilic. The alkene undergoes varieties of addition reaction via different mechanisms.
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compound that is formed when
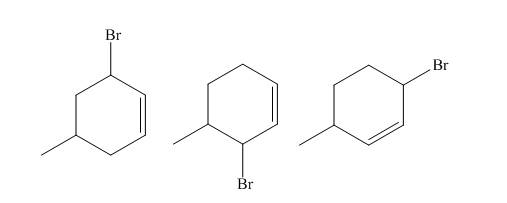
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
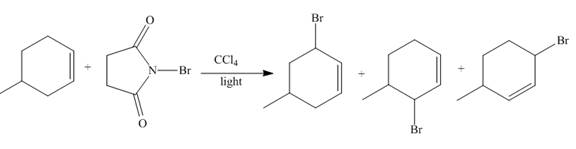
Figure 2
The reaction of an alkene with N-bromosuccinimide in the presence is the free-radical reaction. In this reaction, allylic bromination is observed instead of an addition to the alkene. The N-bromosuccinimide acts as radical initiator. This molecule breaks the
The principal organic compound that is formed when
(c)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when product(s) of part (b) undergo solvolysis in aqueous acetone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The nucleophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which a nucleophile attacks at the electrophilic carbon and eliminates another group. The
The
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (b) undergo solvolysis in aqueous acetone are shown below.
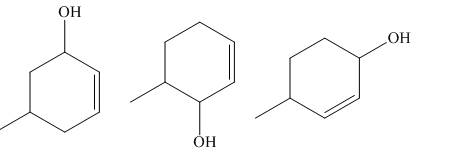
Explanation of Solution
The products of part (b) are shown below.
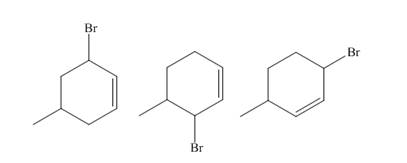
Figure 3
The reaction of product(s) of part (b) on solvolysis in aqueous acetone is shown below.
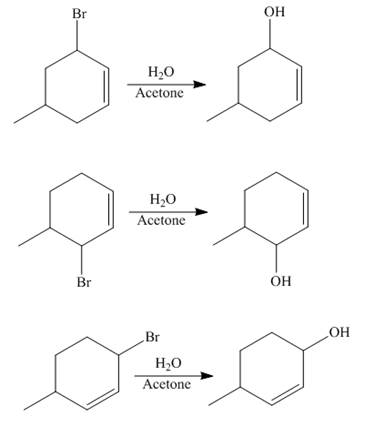
Figure 4
The nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place when solvolysis of products of part (b) is done. The bromine group is substituted by the hydroxyl group giving rise to the formation of an allylic alcohol.
The principal organic compound that is formed when product(s) of part (b) undergo solvolysis in aqueous acetone is shown in Figure 4.
(d)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when product(s) of part (b) are reacted with
Concept introduction:
The reaction of an
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (b) are reacted with
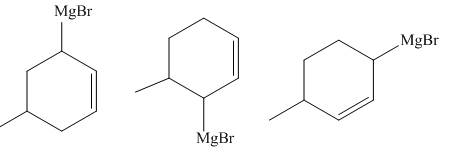
Explanation of Solution
The products of part (b) are shown below.

Figure 3
The reaction that occurs when product(s) of part (b) are reacted with
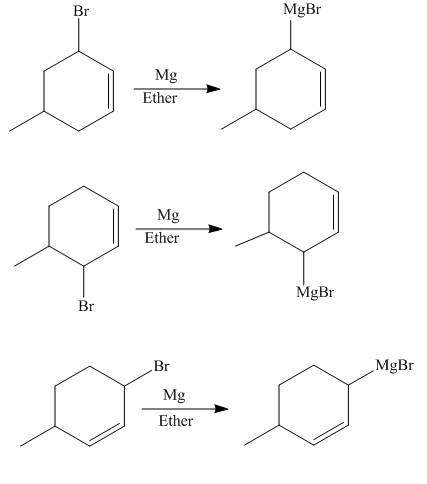
Figure 5
The allylic halide also undergoes the same kind of reactions as the alkyl halide with magnesium metal in dry ether. They also lead to the formation of Grignard reagent but this time with the allylic group.
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (b) are reacted with
(e)
Interpretation:
The principal organic compound that is expected when product(s) of part (d) are reacted with
Concept introduction:
The nucleophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which a nucleophile attacks at the electrophilic carbon and eliminates another group. The rate of reaction depends upon the nucleophilicity and concentration of the nucleophile.
The
Answer to Problem 17.23AP
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (d) are reacted with
Explanation of Solution
The products of part (d) are shown below.

Figure 6
The reaction of product(s) of part (d) with
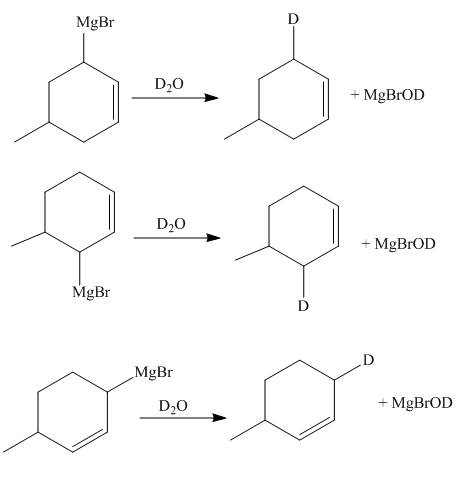
Figure 7
The Grignard reagents are highly reactive towards moisture. The carbon chain on the Grignard reagent gets the hydrogen in place of
The principal organic compounds that are formed when product(s) of part (d) are reacted with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- CUE COLUMN NOTES (A. Determine Stereoisomers it has ⑤ Identify any meso B compounds cl Br cl -c-c-c-c-¿- 1 CI C- | 2,4-Dichloro-3-bromopentanearrow_forwardThe acid-base chemistry of both EDTA and EBT are important to ensuring that the reactions proceed as desired, thus the pH is controlled using a buffer. What percent of the EBT indicator will be in the desired HIn2- state at pH = 10.5. pKa1 = 6.2 and pKa2 = 11.6 of EBTarrow_forwardWhat does the phrase 'fit for purpose' mean in relation to analytical chemistry? Please provide examples too.arrow_forward
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density × NO2 ○ donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O electron-rich electron-deficient no inductive effects O no resonance effects O similar to benzene E [ CI O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Explanation Check ○ donating withdrawing no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forwardUnderstanding how substituents activate Rank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation HN NH2 Check X (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Aarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and electron-withdrawing effects on benzene For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density Molecule CF3 O donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene CH3 O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects O donating O withdrawing Ono resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Explanation Check Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- * Hint: Think back to Chem 1 solubility rules. Follow Up Questions for Part B 12. What impact do the following disturbances to a system at equilibrium have on k, the rate constant for the forward reaction? Explain. (4 pts) a) Changing the concentration of a reactant or product. (2 pts) b) Changing the temperature of an exothermic reaction. (2 pts) ofarrow_forwardDraw TWO general chemical equation to prepare Symmetrical and non-Symmetrical ethers Draw 1 chemical reaction of an etherarrow_forwardPlease help me with the following questions for chemistry.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

