
(A)
To Compute:
What will be the payoff to the put,
Introduction:
The payoff to the put,
Explanation of Solution
Valuation of one year European put option using the two-state approach is described as
follows:
The put price for increase factor of 1.1,
decrease factor of 0.95,
$110.
Calculate the probable value of put, in case stock price increases (
(B)
To Compute:
What will be the payoff,
Introduction:
The payoff,
Explanation of Solution
The hedge ratio at this point can be calculated by using the following formula:
Substitute the value to calculate hedge ratio as follows:
Hence, the hedge ratio is
The final stock price of the portfolio that will be worth $121 at expiry regardless of the final stock price is as follows:
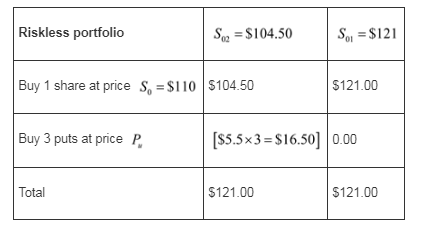
The portfolio must have a current market value equal to the
Calculate the value of put in case stock price decreases
The put price for increase factor of 1.1,
decrease factor of 0.95,
$110
Calculation of the hedge ratio:
The hedge ratio at this point can be calculated by using the following formula:
Therefore, the hedge ratio is -1.0
The final stock price of the portfolio that will be worth $110 at expiry is as follows:
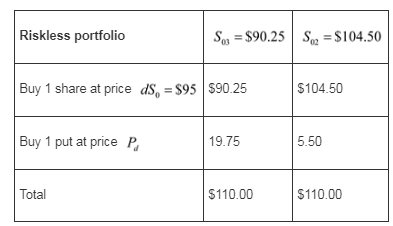
The portfolio must have a current market value equal to the present value of $110,which is defined by the following equation:
Hence, the value of put in case stock price decrease is $9.762.
Calculate P using the values of
The put can increase to a value of
Initial value.
The put can fall to a value of
Initial value.
Calculate hedge ratio at this point as follows:
Thus, the payoff,
(C)
To Compute:
Value the put option using the risk-neutral shortcut described in the box. Confirm that your answer matches the value you get using the two-state approach.
Introduction:
Explanation of Solution
The portfolio will be worth $60.53 at expiry irrespective of the final stock price as follows:
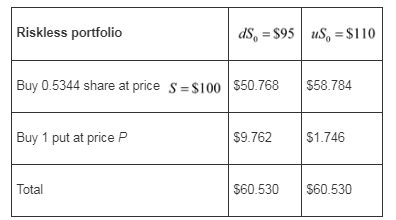
The portfolio must have a market value equal to the present value of $60.53 which is defined by the following equation:
Hence, the value of put option binomial model option pricing is $4.208
Valuation of put option using risk neutral shortcut is described as follows:
Formula for risk neutral probability is as follows:
Here,
u is factor by which stock increases
d is factor by which stock increases
Calculate the risk neutral probability that the stock price will increase as follows:
Calculate the expected cash flows at expiration and discount it by the risk free rate to find
and
Calculate
Calculate
Calculate the expected cash flow in 6 months and discount the E(CF) by the 6 month risk free
Rate as follows:
Hence, the value of put option using risk neutral shortcut is $4.208
Therefore, the value of put option through two state approach and risk neutral shortcut is same, that is, $4.208.
Therefore, the value of put option through two state approach and risk neutral shortcut is same, that is, $4.208.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
CONNECT WITH LEARNSMART FOR BODIE: ESSE
- PLEASE ANSWER THE COLUMN FULLY AND CORRECTLY PLEASE DO THE RIGHT CALCULATION DOUBLE CHECK AS WELL TO GIVE ME THE RIGHT ANSWER REQUIRED: Given the following information, what are the NZD/SGD currency against currency bid-ask quotations? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 4 decimal places. Bank Quotations American Terms European Terms Bid Ask Bid Ask New Zealand dollar 0.733 0.7340 1.3870 1.3884 Singapore dollar 0.6186 0.6191 1.6423 1.6436 answer Bid Ask New Zealand dollar ? ? Singapore dollar ? ?arrow_forwardAbout this Assignment For the Corporate Finance 301 assignment, you will submit a research paper that analyzes and discusses organizational financial risks. You will apply knowledge acquired in the course and use the concepts of multiple financial risks as the basis of research and analysis. The research paper should follow APA formatting style. Audience: upper-level business students. Project Prompt Write a 1,000-1,200-word analysis discussing financial risk concepts and assess the impact of the different financial risks on an organization. For this assignment, you will structure your assignment using four research paper sections associated with corporate risk management, as studied in the course. Base your research paper on the financial statements analyzed in Corporate Finance 301 assignment 2 and apply the knowledge acquired in the analysis. Define each financial risk, discuss the risk associated components, and evaluate the financial risks and how they affect the corporation's…arrow_forwardBobby Nelson, made deposits of $880 at the end of each year for 6 years. Interest is 6% compounded annually. What is the value of Bobby’s annuity at the end of 6 years?arrow_forward
- 1. Find the future value if $1,250 is invested in Simple interest account paying 6.5%: a. for 5 years b. for 20 years 2. Find the future amount $ 35,000 is invested for 30 years at 4.25% compounded: a. annually b. Quarterly c. monthly d. weekly 3. How much should be put into an account today that pays 7.75% compounded monthly if you need $10,000 in 5 years. 4. Find the effective rate for: a. 5.75% compounded quarterly b. 6.25% compounded daily. 5. $50 is invested at the end of each month into an account paying 7.5% compounded monthly. How much will be in the account after 5 years?…arrow_forwardSolve step by step no aiarrow_forwardDont use ai solve itarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





