
Concept explainers
(1)
Other postretirement benefits: The postretirement benefits which are provided by employers, other than pensions, like medical insurance, life insurance, and legal services, and healthcare benefits, are referred to as other postretirement benefits.
Accumulated benefit obligation (ABO): This is the estimated present value of future retirement benefits, accumulated based on the current compensation levels.
To draw: The time line that depicts S’s attribution period for retiree benefits and expected retirement period.
(1)
Explanation of Solution
Draw the timeline.
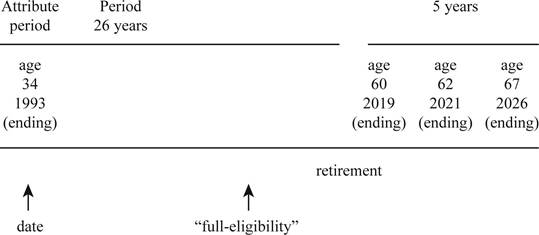
Figure (1)
(2)
To calculate: The present value of the net benefits as of expected retirement date.
(2)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the
| Calculation of present value of net benefits | |||
| Year |
Net Cost (a) |
Present Value of $1 (n=1-5; i=6%) (b) |
Present value |
| 2022 | $4,000 | 0.94340 | $3,774 |
| 2023 | $4,400 | 0.89000 | $3,916 |
| 2024 | $2,300 | 0.83962 | $1,931 |
| 2025 | $2,500 | 0.79209 | $1,980 |
| 2026 | $2,800 | 0.74726 | $2,092 |
| Total | $13,693 | ||
Table (1)
Note: Refer Table 2 in Appendix for the present value factor of $1.
(3)
To calculate: Company’s expected postretirement benefit obligation at the end of 2016 with respect to S.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
The EPBO is the present value of lump-sum net benefits.
The present value of $1 at the rate of 6% for 5 periods is 0.74726 (Refer to Table 2 in Appendix).
(4)
To calculate: The Company’s accumulated postretirement benefit obligation at the end of 2016 with respect to S.
(4)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation.
(5)
To calculate: Company’s accumulated postretirement benefit obligation at the end of 2017 with respect to S.
(5)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate APBO at the end of 2017.
Working Note:
Calculate company’s expected postretirement benefit obligation at the end of 2017.
The EPBO is the present value of lump-sum net benefits.
The present value of $1 at the rate of 6% for 4 periods is 0.79209 (Refer to Table 2 in Appendix).
Conclusion: Therefore, the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation(APBO) at the end of 2017 is$10,012.
(6)
To calculate: The service cost to be included in 2017 postretirement benefit expense.
(6)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the service cost for 2017.
(7)
To calculate: The interest cost to be included in 2019 postretirement benefit expense.
(7)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the interest cost for 2017.
(8)
To show: The changes APBO during 2017 by reconciling the beginning and ending balances.
(8)
Explanation of Solution
The following table shows the APBO at the end of 2017.
| Calculation of APBO | |
| APBO at the beginning of 2017 | $9,051 |
| Add: Service cost | $417 |
| Add: Interest cost | $543 |
| APBO at the end of 2017 | $10,011 |
Table (2)
Note: The difference of $1 in APBO at the end of 2017 is due to rounding. Refer to Requirements (4), (5), and (6) for APBO at the beginning, service cost, and interest cost.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING WITH AIR FRANCE-KLM 2013 ANNUAL REPORT
- Can you explain this financial accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardIn the first two years of operations, Expos company reports taxable income of $125,000 and $65,000, respectively. In the first two years, the company paid $50,000 and $13,000. It is now the end of the third year, and the company has a loss of $160,000 for tax purposes. The company carries losses to the earliest year possible. The tax rate is currently 25%. Required Compute the amount of income tax payable or receivable in the current (third) year.arrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forward
- Can you solve this financial accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this financial accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2024, Sunfish Co. issued a $22 million, 8%, 6-year convertible bond with annual coupon payments. Each $1,000 bond was convertible into 35 shares of Sunfish's common shares. Shark Investments purchased the entire bond issue for $22.7 million on January 1, 2024. Shark estimated that without the conversion feature, the bonds would have sold for $21,013,098 (to yield 9%). On January 1, 2025, Shark converted bonds with a par value of $8.8 million. At the time of conversion, the shares were selling at $30 each. Required Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of convertible bonds. Prepare the journal entry to record the conversion according to IFRS (book value method). Prepare the journal entry to record the conversion according ASPE (market value method).arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





