
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 76E
Methyl red has the following structure:
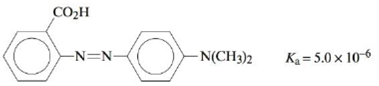
It undergoes a color change from red to yellow as a solution gets more basic. Calculate an approximate pH range for which methyl red is useful. What is the color change and the pH at the color change when a weak acid is titrated with a strong base using methyl red as an indicator? What is the color change and the pH at the color change when a weak base is titrated with a strong acid using methyl red as an indicator? For which of these two types of titrations is methyl red a possible indicator?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
The following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method:
Regular Tomato Sauce
Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce
340.0
262.7
QUESTION: For both groups of data provide answers to the calculations attached in the image
7. Concentration and uncertainty in the estimate of concentration (class data)
Class mean for sample (Regular)
|[Cl-] (mmol/L) class mean
Sn
za/2
95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L)
[Na+] (mg/100 mL)
95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)
The following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method:
Regular Tomato Sauce
Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce
223.4
148.7
353.7
278.2
334.6
268.7
305.6
234.4
340.0
262.7
304.3
283.2
244.7
143.6
QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.
Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemistry
Ch. 15 - What is meant by the presence of a common ion? How...Ch. 15 - Define a buffer solution. What makes up a buffer...Ch. 15 - One of the most challenging parts of solving...Ch. 15 - A good buffer generally contains relatively equal...Ch. 15 - Draw the general titration curve for a strong acid...Ch. 15 - Instead of the titration of a strong acid by a...Ch. 15 - Sketch the titration curve for a weak acid...Ch. 15 - Sketch the titration curve for a weak base...Ch. 15 - What is an acidbase indicator? Define the...Ch. 15 - Why does an indicator change from its acid color...
Ch. 15 - What are the major species in solution after...Ch. 15 - A friend asks the following: Consider a buffered...Ch. 15 - Mixing together solutions of acetic acid and...Ch. 15 - Sketch two pH curves, one for the titration of a...Ch. 15 - Sketch a pH curve for the titration of a weak acid...Ch. 15 - You have a solution of the weak acid HA and add...Ch. 15 - You have a solution of the weak acid HA and add...Ch. 15 - The common ion effect for weak acids is to...Ch. 15 - Prob. 12QCh. 15 - A best buffer has about equal quantities of weak...Ch. 15 - Consider the following pH curves for 100.0 mL of...Ch. 15 - An acid is titrated with NaOH. The following...Ch. 15 - Consider the following four titrations. i. 100.0...Ch. 15 - Figure 14-4 shows the pH curves for the titrations...Ch. 15 - Acidbase indicators mark the end point of...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.10 M...Ch. 15 - Consider the following two acids: pKa1 = 2.98;...Ch. 15 - How many of the following are buffered solutions?...Ch. 15 - Which of the following can be classified as buffer...Ch. 15 - A certain buffer is made by dissolving NaHCO3 and...Ch. 15 - A buffer is prepared by dissolving HONH2 and...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following...Ch. 15 - Compare the percent dissociation of the acid in...Ch. 15 - Compare the percent ionization of the base in...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of HCl is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of HCl is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of NaOH is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.020 mole of NaOH is added...Ch. 15 - Which of the solutions in Exercise 21 shows the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 34ECh. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 1.00 M HNO2...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.60 M HF...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.10 mole of NaOH is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.10 mole of NaOH is added...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following buffered...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following buffered...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a buffered solution prepared...Ch. 15 - A buffered solution is made by adding 50.0 g NH4Cl...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.010 mole of gaseous HCl...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH after 0.15 mole of solid NaOH is...Ch. 15 - Some K2SO3 and KHSO3 are dissolved in 250.0 mL of...Ch. 15 - An aqueous solution contains dissolved C6H5NH3Cl...Ch. 15 - Calculate the mass of sodium acetate that must be...Ch. 15 - What volumes of 0.50 M HNO2 and 0.50 M NaNO2 must...Ch. 15 - Consider a solution that contains both C5H5N and...Ch. 15 - Calculate the ratio [NH3]/[NH4+] in...Ch. 15 - Carbonate buffers are important in regulating the...Ch. 15 - When a person exercises, muscle contractions...Ch. 15 - Consider the acids in Table 13-2. Which acid would...Ch. 15 - Consider the bases in Table 13-3. Which base would...