![OWLv2 for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)](https://s3.amazonaws.com/compass-isbn-assets/textbook_empty_images/large_textbook_empty.svg)
OWLv2 for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305106734
Author: Frederick A. Bettelheim; William H. Brown; Mary K. Campbell; Shawn O. Farrell; Omar Torres
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 17.14P
17-14 Following are structural formulas for two steroid hormones.
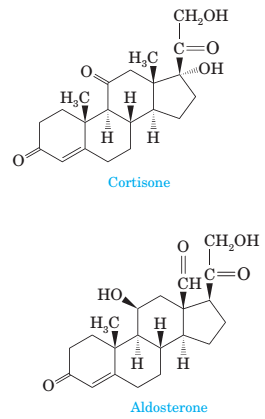
(a) Name the functional groups in each.
(b) Mark all stereocenters in each hormone and state how many stereoisomers are possible for each.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q5: Label each chiral carbon in the following molecules as R or S. Make sure the stereocenter
to which each of your R/S assignments belong is perfectly clear to the grader. (8pts)
R
OCH 3
CI H
S
2pts for each R/S
HO
R
H
!!! I
OH
CI
HN
CI
R
H
Calculate the proton and carbon chemical shifts for this structure
A.
B.
b. Now consider the two bicyclic molecules A. and B. Note that A. is a dianion
and B. is a neutral molecule. One of these molecules is a highly reactive
compound first characterized in frozen noble gas matrices, that self-reacts
rapidly at temperatures above liquid nitrogen temperature. The other
compound was isolated at room temperature in the early 1960s, and is a
stable ligand used in organometallic chemistry. Which molecule is the more
stable molecule, and why?
Chapter 17 Solutions
OWLv2 for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
Ch. 17.2 - Problem 17-1 Wrtie the IUPAC name for each...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.2PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.3PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 17.4PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 17.5PCh. 17.4 - Problem 17-6 Show the reaction of benzaldehyde...Ch. 17.4 - Problem 17-7 Identify all hemiacetals and acetals...Ch. 17.5 - Prob. 17.8PCh. 17 - 17-9 Answer true or false. (a) The one aldehyde...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.10P
Ch. 17 - 17-11 What is the difference in structure between...Ch. 17 - 17-12 Is it possible for the carbon atom of a...Ch. 17 - 17-13 Which compounds contain carbonyl groups?Ch. 17 - 17-14 Following are structural formulas for two...Ch. 17 - 17-15 Draw structural formulas for the four...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.16PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.17PCh. 17 - 17-18 Draw structural formulas for these ketones....Ch. 17 - 17-19 Write the JUPAC names for these compounds.Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.20PCh. 17 - 17-2 1 Explain why each name is incorrect. Write...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.22PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.23PCh. 17 - 17-24 In each pair of compounds, select the one...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.25PCh. 17 - 17-26 Account for the fact that acetone has a...Ch. 17 - 17-27 Pentane, 1-butanol, and butanal all have...Ch. 17 - 17-28 Show how acetaldehyde can form hydrogen...Ch. 17 - 17-29 Why can’t two molecules of acetone form a...Ch. 17 - 17-30 Answer true or false. (a) The reduction of...Ch. 17 - 17-3 1 Draw a structural formula for the principal...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.32PCh. 17 - 17-33 What simple chemical test could you use to...Ch. 17 - 17-34 Explain why liquid aldehydes are often...Ch. 17 - 17-35 Suppose that you take a bottle of...Ch. 17 - 17-36 Explain why the reduction of an aldehyde...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.37PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.38PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.39PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.40PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.41PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.42PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.43PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.44PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.45PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.46PCh. 17 - 17-47 What is the characteristic structural...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.48PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.49PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.50PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.51PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.52PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.53PCh. 17 - 17-54 Following is the structure of...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.55PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.56PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.57PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.58PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.59PCh. 17 - 17-60 1-Propanol can be prepared by the reduction...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.61PCh. 17 - 17-62 Show how to bring about these conversions....Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.63PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.64PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.65PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.66PCh. 17 - 17-67 Draw structural formulas for these...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.68PCh. 17 - 17-69 Propanal (bp 49°C) and 1-propanol (bp 97°C)...Ch. 17 - 17-70 What simple chemical test could you use to...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.71PCh. 17 - 17-72 The following molecule is an enediol; each...Ch. 17 - 17-73 Alcohols can be prepared by the...Ch. 17 - 17-74 Glucose, C6H12O6, contains an aldehyde group...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.75PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.76PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.77PCh. 17 - 17-78 Complete the following equation for these...Ch. 17 - 17-79 Write an equation for each conversion. (a)...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole
Lipids - Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dmoH5dAvpY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY