
Concept explainers
The net force exerted on each charge by other charges.
Answer to Problem 51QAP
Net force on charge A is 36.3 N at angle
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Charge A, charge B and charge C are placed in a coordinate system as shown below.
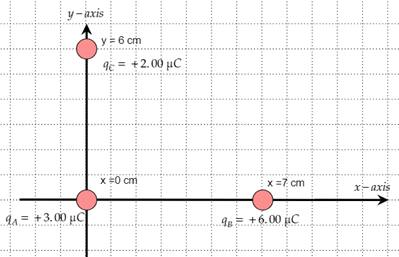
Formula used:
From Coulomb's law
Calculation:
For charge A,
x component of net force on charge A :
Because charges A and B have the same sign, the force on charge A is repulsive and acts in the
negative x direction.
Thus, the net force on charge A in the x -direction is - 33.0 N.
The y component of net force on charge A :
Because charges A and C have the same sign, the force on charge A is repulsive and acts in the
negative y -direction.
Thus, the net force on charge A in the y -direction is -15.0 N
The magnitude of the net force on charge A :
The direction of the net force on charge A :
For charge B,
x component of net force on charge B :
y component of net force on charge B :
Because charges C and B have the same sign, the force on charge B is repulsive and acts in the negative y-direction. Thus, the net force on charge B in the y -direction is -8.26 N
The magnitude of the net force on charge B :
The direction of the net force on charge B :
For charge C,
x component of net force on charge C :
Because charges C and B have the same sign, the force on charge C is repulsive and acts in the
negative x direction. Thus, the net force on charge C in the x-direction is -9.64 N
y component of net force on charge C :
The magnitude of the net force on charge C :
The direction of the net force on charge C :
Conclusion:
Net force on charge A is 36.3 N at angle
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS,VOLUME 1
- An electron and a proton are each moving at 755 km/s in perpendicular paths as shown in (Figure 1). At the instant when they are at the positions shown, find the magnitude and direction of the total magnetic field they produce at the origin. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field the electron produces at the location of the proton. Find the magnitude and direction of the total magnetic and electric force that the electron exerts on the proton. Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardConsider the series M8 3 ཱ|༤༠ n=0 5n a. Find the general formula for the sum of the first k terms. Your answer should be in terms of k. Sk=3 1 5 5 k b. The sum of a series is defined as the limit of the sequence of partial sums, which means k 3 5n 1- = lim 3 k→∞ n=0 4 15 4 c. Select all true statements (there may be more than one correct answer): A. The series is a geometric series. B. The series converges. C. The series is a telescoping series (i.e., it is like a collapsible telescope). D. The series is a p-series.arrow_forwardA uniform ladder of length L and weight w is leaning against a vertical wall. The coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the floor is the same as that between the ladder and the wall. If this coefficient of static friction is μs : 0.535, determine the smallest angle the ladder can make with the floor without slipping. ° = A 14.0 m uniform ladder weighing 480 N rests against a frictionless wall. The ladder makes a 55.0°-angle with the horizontal. (a) Find the horizontal and vertical forces (in N) the ground exerts on the base of the ladder when an 850-N firefighter has climbed 4.10 m along the ladder from the bottom. horizontal force magnitude 342. N direction towards the wall ✓ vertical force 1330 N up magnitude direction (b) If the ladder is just on the verge of slipping when the firefighter is 9.10 m from the bottom, what is the coefficient of static friction between ladder and ground? 0.26 × You appear to be using 4.10 m from part (a) for the position of the…arrow_forward
- Your neighbor designs automobiles for a living. You are fascinated with her work. She is designing a new automobile and needs to determine how strong the front suspension should be. She knows of your fascination with her work and your expertise in physics, so she asks you to determine how large the normal force on the front wheels of her design automobile could become under a hard stop, ma when the wheels are locked and the automobile is skidding on the road. She gives you the following information. The mass of the automobile is m₂ = 1.10 × 103 kg and it can carry five passengers of average mass m = 80.0 kg. The front and rear wheels are separated by d = 4.45 m. The center of mass of the car carrying five passengers is dCM = 2.25 m behind the front wheels and hcm = 0.630 m above the roadway. A typical coefficient of kinetic friction between tires and roadway is μk 0.840. (Caution: The braking automobile is not in an inertial reference frame. Enter the magnitude of the force in N.)…arrow_forwardJohn is pushing his daughter Rachel in a wheelbarrow when it is stopped by a brick 8.00 cm high (see the figure below). The handles make an angle of 0 = 17.5° with the ground. Due to the weight of Rachel and the wheelbarrow, a downward force of 403 N is exerted at the center of the wheel, which has a radius of 16.0 cm. Assume the brick remains fixed and does not slide along the ground. Also assume the force applied by John is directed exactly toward the center of the wheel. (Choose the positive x-axis to be pointing to the right.) (a) What force (in N) must John apply along the handles to just start the wheel over the brick? (No Response) N (b) What is the force (magnitude in kN and direction in degrees clockwise from the -x-axis) that the brick exerts on the wheel just as the wheel begins to lift over the brick? magnitude (No Response) KN direction (No Response) ° clockwise from the -x-axisarrow_forwardAn automobile tire is shown in the figure below. The tire is made of rubber with a uniform density of 1.10 × 103 kg/m³. The tire can be modeled as consisting of two flat sidewalls and a tread region. Each of the sidewalls has an inner radius of 16.5 cm and an outer radius of 30.5 cm as shown, and a uniform thickness of 0.600 cm. The tread region can be approximated as having a uniform thickness of 2.50 cm (that is, its inner radius is 30.5 cm and outer radius is 33.0 cm as shown) and a width of 19.2 cm. What is the moment of inertia (in kg. m²) of the tire about an axis perpendicular to the page through its center? 2.18 x Sidewall 33.0 cm 30.5 cm 16.5 cm Treadarrow_forward
- A person on horseback is on a drawbridge which is at an angle = 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure. The center of mass of the person-horse system is d = 1.35 m from the end of the bridge. The bridge is l = 7.00 m long and has a mass of 2,300 kg. A cable is attached to the bridge 5.00 m from the frictionless hinge and to a point on the wall h = 12.0 m above the bridge. The mass of person plus horse is 1,100 kg. Assume the bridge is uniform. Suddenly (and most unfortunately for the horse and rider), the ledge where the bridge usually rests breaks off, and at the same moment the cable snaps and the bridge swings down until it hits the wall. ÚI MAJI A TLA MAJA AUTA (a) Find the angular acceleration (magnitude, in rad/s²) of the bridge once it starts to move. 2.22 Use the rotational analogue of Newton's second law. The drawbridge can be modeled as a rod, with rotation axis about one end. rad/s² (b) How long (in s) does the horse and rider stay in contact with the bridge…arrow_forwardTwo long, parallel wires carry currents of I₁ = 2.70 A and I2 = 4.85 A in the directions indicated in the figure below, where d = 22.0 cm. (Take the positive x direction to be to the right.) 12 (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at a point midway between the wires. magnitude direction 3.91 270 μπ ⚫ counterclockwise from the +x axis (b) Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P, located d = 22.0 cm above the wire carrying the 4.85-A current. magnitude direction Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. μT The response you submitted has the wrong sign.° counterclockwise from the +x axisarrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning The mass of a particular eagle is twice that of a hunted pigeon. Suppose the pigeon is flying north at Vi2 = 16.1 m/s when the eagle swoops down, grabs the pigeon, and flies off. At the instant right before the attack, the eagle is flying toward the pigeon at an angle 0 = 64.3° below the horizontal and a speed of Vi,1 = 37.9 m/s. What is the speed of of the eagle immediately after it catches its prey? What is the magnitude & of the angle, measured from horizontal, at which the eagle is flying immediately after the strike? Uf = II x10 TOOLS Vi.1 Vi,2 m/sarrow_forward
- What is the equivalent resistance if you connect a 1.7 Ohm, a 9.3 Ohm, and a 22 Ohm resistor in series? (Give your answer as the number of Ohms.)arrow_forwardThree wires meet at a junction. One wire carries a current of 5.2 Amps into the junction, and a second wire carries a current of 3.7 Amps out of the junction. What is the current in the third wire? Give your answer as the number of Amps, and give a positive number if the current in that wire flows out of the junction, or a negative number if the current in that wire flows into the junction.arrow_forwardWhat is the equivalent resistance if you connect a 4.5 Ohm, a 6.8 Ohm, and a 15 Ohm resistor in parallel? (Give your answer as the number of Ohms.)arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





