
a)1
Determine the total materials cost variance, price and usage variance, the cause of variance and responsible management position.
a)1
Explanation of Solution
Compute the total variance:
Hence, the total variances are $336,200 which is an unfavorable variance.
Compute the total materials price variance:
Hence, the total materials price variances are $172,200 which is an unfavorable variance.
Compute the total materials usage variance:
Hence, the total materials usage variances are $164,000 which is unfavorable variance.
K Company paid more than the budgeted for planks of wood.
The purchasing agent is responsible for the price variance. The variances are occurred because of factors like lumber shortage, and inflation.
K Company used more materials than planned which leads to unfavorable usage variance.
The production supervisor is the responsible party. The variances are occurred because of factors like lack of physically control over inventory and lack of motivation to workers.
2)
Determine the labor cost, price, and usage variance and the cause of variance and responsible management position.
2)
Explanation of Solution
Compute the total labor cost variance:
Hence, the labor variance is $49,200 which is an unfavorable variance.
Compute the labor price variance:
Hence, the labor price variance is $118,900 which is an unfavorable variance.
Compute the labor usage variance:
Hence, the labor usage variance is $69,700 which is a favorable variance.
K Company paid more than the budgeted.
The personnel manager and production supervisors are responsible for the variance. The variances are occurred because of factors like the minimum wages could have been raised by the government.
K Company used less labor than planned which leads to favorable usage variance.
The production supervisor or personal managers are the responsible party. These people motivate the employees and hired more competent people.
3)
Determine the fixed cost spending and variance and the cause of variance and refer whether the actual fixed cost per unit is lower or higher than the budgeted fixed cost per unit.
3)
Explanation of Solution
Compute the fixed cost spending variance:
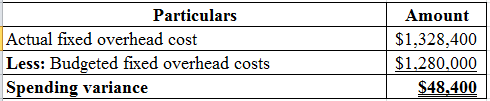
Table (1)
Hence, the spending variance is $48,400 which is unfavorable variance.
Compute the fixed cost volume variance:
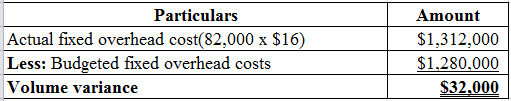
Table (2)
Hence, the volume variance is $32,000 which is favorable variance.
Working note:
Calculate the the predetermined overhead rate:
Hence, the predetermined overhead rate is $16 per table.
The Company K has paid more than the planned with respect to fixed cost. The plant manager is responsible for the rent on manufacturing equipment. The personnel manager is responsible for the salaries paid to the company supervisor.
More units were produced and sold which leads to favorable volume variance. This reduces the fixed cost per unit.
b)
Indicate that the total of material, labor, and overheads variance are equal to the total flexible
b)
Explanation of Solution
Note:
Refer the above part for the calculated values.
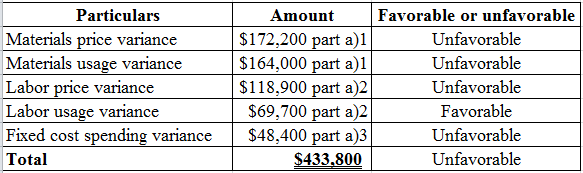
Table (3)
c)
Discuss the reaction of Person D reacts to the variance information
c)
Explanation of Solution
Discuss the reaction of Person D reacts to the variance information:
Person D should make an impartible and fair investigation on the responsible parties and causes.
Monitoring the performance is sufficient for the improvement and in the circumstances of intentional disregard and consistent incompetence the disciplinary actions can be taken.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Answer please general accounting questionsarrow_forwardA retail store suffered a fire on November 10, destroying its merchandise inventory. The following data were obtained from accounting records: Beginning Inventory (Jan. 1): $180,000 • Net Purchases (Jan. 1 - Nov. 10): $1,500,000 • Net Sales (Jan. 1 - Nov. 10): $2,700,000 • Estimated Gross Profit Rate: 40%arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning  Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning