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.40 M...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.20 M HOCl...Ch. 15 - Which of the following mixtures would result in...Ch. 15 - Which of the following mixtures would result in a...Ch. 15 - What quantity (moles) of NaOH must be added to 1.0...Ch. 15 - Calculate the number of moles of HCl(g) that must...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of a generic weak acid HA...Ch. 15 - Sketch the titration curve for the titration of a...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 40.0 mL of 0.200 M HClO4...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 80.0 mL of 0.100 M...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.200 M...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.100 M...Ch. 15 - Lactic acid is a common by-product of cellular...Ch. 15 - Repeat the procedure in Exercise 61, but for the...Ch. 15 - Repeat the procedure in Exercise 61, but for the...Ch. 15 - Repeat the procedure in Exercise 61, but for the...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH at the halfway point and at the...Ch. 15 - In the titration of 50.0 mL of 1.0 M methylamine,...Ch. 15 - You have 75.0 mL of 0.10 M HA. After adding 30.0...Ch. 15 - A student dissolves 0.0100 mole of an unknown weak...Ch. 15 - Two drops of indicator HIn (Ka = 1.0 109), where...Ch. 15 - Methyl red has the following structure: It...Ch. 15 - Potassium hydrogen phthalate, known as KHP (molar...Ch. 15 - A certain indicator HIn has a pKa of 3.00 and a...Ch. 15 - Which of the indicators in Fig. 14-8 could be used...Ch. 15 - Prob. 80ECh. 15 - Which of the indicators in Fig. 14-8 could be used...Ch. 15 - Prob. 82ECh. 15 - Estimate the pH of a solution in which bromcresol...Ch. 15 - Estimate the pH of a solution in which crystal...Ch. 15 - A solution has a pH of 7.0. What would be the...Ch. 15 - A solution has a pH of 4.5. What would be the...Ch. 15 - When a diprotic acid, H2A. is titrated with NaOH,...Ch. 15 - Consider die titration of 50.0 mL of 0.10 M H3A...Ch. 15 - Derive an equation analogous to the...Ch. 15 - a. Calculate the pH of a buffered solution that is...Ch. 15 - Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, commonly called...Ch. 15 - You make 1.00 L of a buffered solution (pH = 4.00)...Ch. 15 - You have the following reagents on hand: Solids...Ch. 15 - Prob. 94AECh. 15 - Phosphate buffers are important in regulating the...Ch. 15 - When a diprotic acid, H2A, is titrated with NaOH,...Ch. 15 - Consider the blood buffer system discussed in the...Ch. 15 - What quantity (moles) of HCl(g) must be added to...Ch. 15 - Prob. 99AECh. 15 - The following plot shows the pH curves for the...Ch. 15 - Calculate the volume of 1.50 102 M NaOH that must...Ch. 15 - Prob. 102AECh. 15 - A certain acetic acid solution has pH = 2.68....Ch. 15 - A 0.210-g sample of an acid (molar mass = 192...Ch. 15 - The active ingredient in aspirin is...Ch. 15 - One method for determining the purity of aspirin...Ch. 15 - A student intends to titrate a solution of a weak...Ch. 15 - A student titrates an unknown weak acid, HA, to a...Ch. 15 - A sample of a certain monoprotic weak acid was...Ch. 15 - The pigment cyanidin aglycone is one of the...Ch. 15 - Consider 1.0 L of a solution that is 0.85 M HOC6H5...Ch. 15 - What concentration of NH4Cl is necessary to buffer...Ch. 15 - Consider the following acids and bases: HCO2H Ka =...Ch. 15 - Consider a buffered solution containing CH3NH3Cl...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 150.0 mL of 0.100 M HI...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.100 M HCN...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.200 M...Ch. 15 - Consider the following four titrations (iiv): i....Ch. 15 - Another way to treat data from a pH titration is...Ch. 15 - A buffer is made using 45.0 mL of 0.750 M HC3H5O2...Ch. 15 - A 0.400-M solution of ammonia was titrated with...Ch. 15 - What volume of 0.0100 M NaOH must be added to 1.00...Ch. 15 - Consider a solution formed by mixing 50.0 mL of...Ch. 15 - Cacodylic acid, (CH3)2AsO2H, is a toxic compound...Ch. 15 - The titration of Na2CO3 with HCl bas the following...Ch. 15 - Consider the titration curve in Exercise 115 for...Ch. 15 - A few drops of each of the indicators shown in the...Ch. 15 - Malonic acid (HO2CCH2CO2H) is a diprotic acid. In...Ch. 15 - A buffer solution is prepared by mixing 75.0 mL of...Ch. 15 - A 10.00-g sample of the ionic compound NaA, where...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution prepared by mixing...Ch. 15 - Consider a solution prepared by mixing the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Why is it unlikely that two neighboring water molecules would be arranged like this?
