
The structure stiffness matrix for the frame.
Answer to Problem 16.1P
The structure stiffness matrix for the frame is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Concept Used:
Write the expression for direction cosine in x-direction.
Here, coordinate of x at near end of the member is
Write the expression for direction cosine in x-direction.
Here, coordinate of y at near end of the member is
Write the global stiffness matrix for the member.
Here, cross-sectional area of the member is
Calculation:
The free body diagram of the frame is shown below.
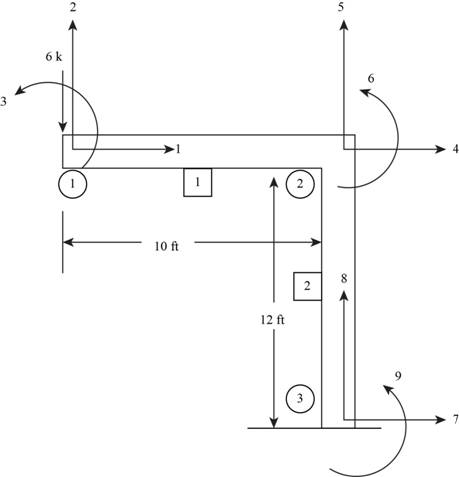
Figure (1)
Consider the member-1.
Calculate direction cosine in x-direction.
Substitute
Calculate direction cosine in y-direction.
Substitute
The stiffness matrix for member-1 is shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Substitute
Consider the member-2.
Calculate direction cosine in x-direction.
Substitute
Calculate direction cosine in y-direction.
Substitute
The stiffness matrix for member-1 is shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Calculate the value of
Substitute
Substitute
The final matrix of the frame by assembling matrices (III) and (IV) is shown below.
Conclusion:
The structure stiffness matrix for the frame is shown below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the slope deflection method, draw the resulting shear force diagran and bending moment diagram. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m, L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200 GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardProblem 2 (A is fixed and C is a pin) Find the reactions and A and C. 10 k- 6 ft 6 ft B A 2 k/ft 15 ftarrow_forward6. A lake with no outlet is fed by a river with a constant flow of 1200 ft3/s. Water evaporates from the surface at a constant rate of 13 ft3/s per square mile of surface area. The surface area varies with the depth h (in feet) as A (square miles) = 4.5 + 5.5h. What is the equilibrium depth of the lake? Below what river discharge (volume flow rate) will the lake dry up?arrow_forward
- Problem 5 (A, B, C and D are fixed). Find the reactions at A and D 8 k B 15 ft A -20 ft C 10 ft Darrow_forwardProblem 4 (A, B, E, D and F are all pin connected and C is fixed) Find the reactions at A, D and F 8 m B 6m E 12 kN D F 4 marrow_forwardProblem 1 (A, C and D are pins) Find the reactions and A, C and D. D 6 m B 12 kN/m 8 m A C 6 marrow_forward
- Uniform Grade of Pipe Station of Point A is 9+50.00. Elevation Point A = 250.75.Station of Point B is 13+75.00. Elevation Point B = 244.10 1) Calculate flowline of pipe elevations at every 50 ft. interval (Half Station). 2) Tabulate station and elevation for each station like shown on example 3) Draw Sketcharrow_forward40m 150N B 40marrow_forwardquantity surveyingarrow_forward
- Quantity Surveyingarrow_forwardquantity surveyingarrow_forwardNote: Please accurately answer it!. I'll give it a thumbs up or down based on the answer quality and precision. Question: What is the group name of Sample B in problem 3 from the image?. By also using the ASTM flow chart!. This unit is soil mechanics btwarrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





