
Concept explainers
1. and 2.
Prepare a schedule to show the impact of the assumed conversion of each convertible security on diluted earnings per share and also show the manner by which the securities that are included in the diluted earnings per share are ranked.
1. and 2.
Explanation of Solution
Earnings per share (EPS): The amount of net income available to each shareholder per common share outstanding is referred to as earnings per share (EPS).
Prepare a schedule to show the impact of the assumed conversion of each convertible security on diluted earnings per share.
| Convertible security | Impact in ($) | Ranking |
| 10.2% bonds (1) | $2.55 | 5 |
| 12.0% bonds (3) | $1.71 | 3 |
| 9.0% bonds (5) | $1.51 | 2 |
| 8.3% | $2.13 | 4 |
| 7.5% preferred stock (7) | $1.25 | 1 |
(Table 1)
Working notes:
(1) Calculate the impact of the 10.2% bonds on diluted earnings per share.
(2) Calculate the Premium on amortized bond for 20 year life:
(3) Calculate the impact of the 12.0% bonds on diluted earnings per share.
(4) Calculate the discount on amortized bond for 10 year life:
(5) Calculate the impact of the 9.0% bonds on diluted earnings per share.
(6) Calculate the impact of the 8.3% preferred stock on diluted earnings per share.
(7) Calculate the impact of the 7.5% preferred stock on diluted earnings per share.
3. and 4.
Calculate the basic earnings per share and diluted earnings per share.
3. and 4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the basic earnings per share and diluted earnings per share.
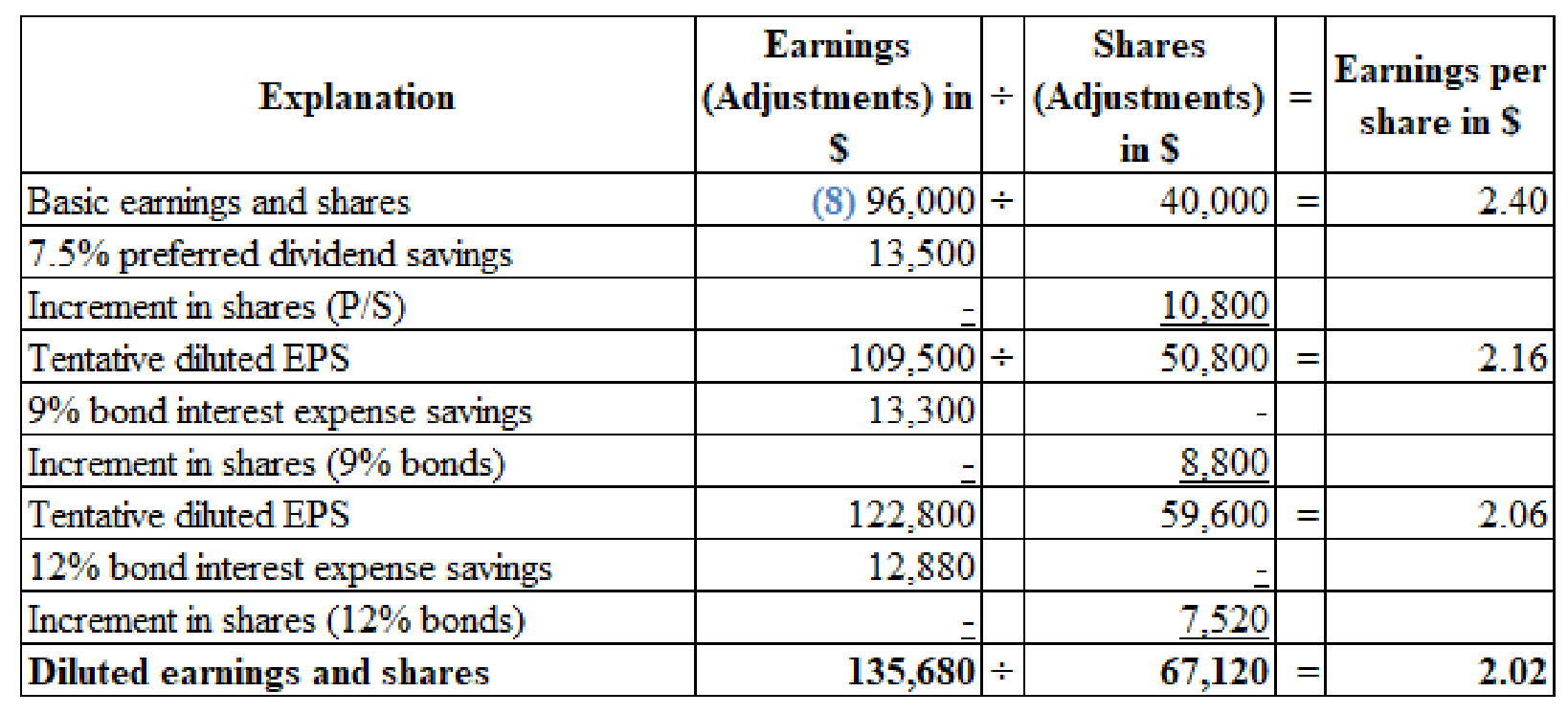
(Figure 1)
Working notes:
(8) Calculate the numerator for the basic earnings per share:
5.
Identify the amount that will be reported as basic and diluted earnings per share for the year 2016.
5.
Explanation of Solution
The Company W must report an amount of $2.40 as basic earnings per share and $2.20 as diluted earnings per share in its 2016 income statement.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING: REPORTING
- Which account is closed at the end of the accounting period? A. Accumulated Depreciation B. Salaries Payable C. Service Revenue D. Retained Earnings need carrow_forwardWhich account is closed at the end of the accounting period?A. Accumulated DepreciationB. Salaries PayableC. Service RevenueD. Retained Earningsarrow_forward12. Which account is closed at the end of the accounting period?A. Accumulated DepreciationB. Salaries PayableC. Service RevenueD. Retained Earningsneed helparrow_forward
- 12. Which account is closed at the end of the accounting period?A. Accumulated DepreciationB. Salaries PayableC. Service RevenueD. Retained Earningsarrow_forwardWhich account is closed at the end of the accounting period?A. Accumulated DepreciationB. Salaries PayableC. Service RevenueD. Retained Earningsneed helparrow_forwardWhich account is closed at the end of the accounting period?A. Accumulated DepreciationB. Salaries PayableC. Service RevenueD. Retained Earningsarrow_forward
- The principle that requires companies to record expenses in the same period as the revenues they help generate is the:A. Revenue Recognition PrincipleB. Consistency PrincipleC. Matching PrincipleD. Cost Principleneed hekparrow_forwardNo AI The principle that requires companies to record expenses in the same period as the revenues they help generate is the:A. Revenue Recognition PrincipleB. Consistency PrincipleC. Matching PrincipleD. Cost Principlearrow_forwardThe principle that requires companies to record expenses in the same period as the revenues they help generate is the:A. Revenue Recognition PrincipleB. Consistency PrincipleC. Matching PrincipleD. Cost Principlearrow_forward
- No ai 14. A company receives a bill for electricity to be paid next month. What is the journal entry today?A. Debit Utilities Expense; Credit Accounts PayableB. Debit Cash; Credit Utilities ExpenseC. Debit Accounts Payable; Credit Utilities ExpenseD. No entry until payment is madearrow_forward14. A company receives a bill for electricity to be paid next month. What is the journal entry today?A. Debit Utilities Expense; Credit Accounts PayableB. Debit Cash; Credit Utilities ExpenseC. Debit Accounts Payable; Credit Utilities ExpenseD. No entry until payment is made i need helparrow_forward14. A company receives a bill for electricity to be paid next month. What is the journal entry today?A. Debit Utilities Expense; Credit Accounts PayableB. Debit Cash; Credit Utilities ExpenseC. Debit Accounts Payable; Credit Utilities ExpenseD. No entry until payment is made helparrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning

