To plot:
The graph of elastic modulus versus the volume percent of tungsten (WC) using upper–and lower–bound expressions.
Answer to Problem 1QP
The graph of elastic modulus versus the volume fraction of tungsten
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The modulus of elasticity of cobalt
The modulus of elasticity of tungsten
Explanation:
Write the expression for upper–bound modulus of elasticity.
Write the expression for lower–bound modulus of elasticity.
Here,
Conclusion:
Calculate the upper–bound modulus of elasticity.
When, the volume fraction of cobalt is,
Substitute 200 GPa for
When, the volume fraction of cobalt is,
Substitute 200 GPa for
Similarly, the upper–bound modulus of elasticity for different volume fractions are calculated and shown in Table 1.
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 100 | 700 |
| 10 | 90 | 650 |
| 20 | 80 | 600 |
| 30 | 70 | 550 |
| 40 | 60 | 500 |
| 50 | 50 | 450 |
| 60 | 40 | 400 |
| 70 | 30 | 350 |
| 80 | 20 | 300 |
| 90 | 10 | 250 |
| 100 | 0 | 200 |
Table 1
Calculate the lower–bound modulus of elasticity.
When, the volume fraction of cobalt is,
Substitute 200 GPa for
When, the volume fraction of cobalt is,
Substitute 200 GPa for
Similarly, the lower–bound modulus of elasticity for different volume fractions are calculated and shown in Table 2.
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 100 | 700 |
| 10 | 90 | 560 |
| 20 | 80 | 466.67 |
| 30 | 70 | 400 |
| 40 | 60 | 350 |
| 50 | 50 | 311.11 |
| 60 | 40 | 280 |
| 70 | 30 | 254.55 |
| 80 | 20 | 233.33 |
| 90 | 10 | 215.38 |
| 100 | 0 | 200 |
Table 2
Refer Table 1 and Table 2.
Take the volume fraction of tungsten
Plot the graph of elastic modulus versus the volume fraction of tungsten
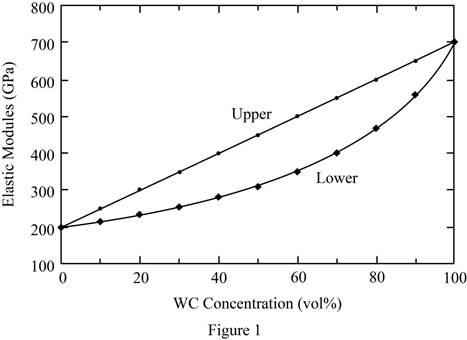
Thus, the graph of elastic modulus versus the volume fraction of tungsten
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering, Binder Ready Version: An Integrated Approach
- 2. Design a trapezoidal ditch to carry Q = 1000 cfs. The ditch will be a lined channel, gravel bottom with sides shown below on a slope of S = 0.009. The side slopes of the 20-ft wide ditch will be 1 vertical to 3 horizontal. a) Determine the normal depth of flow (yn) using the Normal value for Manning's n. b) If freeboard requirements are 25% of the normal depth, how deep should the ditch be constructed? c) Classify the slope. T b Уп Z 1 Yn + FBarrow_forward← Homework 8 View Policies Show Attempt History Current Attempt in Progress A liquid mixture of benzene and toluene containing 52.0 wt% benzene at 100.0 °C and pressure Po atm is fed at a rate of 32.5 m³/h into a heated flash tank maintained at a pressure Ptank Material Balances Correct. 0.67/1 === Attempts: 1 of 5 used Calculate Ptank (atm), the mole fraction of benzene in the vapor, and the molar flow rates of the liquid and vapor products. Ptank .544 atm Ybz .657 mol benzene/mol vapor product nvapor 55.8 mol/s nliquid 37.6 mol/s Hint GO Tutorial Energy Balance Check heat capacities. Calculate the required heat input rate in kilowatts. i 0.447 kW Hint GO Tutorial Save for Later Assistance Used Attempts: 2 of 5 used Assistance Used Attempts: 1 of 5 used Submit Answerarrow_forwardView Policies Show Attempt History Current Attempt in Progress Homework 8 A stream of pure cyclopentane vapor flowing at a rate of 1650 L/s at 190.0°C and 1 atm enters a cooler in which 50.0% of the feed is condensed at constant pressure. Question 4 of 5 Correct What is the temperature at the condenser outlet? 49.3 °℃ eTextbook and Media Hint Enthalpy Table Your Answer Correct Answer (Used) 0.67/1 E Attempts: 1 of 5 used Prepare and fill in an inlet-outlet enthalpy table. Use a reference state of liquid cyclopentane at the boiling point. In T = 190.0°C Out T=49.3°C Substance n (mol/s) Ĥ (kJ/mol) n (mol/s) Ĥ (kJ/mol) C5H10(1) 0.0 21.708 0.0 C5H10(V) 43.416 43.687 21.708 27.30 Heat Check significant figures and sign. Calculate the required cooling rate (a positive number). ! kW Hint Save for Later Attempts: 3 of 5 used Submit Answerarrow_forward
- View Policies Show Attempt History Current Attempt in Progress A liquid mixture of benzene and toluene containing 52.0 wt% benzene at 100.0 °C and pressure Po atm is fed at a rate of 32.5 m³/h into a heated flash tank maintained at a pressure Ptank Your answer is partially correct. 1.312 atm Assistance Used 0.58/1 Calculate Ptank (atm), the mole fraction of benzene in the vapor, and the molar flow rates of the liquid and vapor products. Ptank i atm .657 Ybz mol benzene/mol vapor product nvapor 55.8 mol/s nliquid 37.6 mol/s Hint GO Tutorial Save for Later Energy Balance Calculate the required heat input rate in kilowatts. i kW GO Tutorial Save for Later Assistance Used Attempts: 1 of 5 used Submit Answer Assistance Used Attempts: 0 of 5 used Submit Answerarrow_forward340 lb 340 lb Δarrow_forwardView Policies Show Attempt History Current Attempt in Progress Saturated steam at 342.1°C is used to heat a countercurrently flowing stream of methanol vapor from 70.0°C to 321.7°C in an adiabatic heat exchanger. The flow rate of the methanol is 5530 standard liters per minute, and the steam condenses and leaves the heat exchanger as liquid water at 95.0°C. Physical Property Tables Entering Steam Homework 8 Question 3 of 5 Check unit conversions. Calculate the required flow rate of the entering steam in m³/min. 0.0165 m³/min eTextbook and Media Hint Save for Later Heat Transferred * Check units and significant figures. Calculate the rate of heat transfer from the water to the methanol (kW). i 58.7 kW Hint Save for Later 0/1 EE Attempts: 1 of 5 used Submit Answer Attempts: 1 of 5 used Submit Answerarrow_forward
- P15.45 WP A stainless steel pipe (Figure P15.45) with an outside diameter of 2.375 in. and a wall thickness of 0.109 in. is subjected to a bending moment M = 50 lb ft and an internal pressure of 180 psi. Determine the absolute maximum shear stress on the outer surface of the pipe. M FIGURE P15.45 Marrow_forward10.72 What power must the pump supply to the system to pump the oil from the lower reservoir to the upper reservoir at a rate of 0.3 m³/s? Sketch the HGL and the EGL for the system. p=940 kg/m³ v = 10-5 m²/s Elevation 100 m Elevation 112 m L= 150 m Oil Steel pipe D = 30 cm Problem 10.72arrow_forwardL / 83° 28° $75°E M 202° Q2: The scanning process was completed from point J to point N. The direction of the straight line was LM and the angles of deviation are shown in the figure below. Find the direction of the remaining sides? Narrow_forward
- Q3: The scanning process was completed from point F to point G. The direction of the line Fl and the angles of deviation and interior are shown in the figure below. Find the direction of the remaining sides? Azimn = 60° F 52° 52° 72° R= 572.958/D ° T-R tan(A/2) • LC 2R sin (A/2) • E-R (sec(A/2)-1) • M-R (1-cos (A/2)) L= 10 A/D •C=2R sin(2D/2) • d=Dc/10 c' 2R sin (d/2) • Y= √√R2-X2-K • K= R2- K=R-M G H معادلات :مفيدةarrow_forwardPlease write me Background Reviews;arrow_forward4. In a table of vector differential operators, look up the expressions for V x V in a cylindrical coordinate system. (a) Compute the vorticity for the flow in a round tube where the velocity profile is = vo [1-(³] V₂ = Vo (b) Compute the vorticity for an ideal vortex where the velocity is Ve= r where constant. 2πг (c) Compute the vorticity in the vortex flow given by Ve= r 2лг 1- exp ( r² 4vt (d) Sketch all the velocity and vorticity profiles.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