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Gregor Mendel never saw a gene, yet he concluded that some inherited factors were responsible for the patterns ...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
To test your knowledge, discuss the following topics with a study partner or in writing ideally from memory. Th...
HUMAN ANATOMY
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Why do scientists think that all forms of life on earth have a common origin?
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Give reason(s) for six from the followings [using equations if possible] a. Addition of sodium carbonate to sulfanilic acid in the Methyl Orange preparation. b. What happened if the diazotization reaction gets warmed up by mistake. c. Addition of sodium nitrite in acidified solution in MO preparation through the diazotization d. Using sodium dithionite dihydrate in the second step for Luminol preparation. e. In nitroaniline preparation, addition of the acid mixture (nitric acid and sulfuric acid) to the product of step I. f. What is the main reason of the acylation step in nitroaniline preparation g. Heating under reflux. h. Fusion of an organic compound with sodium. HAND WRITTEN PLEASEarrow_forwardedict the major products of the following organic reaction: u A + ? CN Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te LMUNDARYarrow_forwardSketch the intermediates for A,B,C & D.arrow_forward
- Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? O ? A . If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ㅇ 80 F5 F6 A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente FIGarrow_forwardIn methyl orange preparation, if the reaction started with 0.5 mole of sulfanilic acid to form the diazonium salt of this compound and then it converted to methyl orange [0.2 mole]. If the efficiency of the second step was 50%, Calculate: A. Equation(s) of Methyl Orange synthesis: Diazotization and coupling reactions. B. How much diazonium salt was formed in this reaction? C. The efficiency percentage of the diazotization reaction D. Efficiency percentage of the whole reaction.arrow_forwardHand written equations pleasearrow_forward
- Hand written equations pleasearrow_forward> each pair of substrates below, choose the one that will react faster in a substitution reaction, assuming that: 1. the rate of substitution doesn't depend on nucleophile concentration and 2. the products are a roughly 50/50 mixture of enantiomers. Substrate A Substrate B Faster Rate X Ś CI (Choose one) (Choose one) CI Br Explanation Check Br (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Farrow_forwardNMR spectrum of ethyl acetate has signals whose chemical shifts are indicated below. Which hydrogen or set of hydrogens corresponds to the signal at 4.1 ppm? Select the single best answer. The H O HỌC—C—0—CH, CH, 2 A ethyl acetate H NMR: 1.3 ppm, 2.0 ppm, 4.1 ppm Check OA B OC ch B C Save For Later Submit Ass © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center |arrow_forward
- How many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. O ✓ No additional Hs to color in top molecule ง No additional Hs to color in bottom…arrow_forwardin the kinetics experiment, what were the values calculated? Select all that apply.a) equilibrium constantb) pHc) order of reactiond) rate contstantarrow_forwardtrue or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemical Principles in the LaboratoryChemistryISBN:9781305264434Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert RossiPublisher:Brooks Cole
Chemical Principles in the LaboratoryChemistryISBN:9781305264434Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert RossiPublisher:Brooks Cole Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305264434
Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:Brooks Cole

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry | Acids & Bases; Author: Ninja Nerd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AOr_5tbgfQ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY