
Glacier Products Inc. is a wholesaler of rock climbing gear. The company began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to securities acquired by Glacier Products Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
- 1.
Journalize the entries to record the preceding transactions. - 2. Prepare the investment-related asset and stockholders’ equity
balance sheet presentation for Glacier Products Inc. on December 31, Year 2, assuming that theRetained Earnings balance on December 31, Year 2, is $700,000.
(1)
Journalize the stock investment transactions for Company G.
Explanation of Solution
Equity investments: Equity investments are stock instruments which claim ownership in the investee company and pay a dividend revenue to the investor company.
Equity method: Equity method is the method used for accounting equity investments which claim a significant influence of above 20% but less than 50% in the outstanding stock of the investee company.
Available-for-sale securities: These are short-term or long-term investments in debt and equity securities with an intention of holding the investment for some strategic purposes like meeting liquidity needs, or manage interest risk.
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 9,000 shares of Company M, at $40 per share.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| January | 18 | Investments–Company M Stock | 360,000 | ||
| Cash | 360,000 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (1)
- Investments–Company M Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company M for 9,000 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| July | 22 | Cash | 27,000 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 27,000 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (2)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for sale of 500 shares of Company M, at $58, with a brokerage of $100.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| October | 5 | Cash | 28,900 | ||
| Gain on Sale of Investments | 8,900 | ||||
| Investments–Company M Stock | 20,000 | ||||
| (To record sale of shares) | |||||
Table (3)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Gain on Sale of Investments is an expense account. Since expenses and losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Investments–Company M Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are sold, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Calculate the realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Step 1: Compute cash received from sale proceeds.
Step 2: Compute cost of stock investment sold.
Step 3: Compute realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Note: Refer to Steps 1 and 2 for value and computation of cash received and cost of stock investment sold.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company M for 8,500 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| December | 18 | Cash | 25,500 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 25,500 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company M’s stock.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of available-for-sale securities transaction.
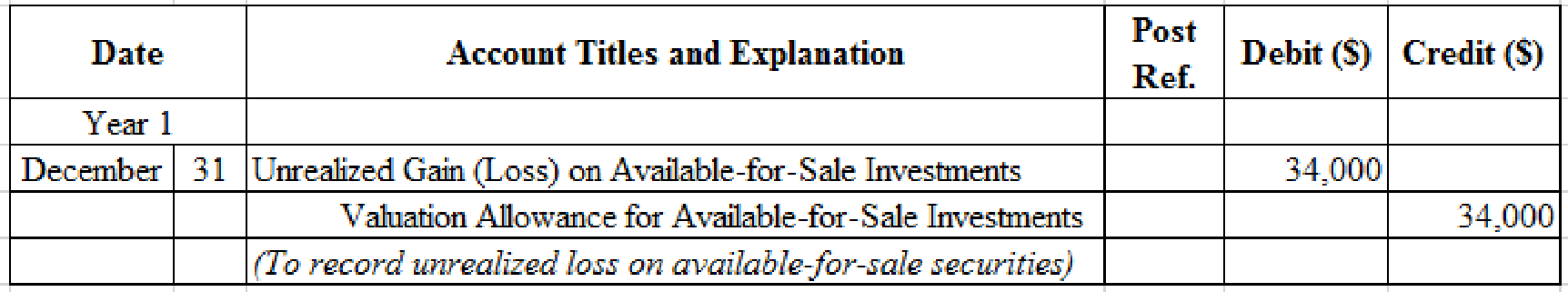
Table (5)
- Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Available-for-Sale Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since loss has occurred and losses reduce stockholders’ equity value, and a decrease in stockholders’ equity value is debited.
- Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is credited because the market price was decreased (loss) to $306,000 from the cost of $340,000.
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31, Year 1.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Available-for-sale investments at fair value, December 31, | $306,000 |
| Less: Available-for-sale investments at cost, December 31, | (340,000) |
| Unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale investments | $(34,000) |
Table (6)
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 75,000 shares out of the outstanding stock of 250,000 shares of Company H at $800,000.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| January | 25 | Investment in Company H Stock | 800,000 | ||
| Cash | 800,000 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares of Company H for cash) | |||||
Table (7)
- Investment in Company H Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company M for 8,500 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| July | 16 | Cash | 25,500 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 25,500 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (8)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company M for 8,500 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| December | 16 | Cash | 27,200 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 27,200 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (9)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for dividends received from Company H.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| December | 31 | Cash | 38,000 | ||
| Investment in Company H Stock | 38,000 | ||||
| (To record dividends received from Company H) | |||||
Table (10)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Investment in Company H Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are reduced as an effect of receipt of dividends, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare journal entry for share of income received from Company H.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| December | 31 | Investment in Company H Stock | 51,000 | ||
| Income of Company H | 51,000 | ||||
| (To record income realized from Company H) | |||||
Table (11)
- Investment in Company H Stock is an asset account. Since income of the investee is reported as the increase in the investment, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Income of Company H is a revenue account. Revenues increase stockholders’ equity value, and an increase in stockholders’ equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of income received from Company H.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of available-for-sale securities transaction.
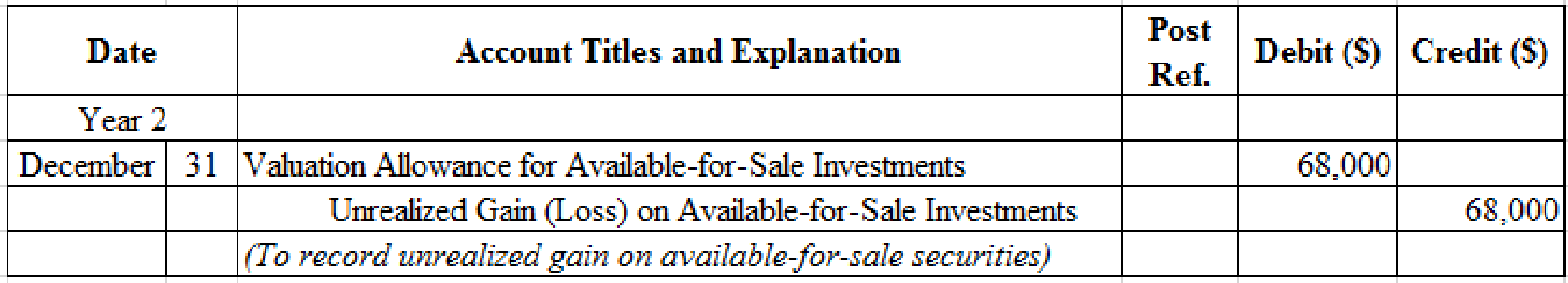
Table (12)
- Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is debited because the market price was increased (loss) to $374,000 from the cost of $306,000.
- Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Available-for-Sale Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since gain has occurred and gains increase stockholders’ equity value, and an increase in stockholders’ equity value is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Available-for-sale investments at fair value, December 31, | $374,000 |
| Less: Available-for-sale investments at cost, December 31, | (306,000) |
| Unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale investments | $68,000 |
Table (13)
(2)
Indicate the presentation of available-for-sale investments, equity method investments, and stockholders’ equity on the balance sheet as on December 31, Year 2.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet presentation:
| Company G | ||
| Balance Sheet (Partial) | ||
| December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | ||
| Available-for-sale investments (at cost) | $340,000 | |
| Add valuation allowance for available-for-sale investments | 34,000 | |
| Available-for-sale investments (at fair value) | $374,000 | |
| Investments: | ||
| Investment in Company I Stock | 813,000 | |
| Stockholders’ equity: | ||
| Retained earnings | 700,000 | |
| Unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale investments | 34,000 | |
Table (14)
Working Notes:
Compute the cost of available-for-sale investments.
Compute valuation allowance balance as on December 31, Year 2.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Valuation allowance credit balance, December 31, Year 1 | $34,000 |
| Valuation allowance debit balance, December 31, Year 2 | 68,000 |
| Valuation allowance balance | $34,000 |
Table (15)
Prepare Investment in Company H Stock account to find the stock investment balance as on December 31, Year 2.
Investment in Company H Stock account
| Investment in Company H Stock | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| Cash | 800,000 | Cash(dividends) | 38,000 | |||
| Income | 51,000 | |||||
| Total | 851,000 | Total | 38,000 | |||
| Balance | $813,000 | |||||
Table (16)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
FINAN.ACCOUNTING-W/DGT ACCESS (LOOSE)
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardMontu Consultants Corporation obtained a building, its surrounding land, and a computer system in a lump-sum purchase for $375,000. An appraisal set the value of the land at $184,500, the building at $144,000, and the computer system at $121,500. At what amount should Montu Consultants record each new asset on its books?arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forward
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forwardI am searching for a clear explanation of this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning

