
Concept explainers
a.
Check whether people can conclude that less than 40% of the districts buses are old.
Find the p-value.
a.
Answer to Problem 64DA
Yes, people cannot conclude that less than 40% of the districts buses are old.
The p-value is 0.181.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
In this case, the test is to check whether less than 40% of the districts buses are old.
Let
From the data, it can be observed that the number of old buses is 28 out of 80.
The level of significance is 0.01.
Therefore, the value of z score using the table B.3: Areas under the normal curve is –2.33.
Decision rule:
Reject the null hypothesis if z < –2.326.
The
Step-by-step procedure to find the test statistic using MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 1 Proportion.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In Number of
events , enter 28. In Number of trials, enter 80. - Enter Hypothesized proportion as 0.40.
- Check Options, enter Confidence level as 99.0.
- Choose greater than in alternative.
- Select Method as Normal approximation.
- Click OK in all dialogue boxes.
Output is obtained as follows:
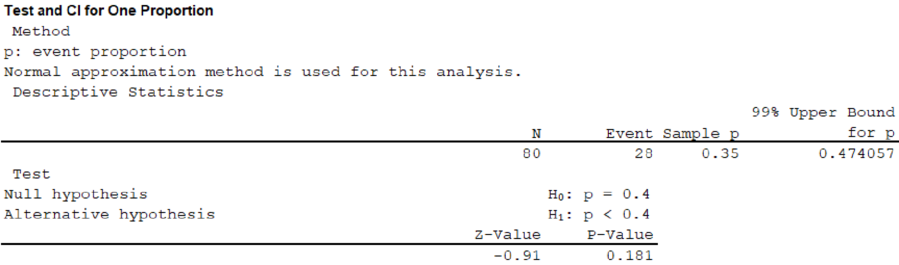
Thus, the value of the test statistic is –0.91 and the p-value is 0.181.
In this case, the critical value is –2.33 and the test statistic is –0.91.
Here, the test statistic –0.91 is greater than the critical value –2.33.
That is, –0.91 > –2.33.
Therefore, do not reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, people cannot conclude that less than 40% of the districts buses are old.
b.
Find the
Check whether the age of the bus is related to the amount of the maintenance cost.
b.
Answer to Problem 64DA
The median maintenance cost and the median age of the buses are $4,179 and 7.00, respectively.
Yes, the age of the bus is related to the amount of the maintenance cost.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
In this case, the test is to check whether the age of the bus is related to the amount of the maintenance cost.
Step-by-step procedure to find the median for age of the bus and maintenance cost using MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display
Descriptive Statistics . - In Variables enter the columns Age and Maintenance cost.
- Choose option statistics, and select Median.
- Click OK.
Output using MINITAB software is obtained as follows:

From the output, the median maintenance cost and the median age of the buses are $4,179 and 7.00, respectively.
Using the given conditions, the
| High Maintenance | Age | ||
| Lower half | Top half | Total | |
| No | 33 | 7 | 40 |
| Yes | 9 | 31 | 40 |
| Total | 42 | 38 | 80 |
The number of degrees of freedom is obtained as follows:
Therefore, the number of degrees of freedom is 1.
Step-by-step procedure to find the critical value using MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot > View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Chi-Square’ distribution.
- Enter Degrees of freedom is 1.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability and Right Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the data value as 0.01.
- Click OK.
Output using MINITAB software is obtained as follows:
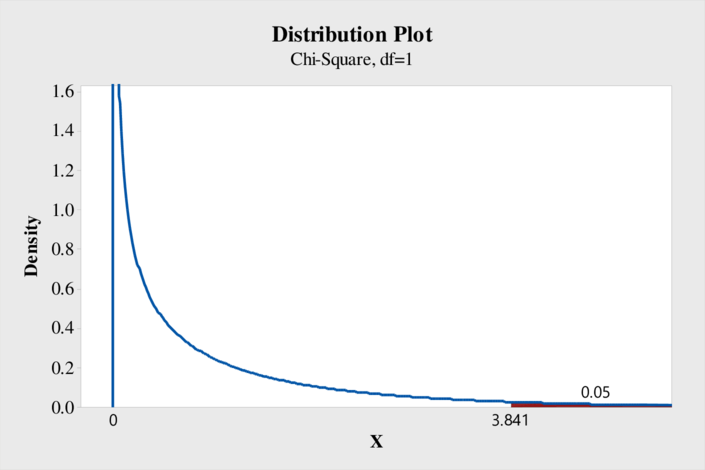
From the output, the critical value of chi-square is 3.841.
The general decision rule is reject the null hypothesis if
Therefore, the decision rule is reject the null hypothesis if
Test statistic:
Step-by-step procedure to find the test statistic using MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Tables > Chi-Square Test for Association.
- Choose Summarized data in a two-way table.
- In Columns containing the table, enter the columns of Lower half and Top half.
- In Rows under Labels for the table, enter the column of High Maintenance.
- Click OK.
