
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119304142
Author: Connie Allen, Valerie Harper
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 17, Problem 1.1BGL
Summary Introduction
To label: The meningeal structures of the spinal cord.
Introduction: The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system that conducts both the sensory and motor information and acts as reflex center. The spinal cord is made up of white and gray matter and is surrounded by three protective envelopes called meninges. The spinal cord consists of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that nourishes the spine and protects it from infection. The spinal cord gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves on each side of the vertebra.
Expert Solution & Answer
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
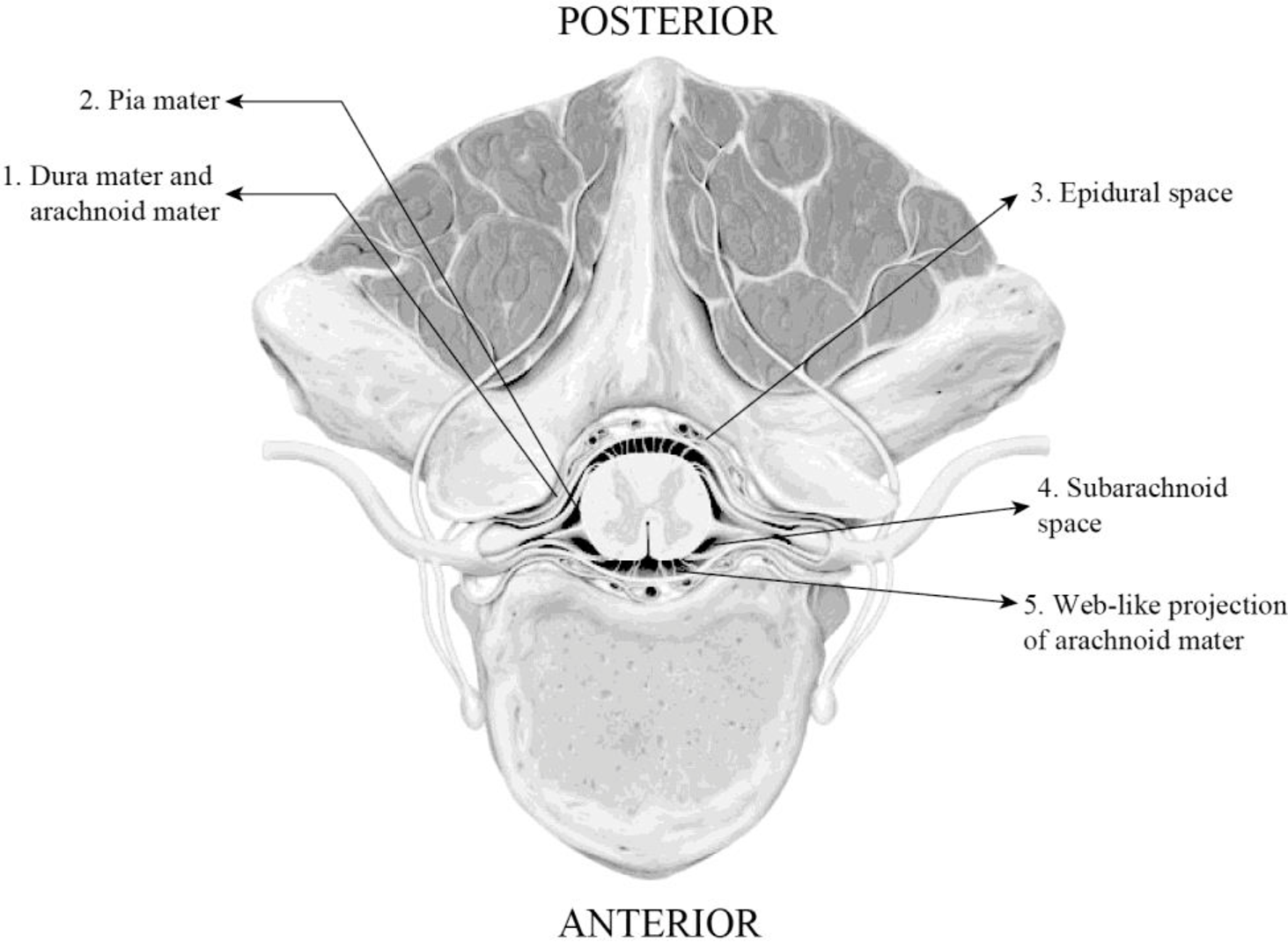
Fig 1: Transverse section of spinal cord showing meninges
Explanation of Solution
The transverse section of the spinal cord shows the following structures:
- 1. Dura mater and arachnoid mater: The dura mater is the outermost layer of the meninges of the spinal cord, which is separated from the vertebral column by the epidural space. The arachnoid mater is a soft layer situated between the dura mater and pia mater.
- 2. Pia mater: It is the innermost meningeal layer, which is a thin membrane that fuses with the filum terminale.
- 3. Epidural Space: It is the outermost part of the spinal canal that contains lymphatics, fatty tissue, spinal nerve roots, and small arteries.
- 4. Subarachnoid space: It is the space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater, which is filled with the cerebrospinal fluid.
- 5. Web-like projection of the arachnoid mater: These projections are also called arachnoid villi or granulations that transfer the CSF back into the bloodstream.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Molecular Biology
Please help. Thank you.
Discuss/define the following:(a) poly A polymerase (b) trans-splicing (c) operon
Molecular Biology
Please help with question. Thank you in advance.
Discuss, compare and contrast the structure of promoters inprokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Molecular Biology
Please help with question. Thank you
You are studying the expression of the lac operon. You have isolated mutants as described below. In the absence of glucose, explain/describe what would happen, for each mutant, to the expression of the lac operon when you add lactose AND what would happen when the bacteria has used up all of the lactose (if the mutant is able to use lactose).1. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent the binding of lactose2. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent release of lactose once lactose hadbound3. Normally the lac repressor gene is located next to (a few hundred base pairs) and upstreamfrom the lac operon. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that move the lac repressor gene 100,000base pairs downstream.4. Mutations in the lac operator that would prevent binding of lac repressor
Chapter 17 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
Ch. 17 - Prob. 1.1BGLCh. 17 - Prob. 2.1BGLCh. 17 - Lebel Figures 17.3 and 17.4
FIGURE 17.3...Ch. 17 - Label the photomicrograph of a transverse section...Ch. 17 - __________. Middle meninx; web-like
Ch. 17 - __________. Tough, outer meninx
Ch. 17 - __________. Space filled with adipose tissue
Ch. 17 - __________. Thin meninx intimate with spinal cord
Ch. 17 - __________ Contains cerebrospinal fluid
Ch. 17 - __________ Extension of pia mater attaching to...
Ch. 17 - __________ Contains neuron cell bodies and...Ch. 17 - __________ Shallow groove on dorsal side of spinal...Ch. 17 - __________ Connects right and left halves of gray...Ch. 17 - __________ Sensory branch of spinal nerve entering...Ch. 17 - __________ Tapered end of spinal cord
Ch. 17 - _______________ Motor branch of spinal nerve...Ch. 17 - ______________ Contains sensory neuron cell...Ch. 17 - ______________ Collection of spinal nerves that...Ch. 17 - _______________ Contains myelinated axons
Ch. 17 - _______________ Contains somatic motor neuron cell...Ch. 17 - _______________ Space in center of spinal cord...Ch. 17 - _______________ Bulge in spinal cord containing...Ch. 17 - _______________ Wide, deep groove on ventral side...Ch. 17 - ________________ Extension of pia mater that...Ch. 17 - ________________ Bulge in spinal cord at T9–T12
Ch. 17 - ________________________
FIGURE 17.7 Transverse...Ch. 17 - Prob. 2.2SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.3SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.4SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.5SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.6SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.7SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.8SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.10SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.11SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.12SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.13SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.14SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 2.15SCSCh. 17 - Prob. 1UYKCh. 17 - Prob. 2UYKCh. 17 - Prob. 3UYKCh. 17 - Prob. 4UYKCh. 17 - Prob. 5UYKCh. 17 - Prob. 6UYKCh. 17 - Prob. 7UYKCh. 17 - Prob. 8UYKCh. 17 - Identify the structural class(es) of neurons whose...Ch. 17 - Prob. 10UYKCh. 17 - Prob. 11UYKCh. 17 - Numbering 1–5, indicate the order of structures...Ch. 17 - Numbering 1–5, indicate the order of structures...Ch. 17 - Numbering 1–5, indicate the order of structures...Ch. 17 - Numbering 1–5, indicate the order of structures...Ch. 17 - Numbering 1–5, indicate the order of structures...Ch. 17 - Numbering 1–4, indicate the order of structures...Ch. 17 - Numbering 1–4, indicate the order of structures...Ch. 17 - Numbering 1–4, indicate the order of structures...Ch. 17 - Numbering 1–4, indicate the order of structures...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You have returned to college to become a phylogeneticist. One of the first things you wish to do is determine how mammals, birds, and reptiles are related. Like any good scientist, you need to consider all available data objectively and without a preconceived “correct” answer. In pursuit of that, you should produce a phylogenetic tree based only on morphological features that show birds and mammals are more closely related. You will then produce a totally different tree, also using morphological features, that shows birds and reptiles are more closely related. Do not forget to include all three groups in both your trees. Based solely off the trees you produce, which relationship would you consider the more likely and why? Once you have answered that question, provide a brief summary of the “modern” understanding of the relationship between these three groups.arrow_forwardtrue or false, the reason geckos can walk on walls is hydrogen bonding between their foot pads and the moisture on the wall.arrow_forwardBiology laboratory problem Please help. thank you You have 20 ul of DNA solution and 6X DNA loading buffer solution. You have to mix your DNA solution and DNA loading buffer before load DNA in an agarose gel. The concentration of the DNA loading buffer must be 1X in the DNA and DNA-loading buffer mixture after you mix them. For that, I will add _____ ul of 6X loading buffer to the 20 ul DNA solution.arrow_forward
- Biology lab problem To make 20 ul of 5 mM MgCl2 solution using 50 mM MgCl2 stock solution and distilled water, I will mix ________ ul of 50 mM MgCl2 solution and ________ ul of distilled water. Please help . Thank youarrow_forwardBiology Please help. Thank you. Biology laboratory question You need 50 ml of 1% (w/v) agarose gel. Agarose is a powder. How would you make it? You can ignore the volume of agarose powder. Don't forget the unit.TBE buffer is used to make an agarose gel, not distilled water. I will add _______ of agarose powder into 50 ml of distilled water (final 50 ml).arrow_forwardAn urgent care center experienced the average patient admissions shown in the Table below during the weeks from the first week of December through the second week of April. Week Average Daily Admissions 1-Dec 11 2-Dec 14 3-Dec 17 4-Dec 15 1-Jan 12 2-Jan 11 3-Jan 9 4-Jan 9 1-Feb 12 2-Feb 8 3-Feb 13 4-Feb 11 1-Mar 15 2-Mar 17 3-Mar 14 4-Mar 19 5-Mar 13 1-Apr 17 2-Apr 13 Forecast admissions for the periods from the first week of December through the second week of April. Compare the forecast admissions to the actual admissions; What do you conclude?arrow_forward
- Analyze the effectiveness of the a drug treatment program based on the needs of 18-65 year olds who are in need of treatment by critically describing 4 things in the program is doing effectively and 4 things the program needs some improvement.arrow_forwardI have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.arrow_forward13. Practice Calculations: 3 colonies were suspended in the following dilution series and then a viable plate count and microscope count was performed. Calculate IDF's, TDF's and then calculate the CFU/mL in each tube by both methods. Finally calculate the cells in 1 colony by both methods. Show all of your calculations in the space provided on the following pages. 3 colonies 56 cells 10 μL 10 μL 100 μL 500 με m OS A B D 5.0 mL 990 με 990 με 900 με 500 μL EN 2 100 με 100 μL 118 colonies 12 coloniesarrow_forward
- Describe and give a specific example of how successionary stage is related to species diversity?arrow_forwardExplain down bellow what happens to the cell in pictures not in words: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education
Nervous System - Get to know our nervous system a bit closer, how does it works? | Neurology; Author: FreeMedEducation;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6O-0CVAgaEM;License: Standard youtube license