
(a)
Interpretation:
The statement “Aniline is an
(a)
Answer to Problem 5MCP
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine with the formula
(b)
Interpretation:
The statement “Aniline has a lower boiling point than benzoic acid” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5MCP
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Aniline is an amine and benzoic acid is
The ability of primary and secondary amines to form
(c)
Interpretation:
The statement “Aniline is planar molecule” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5MCP
The given statement is false because it is slightly pyramidalized molecule.
Explanation of Solution
Aniline is slightly pyramidalized molecule, with hybridization of the nitrogen between
Hence, the given statement is false.
(d)
Interpretation:
The statement “The molecular formula of aniline is
(d)
Answer to Problem 5MCP
The given statement is false because the molecular formula of aniline is
Explanation of Solution
Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine with the formula
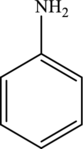
Hence, the statement “Aniline has a molecular formula of
(e)
Interpretation:
The statement “Aniline is a structural isomer of xylene” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(e)
Answer to Problem 5MCP
The given statement is false because both aniline and xylene have different molecular formulas.
Explanation of Solution
Structural isomers are those with same molecular formula but differ in arrangement of atoms.
The molecular formula of aniline is
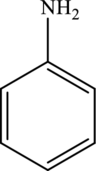
The molecular formula of xylene is
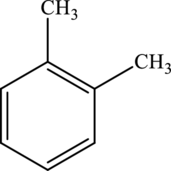
Both these are not structural isomers with each other.
Hence, the statement “aniline is structural isomer of xylene” is false because they have different molecular formulas.
(f)
Interpretation:
The statement “Aniline is more soluble than phenol” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(f)
Answer to Problem 5MCP
The given statement is false because both aniline and phenol are sparingly soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
Aniline does not form hydrogen bonds with water to a very large extent due to the presence of large hydrophobic
The hydroxyl group of phenol is polar in nature, the oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, and hence it attracts shared electrons and acquires partial negative charge. The hydrogen of hydroxyl group in phenol carries partial negative charge. Phenol forms hydrogen bonding with water. However, the large part of phenol molecule is phenyl group is non-polar, thus making it sparingly soluble in water.
Hence, the given statement is false because both aniline and phenol are sparingly soluble in water.
(g)
Interpretation:
The statement “Aniline produces phenylammonium ion in water” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(g)
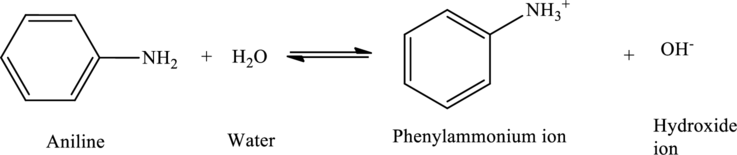
Answer to Problem 5MCP
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Aniline acts as bases, accepting
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC+BIOCHEM (LOOSELEAF)
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forwardUse the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forward
- What is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





