
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid is given below.
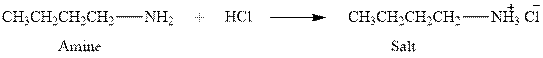
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid gives salt of amine. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the hydrochloric acid. The intermediate then rearranges to give salt of amine.
The complete reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid is given in Figure 1.
Figure 1
The complete reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine and water is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an amine and water is given below.

Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine and water gives ammonium ion and hydroxide ion. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the water. The intermediate then rearranges to give ammonium ion and hydroxide ion.
The complete reaction between an amine and water is given in Figure 2.

Figure 2
The complete reaction between an amine and water is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine and
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is given below.
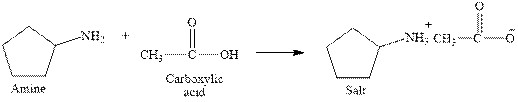
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid gives ammonium salt of carboxylic acid. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the carboxylic acid. The intermediate then rearranges to give ammonium salt of carboxylic acid.
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is given in Figure 3.

Figure 3
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is given below.
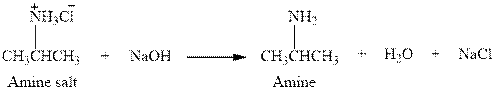
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide gives amine, water and sodium chloride. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of oxygen in sodium hydroxide from the amine salt. The intermediate then rearranges to give amine, water and sodium chloride.
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is given in Figure 4.
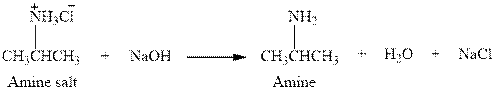
Figure 4
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine gives amide and hydrochloric acid. This happens by the attack of lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine on the carbonyl carbon of acid chloride. The intermediate then rearranges to give amide and hydrochloric acid.
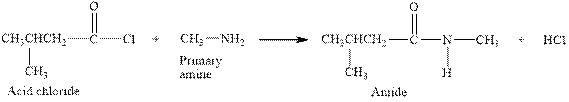
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine is given in Figure 5.

Figure 5
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia is given below.
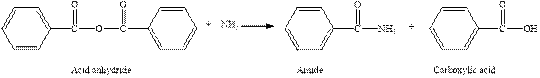
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia gives amide and carboxylic acid. This happens by the attack of lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in ammonia on the carbonyl carbon of acid anhydride. The intermediate then rearranges to give amide and carboxylic acid.
The complete reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia is given in figure 6.
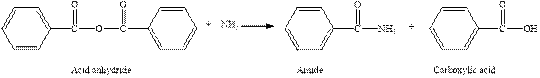
Figure 6
The complete reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia is shown in figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General Organic and Biochemistry
- If the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forwardWhen propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forward
- Does Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forwardExplain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forward
- Indicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forwardIndicate the number of einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy?arrow_forwardA unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forward
- For the condensation reaction between Alanine and histidine write the amididation reaction mechanism using arrows then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction and the one letter code for the product of the reaction.arrow_forwardWrite the amididation reaction mechanism of p-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophen please use arrows.arrow_forwardName the following using IUPAC.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





