
a)
To find:
Individual’s full income, number of working hours if 75% income is devoted to leisure.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Total number of working hours = 8000
Wage per hour = $5
Total income annually :
Amount sacrificed for leisure = $5
Amount to be spent on leisure :
Number of hours for leisure:
Number of working hours= Total hours − Leisure Time
Total working hours is 2000.
Introduction: Envelop theorem states that changes in exogeneous variables must be considered for profit maximizing equations, ignoring the change in endogeneous variable.
b)
To know:
Number of working hours if 75% income is devoted to leisure when rich uncle dies
b)
Explanation of Solution
An annual income, which is left by a rich uncle = $4000
Labor income:
Total number of working hours = 8000
Wage per hour = $5
Labor income annually :
Total income :
Amount spent on leisure:
Therefore, number of leisure hours :
So, Work = Total time − Leisure time
Introduction: Envelop theorem states that changes in exogeneous variables must be considered for profit maximizing equations, ignoring the change in endogeneous variable.
c)
To ascertain:
Number of working hours if 75% income is devoted to leisure when hourly wage is $10.
c)
Explanation of Solution
New wage rate = $10
Non labor income = $4000
Total annual earned income:
Total income:
Amount spent on leisure:
Therefore, time spent on leisure:
So, work = Total time − Leisure time
Introduction: Envelop theorem states that changes in exogeneous variables must be considered for profit maximizing equations, ignoring the change in endogeneous variable.
d)
To Plot:
Graphical representation of supply labor curve..
d)
Explanation of Solution
The supply curve is shown below in the graph:
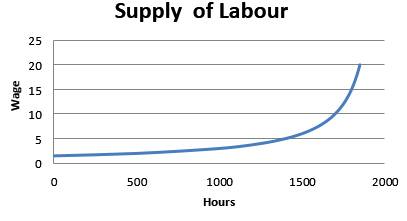
When the wage rate is $5 per hour, number of working hours is S1500
When the wage rate is $10 per hour, number of working hours is 1650.
Introduction: Envelop theorem states that changes in exogeneous variables must be considered for profit maximizing equations, ignoring the change in endogeneous variable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Bundle: Microeconomic Theory: Basic Principles and Extensions, 12th + MindTap Economics, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- how commond economies relate to principle Of Economics ?arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forward
- Outline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forward
 Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





