
Consider the gas-phase reaction between A2 (green) and B2 (red) to form AB at 298 K:
(1) Which of the following reaction mixtures is at equilibrium?
(2) Which of the following reaction mixtures has a negative ΔG value?
(3) Which of the following reaction mixtures has a positive ΔG value?
The partial pressures of the gases in each frame are equal to the number of A2, B2, and AB molecules times 0.10 atm. Round your answers to two significant figures.
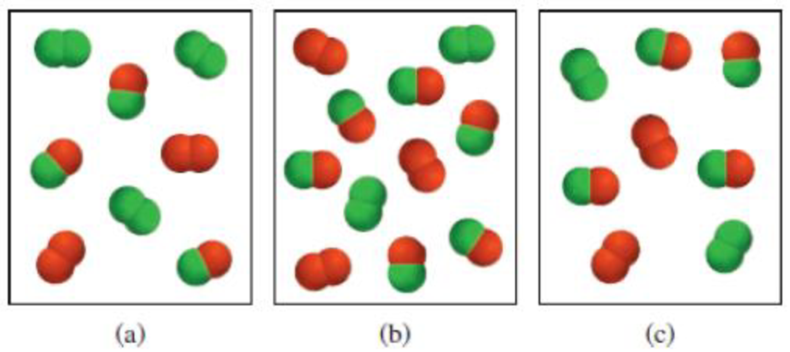
(a)
Interpretation:
The equilibrium process should be determined from the given equilibrium reaction.
Concept Introduction:
Free energy
Free energy (Gibbs free energy) is the term that is used to explain the total energy content in a thermodynamic system that can be converted into work. The free energy is represented by the letter
Explanation of Solution
We calculate the equilibrium constant
The reaction mixture (c) is at equilibrium
(b)
Interpretation:
The negative entropy value has to be calculated and identified for the given equilibrium reaction.
Concept Introduction:
Free energy
Free energy (Gibbs free energy) is the term that is used to explain the total energy content in a thermodynamic system that can be converted into work. The free energy is represented by the letter
Reaction quotient: This type of chemical equilibrium reaction proceeds likely to produced, given either the pressure (or) the concentration of the reactants and the products. The value can be compared to the equilibrium constant, to determine the direction of the reaction that is take place. Then reaction quotient (Qc) the indication of Q can be used to determine which direction will shift to reach of chemical equilibrium process.
Explanation of Solution
The value of
Reaction mixture (a) has a negative
(c)
Interpretation:
The positive entropy value has to be calculate and identified given equilibrium reaction.
Concept Information:
Free energy (Gibbs free energy) is the term that is used to explain the total energy content in a thermodynamic system that can be converted into work. The free energy is represented by the letter
Reaction quotient: This type of chemical equilibrium reaction proceeds likely to produced, given either the pressure (or) the concentration of the reactants and the products. The value can be compared to the equilibrium constant, to determine the direction of the reaction that is take place. Then reaction quotient (Qc) the indication of Q can be used to determine which direction will shift to reach of chemical equilibrium process.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction mixture (b) has positive
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
AVC LOOSELEAF CHEMISTRY W/CONNECT 2 SEM
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forwardShow the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forwardwhat are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward
- 1) a) Give the dominant Intermolecular Force (IMF) in a sample of each of the following compounds. Please show your work. (8) SF2, CH,OH, C₂H₂ b) Based on your answers given above, list the compounds in order of their Boiling Point from low to high. (8)arrow_forward19.78 Write the products of the following sequences of reactions. Refer to your reaction road- maps to see how the combined reactions allow you to "navigate" between the different functional groups. Note that you will need your old Chapters 6-11 and Chapters 15-18 roadmaps along with your new Chapter 19 roadmap for these. (a) 1. BHS 2. H₂O₂ 3. H₂CrO4 4. SOCI₂ (b) 1. Cl₂/hv 2. KOLBU 3. H₂O, catalytic H₂SO4 4. H₂CrO4 Reaction Roadmap An alkene 5. EtOH 6.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 7. Mild H₂O An alkane 1.0 2. (CH3)₂S 3. H₂CrO (d) (c) 4. Excess EtOH, catalytic H₂SO OH 4. Mild H₂O* 5.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH An alkene 6. Mild H₂O* A carboxylic acid 7. Mild H₂O* 1. SOC₁₂ 2. EtOH 3.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/E:OH 5.1.0 Equiv. NaOEt 6. NH₂ (e) 1. 0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 2. Mild H₂O* Br (f) i H An aldehyde 1. Catalytic NaOE/EtOH 2. H₂O*, heat 3. (CH,CH₂)₂Culi 4. Mild H₂O* 5.1.0 Equiv. LDA Br An ester 4. NaOH, H₂O 5. Mild H₂O* 6. Heat 7. MgBr 8. Mild H₂O* 7. Mild H₂O+arrow_forwardLi+ is a hard acid. With this in mind, which if the following compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices LiBr LiI LiF LiClarrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





