
a)
Interpretation:
For the given compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Concept introduction:
Compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Reciprocal of wavelength is called wavenumber or Number of waves in one centimeter is called wavenumber
Unit of wave number is reciprocal of Centimeter.
According to Hooke’s law the factors affecting wave numbers are
1. Bond strength
2. Reduced mass
The conjugated compound produces a signal at lower wavenumber, because it has some single bond character and possess weak bond due to resonance.
To find: the responsible bonds for the IR absorption and wave number of the given compound
a)
Answer to Problem 38PP
The responsible bonds for IR absorption and the wavenumber of the given compound in the IR radiation range between 1600and1850
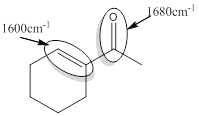
Explanation of Solution
For the given compound A the responsible bonds are,
Conjugated carbonyl and conjugated C=C bonds.
For the conjugated carbonyl bond approximate wavenumber is 1680
For the conjugated C=C bond approximate wavenumber is 1600
For unsaturated or conjugated carbonyl compound there is an introduction of C=C bond separated by one sigma bond.
In conjugated system
In the case of conjugated C=C bond,
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Concept introduction:
Compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Reciprocal of wavelength is called wavenumber or Number of waves in one centimeter is called wavenumber
Unit of wave number is reciprocal of Centimeter.
According to Hooke’s law the factors affecting wave numbers are
1. Bond strength
2. Reduced mass
The conjugated compound produces a signal at lower wavenumber, because it has some single bond character and possess weak bond due to resonance.
To find: the responsible bonds for the IR absorption and wave number of the given compound
(b)
Answer to Problem 38PP
The responsible bonds for IR absorption and the wavenumber of the given compound in the IR radiation range between 1600and1850
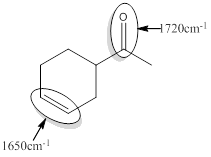
Explanation of Solution
For the given compound B the responsible bonds are
Isolated carbonyl and C=C bonds.
For isolated or saturated carbonyl bond, approximate wavenumber is 1720
For isolated or saturated C=C bond, approximate wavenumber is 1650
Isolated carbonyl group has mostly double bond character.
So, isolated carbonyl compounds produces signal at higher wavenumber of 1720
Like the same way, Isolated C=C has mostly double bond character
So, isolated C=C produces signal at higher wavenumber of 1650
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Concept introduction:
Compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Reciprocal of wavelength is called wavenumber or Number of waves in one centimeter is called wavenumber
Unit of wave number is reciprocal of Centimeter.
According to Hooke’s law the factors affecting wave numbers are
1. Bond strength
2. Reduced mass
The conjugated compound produces a signal at lower wavenumber, because it has some single bond character and possess weak bond due to resonance.
To find: the responsible bonds for the IR absorption and wave number of the given compound
(c)
Answer to Problem 38PP
The responsible bonds for IR absorption and the wavenumber of the given compound in the IR radiation range between 1600and1850
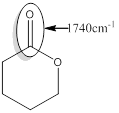
Explanation of Solution
For the given compound C the responsible bond is,
Carbonyl bond of an ester
For isolated or saturated carbonyl bond of an ester, the approximate wavenumber is 1740
Isolated or saturated ester produces the signal of higher wave number than that of conjugated or unsaturated ester of 1700
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Concept introduction:
Compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Reciprocal of wavelength is called wavenumber or Number of waves in one centimeter is called wavenumber
Unit of wave number is reciprocal of Centimeter.
According to Hooke’s law the factors affecting wave numbers are
1. Bond strength
2. Reduced mass
The conjugated compound produces a signal at lower wavenumber, because it has some single bond character and possess weak bond due to resonance.
To find: the responsible bonds for the IR absorption and wave number of the given compound
(d)
Answer to Problem 38PP
The responsible bonds for IR absorption and the wavenumber of the given compound in the IR radiation range between 1600and1850
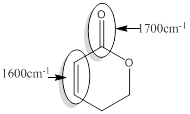
Explanation of Solution
For the given compound D the responsible bonds are,
Conjugated carbonyl bond of an ester
Conjugated C=C bond.
For conjugated carbonyl bond of an ester, the approximate wavenumber is 1700
For the conjugated C=C bond approximate wavenumber is 1600
Conjugated or unsaturated ester produces the signal of lower wave number than that of Isolated or saturated ester. In conjugated system
The reason behind it is conjugated carbonyl bond of an ester has single bond character due to resonance and therefore this bond is merely weaker.
In the case of conjugated C=C bond,
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Concept introduction:
Compounds that absorbing the IR radiation in the range between 1600and 1850
Reciprocal of wavelength is called wavenumber or Number of waves in one centimeter is called wavenumber
Unit of wave number is reciprocal of Centimeter.
According to Hooke’s law the factors affecting wave numbers are
1. Bond strength
2. Reduced mass
The conjugated compound produces a signal at lower wavenumber, because it has some single bond character and possess weak bond due to resonance.
To find: the responsible bonds for the IR absorption and wave number of the given compound
(e)
Answer to Problem 38PP
The responsible bonds for IR absorption and the wavenumber of the given compound in the IR radiation range between 1600and1850

Explanation of Solution
For the given compound E the responsible bond for IR absorption is,
Isolated or saturated C=C bond.
For isolated or saturated C=C bond, approximate wavenumber is 1650
Isolated C=C produces signal at higher wavenumber of 1650
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
ORG.CHEM EBOOK W/BBWILEY PLUS>CUSTOM<
- i need help identifying the four carbon oxygen bonds in the following:arrow_forwardImagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule HO H3N + The solution is... X O acidic OH O basic H3N-CH-C-O O neutral ○ (unknown) O acidic ○ basic CH2 CH 3-S-CH2 O neutral ○ (unknown) H3N O OH O acidic O basic Oneutral O (unknown) 0 H3N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 O acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? olo Ar BHarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughs need other product (product in picture is wrong dont submit the same thing)arrow_forward
- I have a 2 mil plastic film that degrades after 22 days at 88C and at 61C takes 153 days. What is the failure at 47C in days.arrow_forwardIf a 5 film plastic film degraded in 30 days at 35C and the same film degraded in 10 days at 55 C and 2 days at 65C what would the predicted life time be at 22C for the same film?arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- I have a aqueous solution (175 ml) of iridium trichloride containing 8,750 ppm Iridium by ICP OES analysis. What is the percent concentration of Iridium trichloride in aquous solution and provide the concentration in moles per liter, percentage by weight.arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





