
Concept explainers
RECALL Define the following terms: polysaccharide, furanose, pyranose, aldose, ketose, glycosidic bond, oligosaccharide, glycoprotein.
Interpretation:
The given terms are to be defined.
Concept introduction:
A long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds is known as a polysaccharide. A five-membered cyclic ring of sugar is furanose and a six-membered cyclic ring is pyranose. A monosaccharide containing an aldehydic group is called an aldose, and if it contains a ketonic group then it is called a ketose. The hydroxyl
Answer to Problem 1RE
Solution:
Polysaccharide: It is a large molecule made up of a large number of monosaccharides that are bound together with glycosidic linkages.
Pyranose: It is a six-membered cyclic sugar consisting of five carbon atoms along with one oxygen atom.
Furanose: It is a five-membered cyclic sugar consisting of four carbon atoms along with one oxygen atom.
Aldose: It is a monosaccharide (a simple sugar) that contains an aldehydic group
Ketose: It is a monosaccharide (a simple sugar) that contains a ketonic group
Glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage: It is a type of covalent bond that joins one carbohydrate molecule to another carbohydrate molecule.
Oligosaccharide: It is a saccharide polymer that contains a small number of monosaccharides, typically 3–10 monosaccharides molecules.
Glycoproteins: These proteins consist of oligosaccharides that are covalently attached to proteins (or amino acids).
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Polysaccharides, pyranose, furanose, aldose, ketose, glycoside bond, oligosaccharide, and glycoprotein.
Polysaccharide: It is a polymer that consists of a large number of monosaccharides, typically around 20 or more. They are of two types, namely, homopolysaccharides, which consist of a single type of single monosaccharide unit, and heterpolysaccharides, which consist of different monosaccharide units. For example, glycogen, a homopolysacccharide, forms glucose units.
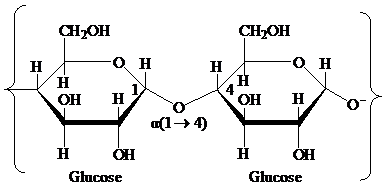
Pyranose: The chemical structure of pyranose contains a six-membered ring, which includes five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. The formation of pyranose takes place by the reaction of alcoholic group of carbon-5 of an open chain with the aldehydic group of carbon-1 of a similar chain.
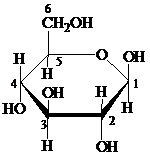
Furanose: The chemical structure of furanose contains a five-membered ring that includes four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. The formation of pyranose takes place by the reaction of alcoholic group of carbon-4 of an open chain with the aldehydic group of carbon-1 of a similar chain.
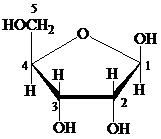
Aldose: This is a class of carbohydrates that has an aldehydic group and is known as polyhydroxy aldehydes. Aldoses are also called reducing sugars for they act as a reducing agent because of the presence of the aldehydic group. They reduce Tollen’s reagent. For example, glucose.
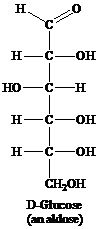
Ketose: This is a class of carbohydrates that have a ketonic group and is also known as polyhydroxy ketones. They are not reducing sugars but they tautomerize themselves to aldoses before acting as a reducing sugar. For example, fructose
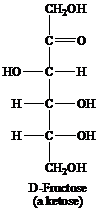
Glycosidic bond: It is a covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate to another carbohydrate or functional group of any other molecule. A substance containing a glycosidic bond is called a glycoside. For example, the glycosidic linkage of two glucose molecules is shown in the following figure:
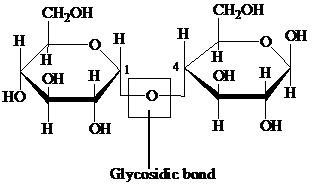
Oligosaccharides: Such carbohydrates contain 3–10 simple sugars that are linked together. They are naturally found in plants and onions. They are soluble fibers and hence easy to digest. Most common examples are sucrose, maltose, and lactose.

Glycoprotein: It is a type of protein that has a carbohydrate attached to it. This carbohydrate is an oligosaccharide that is covalently attach to a polypeptide chain of protein. It is usually found in aloe vera, brown rice, meat, and so on. They play an important function in the reproduction, immune system, hormone balance, and protection of cells.
All the terms have been defined, along with their structures being described.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Biochemistry
- The following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P. Question: Estimate the Vmax and Km. What would be the rate at 2.5 and 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] ?arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardThe following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P Question: what would the rate be at 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] and the enzyme concentration was doubled? Also, the rate given in the table is from product accumulation after 10 minuets of reaction time. Verify these rates represent a true initial rate (less than 5% turnover). Please helparrow_forward
- The following data was obtained on isocitrate lyase from an algal species. Identify the reaction catalyzed by this enzyme, deduce the KM and Vmax , and determine the nature of the inhibition by oxaloacetate. Please helparrow_forwardIn the table below, there are sketches of four crystals made of positively-charged cations and negatively-charged anions. Rank these crystals in decreasing order of stability (or equivalently increasing order of energy). That is, select "1" below the most stable (lowest energy) crystal. Select "2" below the next most stable (next lowest energy) crystal, and so forth. A B 鹽 (Choose one) +2 C +2 +2 (Choose one) D 鹽雞 (Choose one) (Choose one)arrow_forward1. Draw the structures for the fats A. 16:2: w-3 and B. 18:3:49,12,15 2. Name each of the molecules below (image attached)arrow_forward
- draw the structures for the fats A. 16:2:w-3 B 18:3:9,12,15arrow_forward1. Below is a template strand of DNA. Show the mRNA and protein that would result. label the ends of the molecules ( refer to attached image)arrow_forwardAttach the followina labels to the diagram below: helicase, single stranded binding proteins, lagging strand, leading strand, DNA polymerase, primase, 5' ends (3), 3' ends (3) (image attached)arrow_forward
- 1. How much energy in terms of ATP can be obtained from tristearin (stearate is 18:0) Show steps pleasearrow_forwardMultiple choice urgent!!arrow_forward1. Write the transamination reaction for alanine. Indicate what happens next to each of the molecules in the reaction, and under what conditions it happens. 2.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