Output is obtained as follows:
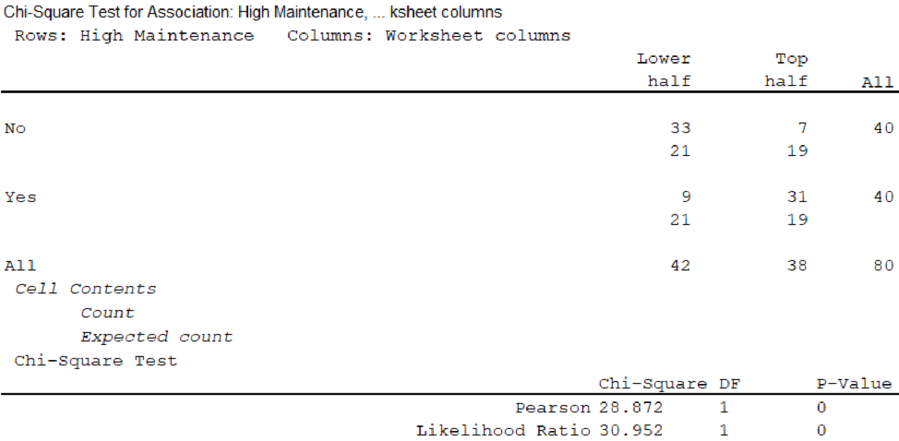
From the output, the test statistic is 28.872.
The critical value is 3.84.
Here, the test statistic is greater than the critical value.
That is, 28.872 > 3.84.
Thus, reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that age of the bus is related to the amount of the maintenance cost.
c.
Check whether there is a relationship between the maintenance cost and the manufacturer of the bus.
c.
Answer to Problem 64DA
No, there is no relationship between the maintenance cost and the manufacturer of the bus.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
In this case, the test is to check whether there is a relationship between the maintenance cost and the manufacturer of the bus.
Using the given conditions, the contingency table for the maintenance cost and manufacturer of the bus is obtained as follows:
| High Maintenance | Manufacturer of the bus | |||
| Bluebird | Keiser | Thompson | Total | |
| No | 25 | 13 | 2 | 40 |
| Yes | 22 | 12 | 6 | 40 |
| Total | 47 | 25 | 8 | 80 |
The number of degrees of freedom is obtained as follows:
Therefore, the number of degrees of freedom is 2.
Step-by-step procedure to find the critical value using MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot > View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Chi-Square’ distribution.
- Enter Degrees of freedom is 1.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability and Right Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the data value as 0.05.
- Click OK.
Output using MINITAB software is obtained as follows:
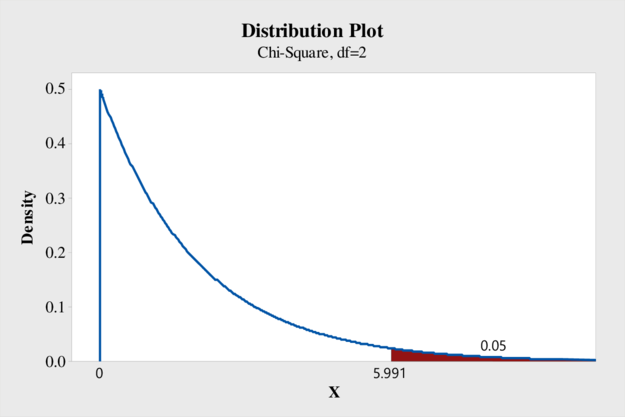
From the output, the critical value of chi-square is 5.991.
The general decision rule is reject the null hypothesis if
Therefore, the decision rule is reject the null hypothesis if
Test statistic:
Step-by-step procedure to find the test statistic using MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Tables > Chi-Square Test for Association.
- Choose Summarized data in a two-way table.
- In Columns containing the table, enter the columns of Lower half and Top half.
- In Rows under Labels for the table, enter the column of High Maintenance.
- Click OK.
Output is obtained as follows:
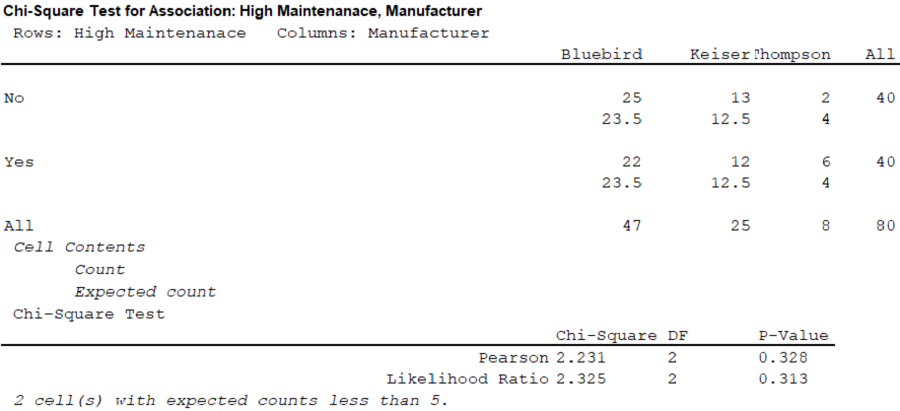
From the output, the test statistic is 2.231.
The critical value is 5.991.
Here, the test statistic is less than the critical value.
That is, 2.231 > 5.991.
Thus, do not reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, there is no sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a relationship between the maintenance cost and the manufacturer of the bus.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
- Find the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardShow all workarrow_forward
- Show all workarrow_forwardplease find the answers for the yellows boxes using the information and the picture belowarrow_forwardA marketing agency wants to determine whether different advertising platforms generate significantly different levels of customer engagement. The agency measures the average number of daily clicks on ads for three platforms: Social Media, Search Engines, and Email Campaigns. The agency collects data on daily clicks for each platform over a 10-day period and wants to test whether there is a statistically significant difference in the mean number of daily clicks among these platforms. Conduct ANOVA test. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: also please provide a step by on getting the answers in excel Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value.arrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


