
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Configuration has to be determined as D- or L- for the structures given below,
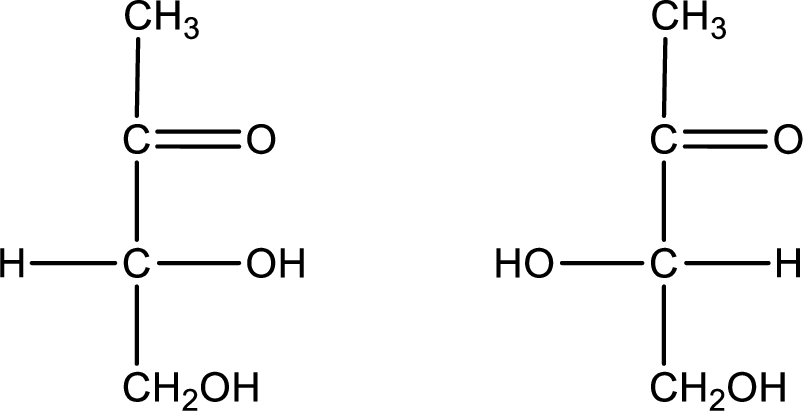
Concept Introduction:
Chiral compounds are optically active and they rotate the plane polarized light. Some compounds rotate the plane polarized light clockwise and some rotate it anticlockwise. Compounds that rotate clockwise are known as dextrorotatory and those which rotate anticlockwise are known as levorotatory. Dextrorotatory compounds are indicated with a “(+)” sign while levorotatory compounds are indicated with a “(-)” sign. In case of sugar, the chiral carbon that contains hydroxyl group farthest from the most oxidized end of the molecule is considered. If the hydroxyl group is present on the right side, then the isomer is said to have D-configuration and if it is present on the left side, then the isomer is said to be in L-configuration.
(b)
Interpretation:
Configuration has to be determined as D- or L- for the structures given below,
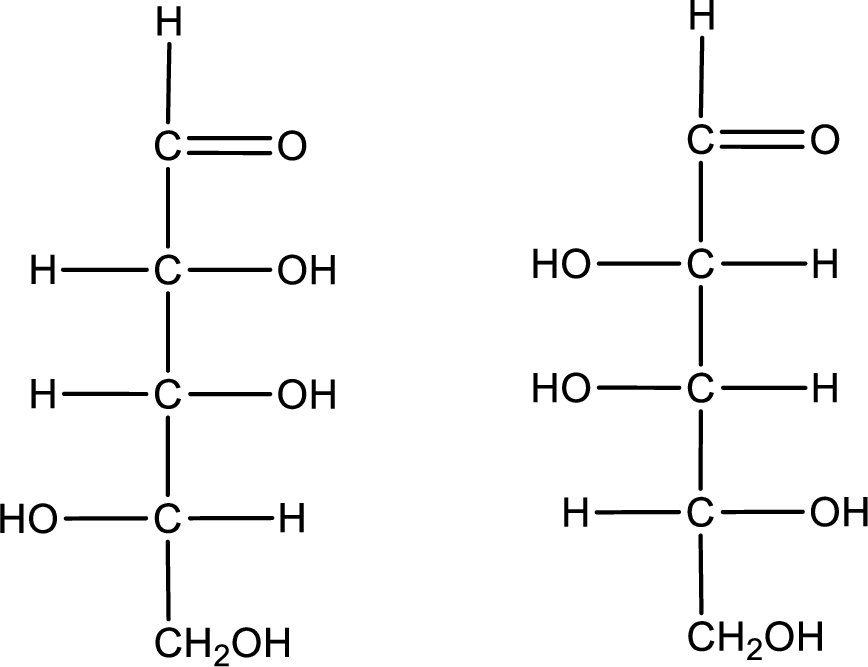
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Interpretation:
Configuration has to be determined as D- or L- for the structures given below,
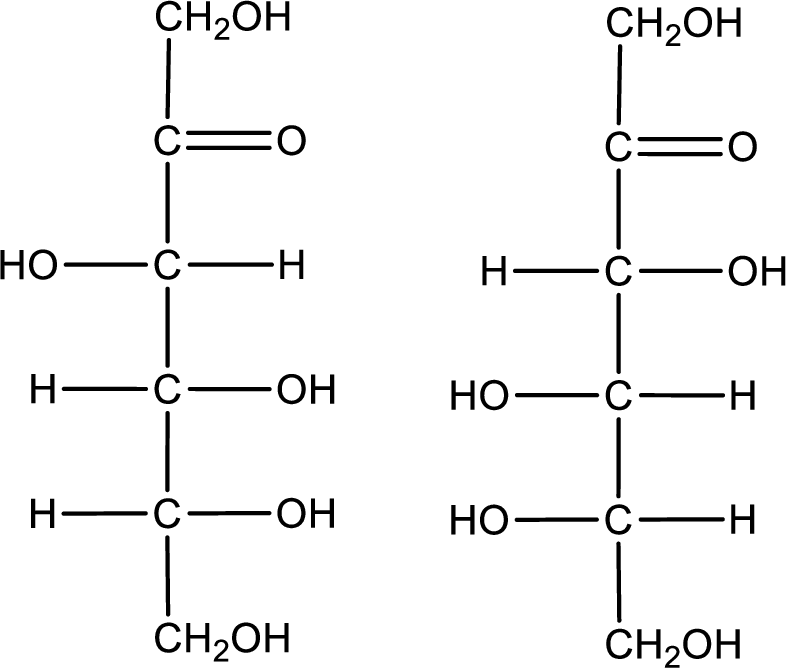
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIOCHEMISTRY(LL)-PKG
- predict the product formed by the reaction of one mole each of cyclohex-2-en-1-one and lithium diethylcuprate. Assume a hydrolysis step follows the additionarrow_forwardPlease handwriting for questions 1 and 3arrow_forwardIs (CH3)3NHBr an acidic or basic salt? What happens when dissolved in aqueous solution? Doesn't it lose a Br-? Does it interact with the water? Please advise.arrow_forward
- © Macmilla Finish resonance structure 3 Select Draw Templates More C H N 0 H H S Erase Which structure is the most stable (lowest energy) resonance contributor? The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and sulfur. All structures are equal in stability. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on sulfur and carbon. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and carbon. Q2Qarrow_forwardThree pure compounds are formed when 1.00 g samples of element x combine with, respectively, 0.472 g, 0.630 g, and 0.789 g of element z. The first compound has the formula x2Z3. find the empricial formula of the other two compoundsarrow_forwardDraw the product and the mechanism A. excess H*; 人 OH H*; B. C. D. excess OH ✓ OH H*; H₂O 1. LDA 2. H*arrow_forward
- In reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIf the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forwardGiven the first-order reaction: aA → products. State its kinetic equation.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





