
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119472780
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 105P
In Fig. 17-35. S1 and S2 are two isotropic point sources of sound. They emit waves in phase at wavelength 0.50 m; they are separated by D = 1.60 m. If we move a sound detector along a large circle centered at the midpoint between the sources, at how many points do waves arrive at the detector (a) exactly in phase and (b) exactly out of phase?
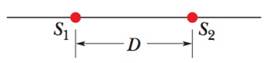
Figure 17-35 Problems 19 and 105.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Hi,
I have canceled, why did you charge me again?
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 17 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
Ch. 17 - Prob. 1QCh. 17 - In Fig. 17-25, two point sources S1, and S2, which...Ch. 17 - In Fig. 17-26, three long tubes A,B, and C are...Ch. 17 - Prob. 4QCh. 17 - In Fig. 17-27, pipe A is made to oscillate in its...Ch. 17 - Prob. 6QCh. 17 - Figure 17-28 shows a moving sound source S that...Ch. 17 - Prob. 8QCh. 17 - For a particular tube, here are four of the six...Ch. 17 - Prob. 10Q
Ch. 17 - You are given four tuning forks. The fork with the...Ch. 17 - Two spectators at a soccer game see, and a moment...Ch. 17 - What is the bulk modulus of oxygen if 32.0 g of...Ch. 17 - Prob. 3PCh. 17 - A column of soldiers, marching at 120 paces per...Ch. 17 - Prob. 5PCh. 17 - A man strikes one end of a thin rod with a hammer....Ch. 17 - SSM WWW A stone is dropped into a well. The splash...Ch. 17 - Prob. 8PCh. 17 - If the form of a sound wave traveling through air...Ch. 17 - Prob. 10PCh. 17 - SSM Diagnostic ultrasound of frequency 4.50 MHz is...Ch. 17 - The pressure in a traveling sound wave is given by...Ch. 17 - A sound wave of the form s = sm coskx t travels...Ch. 17 - Figure 17-32 shows the output from a pressure...Ch. 17 - GO A handclap on stage in an amphitheater sends...Ch. 17 - Two sound waves, from two different sources with...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17PCh. 17 - Prob. 18PCh. 17 - GO Figure 17-35 shows two isotropic point sources...Ch. 17 - Figure 17-36 shows four isotropic point sources of...Ch. 17 - SSM In Fig. 17-37, two speakers separated by...Ch. 17 - In Fig. 17-38, sound with a 40.0 cm wavelength...Ch. 17 - GO Figure 17-39 shows two point sources S1 and S2...Ch. 17 - Suppose that the sound level of a conversation is...Ch. 17 - A sound wave of frequency 300Hz has an intensity...Ch. 17 - Prob. 26PCh. 17 - SSM WWW A certain sound source is increased in...Ch. 17 - Two sounds differ in sound level by 1.00 dB. What...Ch. 17 - Prob. 29PCh. 17 - The source of a sound wave has a power of 1.00 W....Ch. 17 - GO When you crack a knuckle, you suddenly widen...Ch. 17 - Approximately a third of people with normal...Ch. 17 - Male Rana catesbeiana bullfrogs arc known for...Ch. 17 - GO Two atmospheric sound sources A and B emit...Ch. 17 - A point source emits 30.0 W of sound...Ch. 17 - Party hearing. As the number of people at a party...Ch. 17 - Prob. 37PCh. 17 - The water level in a vertical glass tube 1.00 m...Ch. 17 - Prob. 39PCh. 17 - Organ pipe A, with both ends open, has a...Ch. 17 - A violin siring 15.0 cm long and fixed at both...Ch. 17 - A sound wave in a fluid medium is reflected at a...Ch. 17 - SSM In Fig. 17-41, S is a small loudspeaker driven...Ch. 17 - The crest of a Parasaurolophus dinosaur skull is...Ch. 17 - In pipe A, the ratio of a particular harmonic...Ch. 17 - GO Pipe A. which is 1.20 m long and open at both...Ch. 17 - A well with vertical sides and water at the bottom...Ch. 17 - One of the harmonic frequencies of tube A with two...Ch. 17 - SSM A violin string 30.0 cm long with linear...Ch. 17 - Prob. 50PCh. 17 - The A string of a violin is a little too tightly...Ch. 17 - A tuning fork of unknown frequency makes 3.00...Ch. 17 - SSM Two identical piano wires have a fundamental...Ch. 17 - You have five tuning forks that oscillate at close...Ch. 17 - Prob. 55PCh. 17 - An ambulance with a siren emitting a whine at 1600...Ch. 17 - A state trooper chases a speeder along a straight...Ch. 17 - Prob. 58PCh. 17 - GO In Fig. 17-42, a French submarine and a U.S....Ch. 17 - A stationary motion detector sends sound waves of...Ch. 17 - GO A bat is flitting about in a cave, navigating...Ch. 17 - Figure 17-43 shows four tubes with lengths 1.0 m...Ch. 17 - ILWAn acoustic burglar alarm consists of a source...Ch. 17 - A stationary detector measures the frequency of a...Ch. 17 - GO A 2000 Hz siren and a civil defense official...Ch. 17 - GO Two trains are traveling toward each other at...Ch. 17 - SSM WWWA girl is sitting near the open window of a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 68PCh. 17 - SSMA jet plane passes over you at a height of 5000...Ch. 17 - A plane flies at 1.25 times the speed of sound....Ch. 17 - At a distance of 10 km, a 100 Hz horn, assumed to...Ch. 17 - A bullet is fired with a speed of 685 m/s. Find...Ch. 17 - Prob. 73PCh. 17 - The average density of Earths crust 10 km beneath...Ch. 17 - A certain loudspeaker system emits sound...Ch. 17 - Find the ratios greater to smaller of the a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 77PCh. 17 - A trumpet player on a moving railroad flatcar...Ch. 17 - GO In Fig. 17-46, sound of wavelength 0.850 m is...Ch. 17 - GO A detector initially moves at constant velocity...Ch. 17 - SSMa If two sound waves, one in air and one in...Ch. 17 - A continuous sinusoidal longitudinal wave is sent...Ch. 17 - SSMUltrasound, which consists of sound waves with...Ch. 17 - The speed of sound in a certain metal is vm. One...Ch. 17 - An avalanche of sand along some rare desert sand...Ch. 17 - A sound source moves along an x axis, between...Ch. 17 - SSMA siren emitting a sound of frequency 1000 Hz...Ch. 17 - Prob. 88PCh. 17 - Prob. 89PCh. 17 - Prob. 90PCh. 17 - Prob. 91PCh. 17 - You can estimate your distance from a lightning...Ch. 17 - SSMFigure 17-48 shows an air-filled, acoustic...Ch. 17 - Prob. 94PCh. 17 - SSMThe sound intensity is 0.0080 W/m2 at a...Ch. 17 - Four sound waves are to be sent through the same...Ch. 17 - Prob. 97PCh. 17 - A point source that is stationary on an x axis...Ch. 17 - You are standing at a distance D from an isotropic...Ch. 17 - Pipe A has only one open end; pipe B is four times...Ch. 17 - A pipe 0.60 m long and closed at one end is filled...Ch. 17 - A sound wave travels out uniformly in all...Ch. 17 - A police car is chasing a speeding Porsche 911....Ch. 17 - Prob. 104PCh. 17 - In Fig. 17-35. S1 and S2 are two isotropic point...Ch. 17 - Prob. 106PCh. 17 - Kundts method for measuring the speed of sound. In...Ch. 17 - Prob. 108PCh. 17 - In Fig. 17-53, a point source S of sound waves...Ch. 17 - A person on a railroad car blows a trumpet note at...Ch. 17 - A listener at rest with respect to the air and the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Which culture uses NAD+? Use the following choices to answer questions. a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
In humans, hemophilia A (OMIM 306700) is an X-linked recessive disorder that affects the gene for factor VIII p...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Examine the graph in Figure 6.3. Note that the growth rate increases slowly until the optimum is reached and th...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
77. Write a molecular equation for the precipitation reaction that occurs (if any) when each pair of aqueous so...
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. The reason we do not have a solar ecli...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardYou are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forward
- A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forwardWhat are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forward
- A circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forward
- Describe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forwardDiscuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What Are Sound Wave Properties? | Physics in Motion; Author: GPB Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GW6_U553sK8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY